Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Viral Hepatitis Treatment
Background Challenges Treatment Strategies Creative Biolabs' Solutions Workflow Published Data Related Services Resources
Viral hepatitis remains a significant global health concern, affecting millions worldwide and posing challenges in treatment efficacy and drug delivery. At Creative Biolabs, we recognize the critical need for innovative solutions in this field and are dedicated to advancing the application of lipid-based drug delivery systems to enhance the treatment of viral hepatitis. Our integrated formulation design, analytical capabilities, and diverse in vitro and in vivo models enable us to support your research at every stage, from concept to reality.
Background of Viral Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis constitutes a significant global health burden, stemming from infections caused by a diverse group of hepatotropic viruses. The main types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E (HAV, HBV, HCV, HDV, HEV), each with distinct transmission routes, clinical courses, and epidemiological profiles. While some types result in acute, self-limiting infections, chronic forms, particularly Hepatitis B (HBV) and Hepatitis C (HCV), are major drivers of progressive liver diseases. These chronic infections can lead to severe pathologies including hepatic fibrosis, cirrhosis, and ultimately, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) or liver failure, posing immense challenges to global public health.
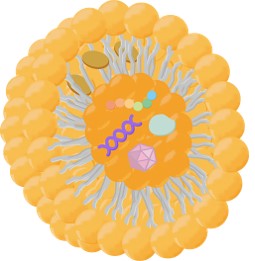
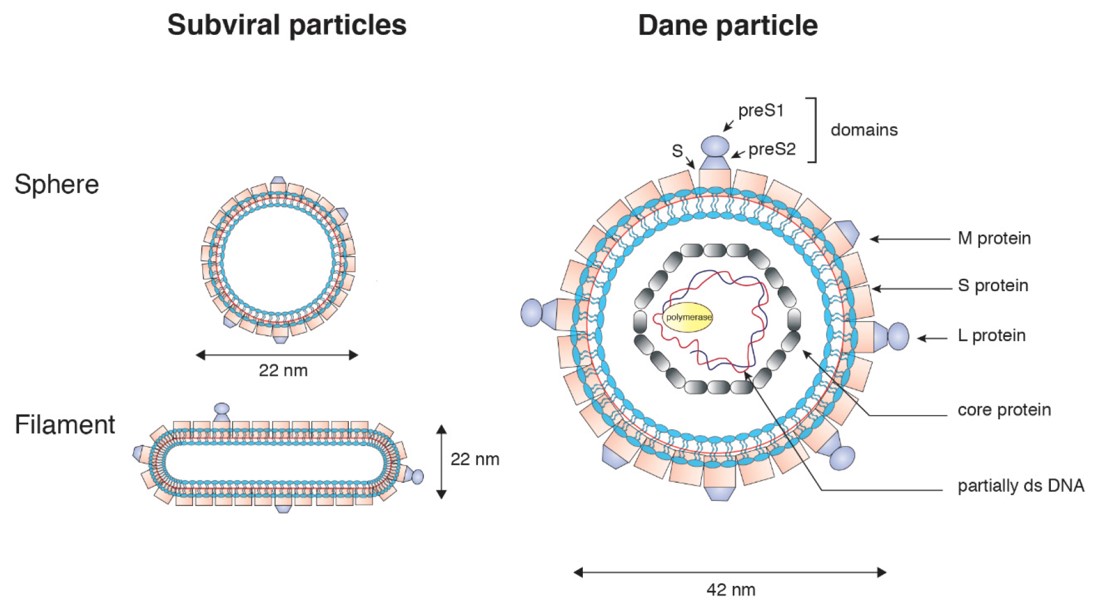 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of HBV particles.1,4
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of HBV particles.1,4
|
Type
|
Classification
|
Viral Genome
|
Transmission Routes
|
|
HAV
|
Picornavirus
|
RNA
|
Fecal-oral
|
|
HBV
|
Hepadnavirus
|
DNA
|
Blood
Sexual contact,
Mother-to-child
Shared needles
|
|
HCV
|
Flavivirus
|
RNA
|
Blood
Shared needles
Mother-to-child
|
|
HDV
|
Deltavirus
|
RNA
|
Blood
Sexual contact
Shared needles,
Mother-to-child
|
|
HEV
|
Hepevirus
|
RNA
|
Fecal-oral
|
Challenges in Hepatitis Therapies
Drug Resistance
Viral evolution leads to resistance against current antivirals, especially in chronic HBV, complicating long-term management.
Off-Target Effects
Systemic drug administration can cause toxicity in healthy tissues, leading to adverse side effects and poor patient compliance.
Poor Bioavailability
Many promising compounds suffer from poor solubility and stability, limiting their absorption and therapeutic potential.
Treatment Strategies for Viral Hepatitis
The evolution of treatment strategies for viral hepatitis reflects a concerted effort to combat these complex and often chronic infections more effectively. From broad-spectrum approaches to highly targeted interventions and gene-editing technologies, the therapeutic landscape is continuously advancing to achieve higher cure rates and minimize adverse effects.
-
Antiviral Therapies: Antiviral drugs such as host-targeted antivirals (HTAs) and direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) (e.g., NS3/4A protease inhibitors, NS5A inhibitors, NS5B polymerase inhibitors) are widely used to suppress viral replication.
-
Gene Editing: This revolutionary technology offers the potential for a functional cure by precisely targeting and disrupting viral DNA (e.g., HBV's persistent cccDNA) or viral RNA, or by modifying host factors essential for viral replication. It aims to eliminate the viral reservoir and prevent relapse, though challenges related to specificity, delivery, and resistance are under active research.
-
Vaccination: Vaccines for hepatitis A and B have significantly reduced the incidence of these diseases.
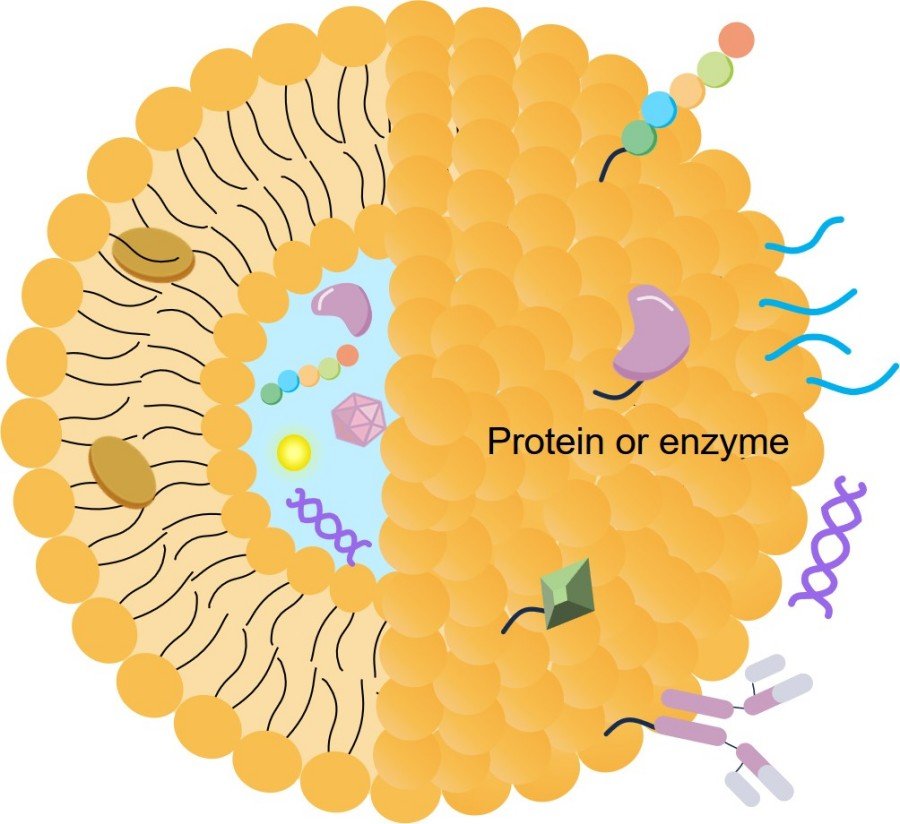
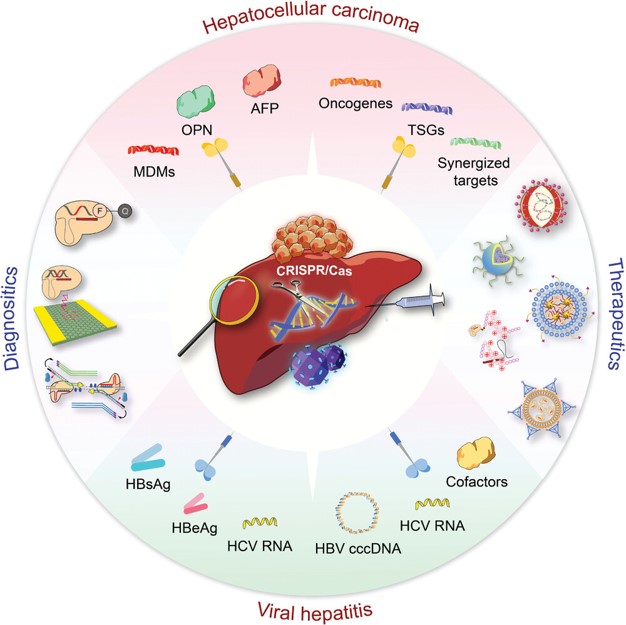 Fig. 2 Gene editing technology for theragnostic of viral hepatitis and HCC.2,4
Fig. 2 Gene editing technology for theragnostic of viral hepatitis and HCC.2,4
However, many of these therapies face challenges such as off-target effects and safety concerns. Antiviral medications may lead to drug resistance and side effects due to non-specific targeting. To address these issues, lipid-based drug delivery systems offer a valuable solution. By encapsulating therapeutic agents within lipid nanoparticles(LNPs) and liposomes, we can enhance targeted delivery to liver cells, reduce systemic exposure, and minimize off-target effects. This approach not only improves the safety profile of treatments but also enhances their efficacy by ensuring higher concentrations of active drugs at the site of infection.
How Creative Biolabs' Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Can Assist Your Project
Creative Biolabs' lipid-based drug delivery systems are engineered to overcome the inherent limitations of traditional drug formulations, particularly for complex therapeutic molecules and challenging disease targets like viral hepatitis. Our customized delivery systems provide a versatile platform for encapsulating a wide range of antivirals drugs, including small molecules, protein/peptide, nucleic acids (e.g., siRNA, mRNA) and vaccines, ensuring their stable and effective delivery.
-
Enhanced Drug Bioavailability
-
Targeted Hepatic Delivery
-
Protection of Sensitive Payloads
-
Sustained Release
-
Enhancing Drug Efficacy
-
Reducing Drug Resistance
-
Enabling Combination Therapies
-
Reduced Systemic Toxicity
Workflow for Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Development for Viral Hepatitis
Published Data
Innovative therapeutic strategies are emerging for the persistent challenge of viral hepatitis, with lipid-based drug delivery systems, particularly LNPs, demonstrating significant promise. These sophisticated carriers are proving to be ideal platforms for targeting the liver, a critical site for many hepatic diseases, including chronic viral infections. Recent research highlights the efficacy of LNPs in delivering genetic material. Specifically, mRNA-LNPs have been engineered to express antibodies, such as G12-scFv, G12-scFv-Fc, and G12-IgG, designed to combat viral antigens. In preclinical studies utilizing an adeno-associated virus (AAV)/HBV mouse model, which mimics persistent HBsAg expression, LNPs encoding G12-scFv-Fc and G12-IgG demonstrated a notable and sustained effect. These systems successfully facilitated the clearance of HBsAg from the serum, showcasing their potential to reduce the viral burden. This indicates a significant step forward in developing targeted and effective therapies for viral hepatitis, leveraging the precision delivery capabilities of LNP technology.
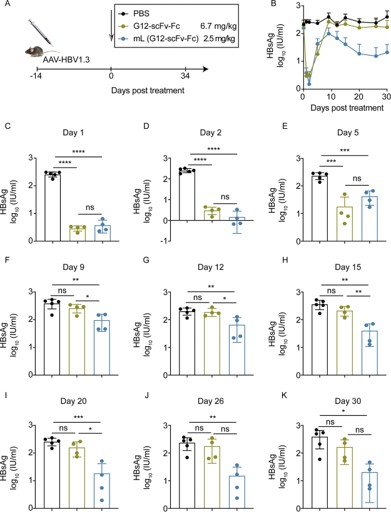 Fig. 3 mL (G12-scFv-Fc) decreased HBsAg in AAV/HBV mouse model.3,4
Fig. 3 mL (G12-scFv-Fc) decreased HBsAg in AAV/HBV mouse model.3,4
At Creative Biolabs, we stand at the forefront of innovation in combining lipid-based drug delivery systems with viral hepatitis treatment. Our functionalized delivery system development platform supports antibody, peptide, aptamer, and other ligand-based liver-targeted delivery. We are committed to helping you advance your research and make a significant impact in the fight against viral hepatitis. Contact us today to learn how our lipid-based drug delivery systems can elevate your research and drive progress in this critical area.
Related Services
Resources
References
-
Herrscher, Charline, Philippe Roingeard, and Emmanuelle Blanchard. "Hepatitis B virus entry into cells." Cells 9.6 (2020): 1486. doi:10.3390/cells9061486.
-
Kong, Huimin, et al. "Advanced nanotheranostics of CRISPR/Cas for viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma." Advanced Science 8.24 (2021): 2102051. doi:10.1002/advs.202102051.
-
Chen, Binfan, et al. "A single dose of Anti-HBsAg antibody-encoding mRNA-LNPs suppressed HBsAg expression: a potential cure of chronic hepatitis B virus infection." MBio 13.4 (2022): e01612-22. doi:10.1128/mbio.01612-22.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
 Fig. 3 mL (G12-scFv-Fc) decreased HBsAg in AAV/HBV mouse model.3,4
Fig. 3 mL (G12-scFv-Fc) decreased HBsAg in AAV/HBV mouse model.3,4

 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of HBV particles.1,4
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of HBV particles.1,4
 Fig. 2 Gene editing technology for theragnostic of viral hepatitis and HCC.2,4
Fig. 2 Gene editing technology for theragnostic of viral hepatitis and HCC.2,4




 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use