Glycomics Quantitative Analysis Service in Milk
Introduction: Precision Glycomics for Functional Product Development
Are you currently facing bottlenecks in characterizing functional ingredients, complexity from glycan heterogeneity, or challenges in authenticating human milk substitutes? Our Glycomics Quantitative Analysis Service helps you establish structure-function claims and secure your supply chain through advanced high-resolution mass spectrometry and specialized chromatography techniques.

Milk is a highly complex bio-matrix, offering much more than basic nutrients. It is a source of highly bioactive carbohydrates, primarily in the form of unconjugated oligosaccharides (like Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs)) and glycoproteins (containing N-linked glycans and O-linked glycans). These molecules play fundamental roles in infant development, including shaping the gut microbiome, providing protection against pathogens, and modulating the infant's immune system. Analyzing these molecules is complex due to their high structural diversity and concentration variability. There are significant differences in the carbohydrate composition of milk from different sources. Studies have shown that human milk, cow's milk, and goat's milk each have their own unique characteristics in terms of carbohydrate composition. More importantly, these milks also differ significantly in the degree of glycosylation modification. The N-glycan chains of whey proteins in human milk and goat's milk are highly fucosylated, while those in cow's milk are highly sialylated. This difference directly affects the nutritional value and biological functions of milk from different sources. Creative Biolabs leverages high-resolution LC-MS to tackle this complexity, providing the precise structural and quantitative data required to establish the composition, authenticity, and functional role of these molecules.
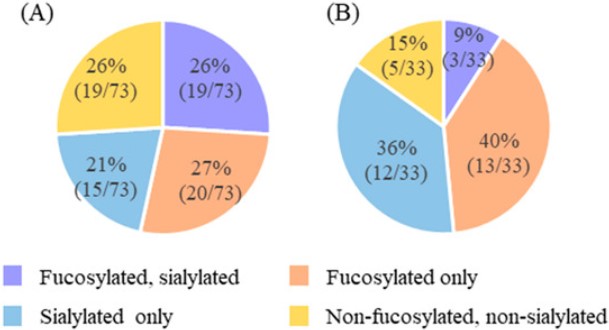 Fig.1 Modification characteristics of N-glycans (A) and O-glycans (B) in human milk.1,3
Fig.1 Modification characteristics of N-glycans (A) and O-glycans (B) in human milk.1,3
Detailed Analysis Process
The value of our milk glycomics quantitative analysis service depends not only on our advanced technology platform but also on standardized operating procedures and a rigorous quality control system. This comprehensive analytical process encompasses everything from sample collection and pretreatment to instrumental analysis and data interpretation. Quality assurance at every stage directly impacts the reliability and accuracy of the final results. Creative Biolabs provides definitive solutions for R&D leaders in infant nutrition, functional foods, and diagnostics whose success hinges on the accurate characterization of complex milk biomolecules.
|
Key Step
|
Activities Involved
|
Expected Outcomes
|
|
Sample preparation
|
Removal of highly abundant proteins and lipids. Selective enrichment and purification of the oligosaccharide and glycoprotein fractions.
|
A clean, concentrated, and desalted glycan fraction ready for high-sensitivity analysis, minimizing matrix interference.
|
|
Optimized LC separation
|
Application of specialized chromatography to resolve isomers.
|
High-efficiency separation of structurally similar glycans, ensuring distinct peaks for accurate MS analysis.
|
|
High-resolution MS/MS acquisition
|
Analysis using our advanced analysis platforms coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) for fragmentation.
|
Acquisition of highly accurate mass data and definitive structural fragmentation patterns for identification and annotation.
|
|
Data processing
|
Utilization of proprietary software and in-house glycan libraries for automated peak detection, relative and absolute quantitation, and structural assignment.
|
A fully annotated list of glycan species with assigned structural details (linkages, composition) and quantitative values.
|
|
Functional interpretation
|
Expert review of quantitative profiles, comparison against reference standards, and generation of a final report linking data to client R&D objectives.
|
Quantifiable reports and annotated glycan maps.
|
Core Technical Platforms
Creative Biolabs provides its service using a tiered approach built on cutting-edge analytical chemistry:
|
Platform
|
Core Principle
|
Glycomics Application
|
|
Label-free LC-MS/MS
|
Soft ionization (ESI) coupled with high mass accuracy analyzers (≤1 ppm error) and fragmentation.
|
Ideal for identifying and structurally characterizing novel or low-abundance glycans in complex matrices.
|
|
UPLC-triple quadrupole MS/MS
|
Targeted multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) transitions on a validated signature peptide or glycan fragment.
|
Used for high-throughput, routine, and cost-effective absolute quantification of 10-20 known, high-priority glycan species (e.g., 2'-FL, LNFPI).
|
|
Chromatography
|
Separation based on hydrophilicity (HILIC) or specific carbon interaction (PGC), optimized to resolve structural isomers.
|
Essential for separating glycans that are isobaric (same mass) but structurally distinct and biologically different.
|
The Necessity and Future of Milk Glycomics Quantitative Analysis
The field of milk glycomics is essential for understanding human and animal nutrition. The variability observed in milk composition - influenced by species, breed, lactation stage, and maternal genetics - makes generalized assays obsolete. Only a highly specialized, multi-stage analytical service can provide the depth needed for modern product development. The necessity stems from the sheer biological importance and chemical complexity of glycans:
Biological function is structure-dependent
Glycans function by acting as decoys for pathogens or binding sites for beneficial bacteria. A minor change in linkage (e.g., α-1,2 vs. α-1,3 fucose) results in a complete loss or change of function. Traditional methods are unable to resolve these functional differences.
The HMO diversity gap
HMOs are the third most abundant solid component in human milk, with over 200 different types identified. Accurate quantification of the endogenous glycan content in a source matrix (like cow or goat milk) is the first step in closing this nutritional gap through targeted fortification.
Authentication
Specific glycan fingerprints can serve as biomarkers to authenticate species origin and detect the blending or adulteration of high-value milk products, securing the supply chain.
Despite the advanced technology, the analysis of milk glycans presents unique difficulties that require expert mitigation:
-
High dynamic range: Glycans in milk range from highly abundant lactose to trace-level glycoproteins, making simultaneous detection difficult. This requires pre-fractionation and sequential LC-MS methods.
-
Matrix complexity: The high concentration of fats, salts, and proteins can suppress the ionization of the target glycans in the MS instrument. We mitigate this through rigorous, optimized solid-phase extraction (SPE) protocols.
-
Isomeric overlap: The vast number of structural isomers (differing only in linkage and branching) requires chromatography methods, like PGC, that prioritize isomer separation over speed.
-
Lack of universal standards: For many of the thousands of potential glycan structures, commercial standards are unavailable. This necessitates the use of in-house characterized standards and reliable relative quantification methods.
Published Data
This study utilized advanced peptidomic and glycomic profiling to conduct the most comprehensive molecular analysis of naturally occurring bioactive peptides and oligosaccharides (OSs) found in ten commercial dairy products. The glycomic results, detailed through analyses like that shown in the following figure, provided a specific breakdown of the complex OS profile. The analysis confirmed that neutral oligosaccharides were the most dominant class, constituting the highest proportion of the total OS content. Furthermore, acidic oligosaccharides were present in significant amounts, with sialyllactose identified as the most abundant individual OS structure. The figure also revealed that fucosylated oligosaccharides were generally found only in trace amounts, with the sole exception being the lactose-free sample, which exhibited an unusual and higher relative abundance of this beneficial OS class. This extensive profiling reveals how processing and formulation steps inherently affect the bioactive composition of dairy, offering a foundation for developing enriched products specifically targeted at improving human health.
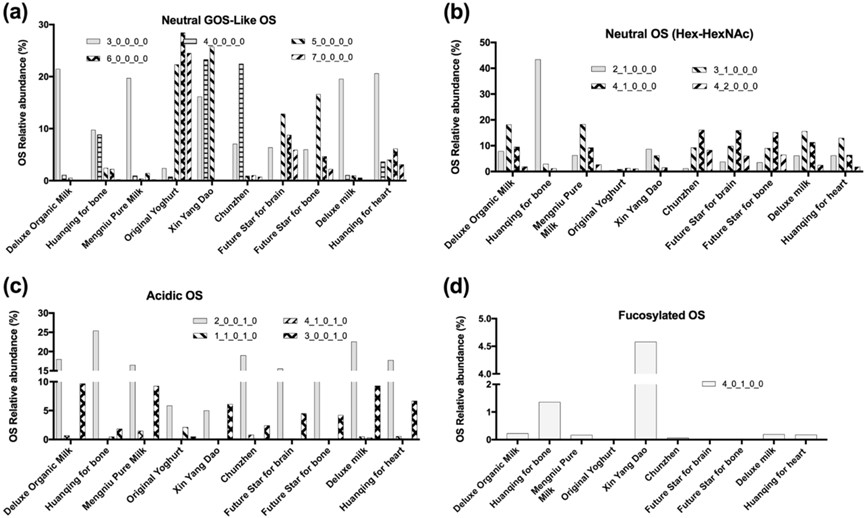 Fig.2 Relative abundance (%) of various oligosaccharides in commercial dairy products.2,3
Fig.2 Relative abundance (%) of various oligosaccharides in commercial dairy products.2,3
FAQs
Why can't we use traditional HPLC with UV detection for glycomics?
Glycans have poor or non-existent UV absorbance, making them invisible to traditional HPLC detectors. More importantly, traditional methods cannot resolve the large number of functional isomers (e.g., 2'-FL vs. 3-FL) that are crucial to biological activity. Only the sensitivity and structural specificity of LC-MS/MS, coupled with specialized columns, can differentiate these compounds and provide actionable data.
We use powdered milk isolates. Does your method accommodate these complex matrix types?
Yes, our sample preparation protocols are specifically designed to handle highly processed matrices like milk powder, protein isolates, and fortified formulas. We utilize optimized liquid-liquid and solid-phase extraction (SPE) techniques to minimize the effects of the complex matrix on the downstream MS analysis, guaranteeing accurate results regardless of the starting material.
How do you report quantitative data, and is it absolute or relative?
We offer both. For known, commercially relevant glycans, we use isotopically labeled internal standards and targeted MRM on our MS platform to deliver absolute quantification. For novel or discovery-phase projects, we provide relative quantification based on normalized peak areas from the MS data, offering a full picture of the entire glycan profile.
Customer Review
Structural Clarity
"Using Creative Biolabs' glycomics quantitative analysis service in milk in our research has significantly improved the structural characterization of low-abundance sialylated glycans. Their MS/MS fragmentation data provided the definitive proof we needed for our patent submission, a level of detail our previous vendor could not reach."- Dr. L**ah, Scientist.
Throughput and Scale
"Using Creative Biolabs' glycomics quantitative analysis service in milk in our research has significantly facilitated the high-throughput profiling of a large cohort study (500+ samples). The label-free quantitative approach was essential for cost-effectiveness, and the results correlated perfectly with our functional microbiome data."- M**kr, Manger.
Authentication Confidence
"Using Creative Biolabs' glycomics quantitative analysis service in milk in our research has significantly improved the authentication of imported milk components. The detailed glycan fingerprinting quickly revealed minor but consistent adulteration with a non-declared species, allowing us to halt a costly supply line before product launch."- C**P, Project leader.
Extended Services
To ensure your R&D objectives are fully met, Creative Biolabs recommends complementing your glycomics quantitative analysis service in milk with our other specialized omics platforms:
Milk proteomics analysis
Targeted and untargeted analysis of caseins and whey proteins to confirm species origin, monitor processing effects, and discover novel bioactive peptides.
Milk lipidomics analysis
Comprehensive profiling of tags and polar lipids using MS to assess nutritional quality, fat-soluble vitamin content, and identify lipid biomarkers for heat stress or adulteration.
Custom biomarker discovery
Utilize our untargeted multi-omics approach to screen and validate novel biomarkers for specific health outcomes or disease states within the milk matrix.
How to Contact Us
Creative Biolabs' glycomics quantitative analysis service in milk offers the definitive, structure-focused analytical depth required to establish functional claims, ensure quality, and accelerate product innovation in the complex world of nutritional science. We translate molecular data into clear, actionable commercial advantage. Please contact us for more information and to discuss your project.
References
-
Yamaguchi, Toshiyuki, et al. "Label-Free Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Quantitation of Relative N-and O-Glycan Concentrations in Human Milk in Japan." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.3 (2024): 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031772.
-
Bhattacharya, Mrittika, et al. "Peptidomic and glycomic profiling of commercial dairy products: identification, quantification and potential bioactivities." npj Science of Food 3.1 (2019): 4. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41538-019-0037-9.
-
Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Services


 Fig.1 Modification characteristics of N-glycans (A) and O-glycans (B) in human milk.1,3
Fig.1 Modification characteristics of N-glycans (A) and O-glycans (B) in human milk.1,3
 Fig.2 Relative abundance (%) of various oligosaccharides in commercial dairy products.2,3
Fig.2 Relative abundance (%) of various oligosaccharides in commercial dairy products.2,3

