Comprehensive and Accurate Starch Analysis Service at Creative Biolabs
As a polysaccharide substance widely found in nature, starch has extremely important applications in many fields such as food, medicine, papermaking, and textiles. Accurate analysis of starch's physical properties is a key link in optimizing product performance, developing new materials, and promoting technological upgrades in related industries. Creative Biolabs focuses on providing comprehensive and professional starch physical property analysis and Starch Content Analysis services to help clients gain an in-depth understanding of starch's molecular structure, physical properties, thermal properties, and other parameters. Through our analysis services, you can obtain starch performance data under different applications and processing conditions, providing strong support for product development and quality control.
Starch Molecular Structure-based Analysis
Molecular weight distribution
The molecular weight distribution of starch has a significant impact on its physical properties and application performance. We accurately determine the weight average molecular weight (Mw), number average molecular weight (Mn), and molecular weight distribution index (Mw/Mn) of starch by gel chromatography (GPC). Starch with a narrow molecular weight distribution exhibits relatively uniform behavior in solution, which helps to prepare products with stable performance. While a wider molecular weight distribution may give starch some special processing properties.
Chain length distribution
Starch is composed of amylose and amylopectin, and their chain length distribution differences greatly affect the functional properties of starch. We use enzymatic hydrolysis to separate the linear and branched parts of starch and then combine high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or ion chromatography to determine the content of different chain-length fragments. Shorter chain lengths may give starch a faster gelatinization rate and a lower gelatinization temperature, while longer chain lengths may be related to the gel strength of starch.
Branching degree
We use nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology to determine the ratio of α-1,4 and α-1,6 glycosidic bonds in starch. The degree of branching of starch has a profound impact on the solubility, gelatinization properties, and rheological properties of starch. Starch with a high degree of branching usually has better water solubility and lower crystallinity and shows unique advantages in food thickening and emulsification. While starch with a low degree of branching may be more inclined to form a gel structure. Through our analysis services, clients gain a deep understanding of the impact of starch branching on product performance and make more scientific decisions.
Degree of polymerization
The degree of polymerization is a key indicator for assessing the size of starch molecules and is directly linked to the physical properties of starch. We use a variety of analysis methods, such as the viscosity method, light scattering method, etc., to determine the degree of polymerization of starch.
Starch Granule Characteristics-based Analysis
1
Particle size distribution
The size and distribution of starch granules have an important impact on their behavior during processing and the performance of the final product. We utilize a laser particle size analyzer to accurately determine the particle size range, average particle size, and particle size distribution curve of starch granules. This analysis helps to optimize the application of starch in food, pharmaceutical, and other fields.
2
Water solubility index
The starch water solubility index is an important indicator to measure the solubility of starch in water. We use specific experimental methods to determine the percentage of the mass of the starch soluble part in water under certain conditions of the total starch mass. Understanding the starch water solubility index helps clients choose the right starch variety according to product requirements and optimize the production process to improve the solubility of starch.
3
Swelling power
We calculate the swelling power of starch by measuring the weight or volume change of starch after absorbing water at different temperatures. Swelling power is associated with the water absorption and gelatinization capacity of starch, impacting the water-holding capacity and flavor of the product.
4
Resolvability
We evaluate starch resolvability by observing the resolvability of starch slurry under different conditions, such as precipitation volume and transmittance changes. Resolvability affects the quality of suspension and emulsion products, and this analysis helps improve formulation and storage stability.
5
Freeze-thaw stability
We conduct repeated freeze-thaw cycle tests on starch slurry to observe its structural and functional changes. Starch with good freeze-thaw stability effectively prevents product quality deterioration during frozen storage, such as ice crystal growth, and other problems. Our freeze-thaw stability analysis service provides clients with reliable evaluation results to help them select starch raw materials suitable for frozen product applications and optimize product formulations.
6
Whiteness and transparency
Starch whiteness and transparency are important parameters to measure its appearance quality and application performance, which directly affect the visual effect of the product. We use professional instruments such as whiteness meters and spectrophotometers to accurately measure the whiteness value of starch and the transmittance of starch paste at specific wavelengths, helping clients develop products with good appearance performance.
Starch Rheology and Gelatinization Properties-based Analysis
The viscosity of the starch solution is one of its important rheological properties, which is of key significance to the production process and product quality control in many fields such as the food and chemical industry. We use a fast viscosity analyzer to measure the viscosity change of starch paste under different temperatures, shear rates, and other conditions.
-
Gelatinization temperature
Gelatinization is an important physical change that occurs in starch during heating, and gelatinization temperature is a key parameter to measure this property of starch. We use differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) to detect the gelatinization temperature and gelatinization enthalpy of starch. This analysis reveals the thermal transition characteristics of starch and helps predict the behavior of starch during heating.
We quantitatively analyze the gel consistency of starch by measuring parameters such as the gel column length of starch paste under certain cooling conditions according to standard methods. Gel consistency is closely linked to the amylose content and molecular structure of starch. In the food industry, it affects the taste, texture, and storage stability of food.
Structural Characterization Analysis
Infrared scanning
We used a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR) to scan starch and obtain its infrared absorption spectrum. By analyzing the position, intensity, and shape of the characteristic absorption peaks in the spectrum, we infer the type of chemical bonds, functional group structure, and intermolecular interactions in the starch molecules. For example, infrared spectroscopy can distinguish between amylose and amylopectin and study the structural changes of starch during gelatinization and aging.
Solid-state NMR
We used solid-state NMR to determine the helical and amorphous structures of starch and gain a deep understanding of its molecular structure, branching, and intermolecular interactions.

X-ray diffractometer
We used an X-ray diffractometer (XRD) to analyze starch samples and obtain their XRD spectra. Through parameters such as the position, intensity, and width of the diffraction peaks in the spectrum, we determine the crystal type, crystallinity, and grain size of starch. The crystalline structure of starch has an important influence on its physical properties. For example, starch with high crystallinity may have a higher gelatinization temperature and better digestibility.
Polarized light and electron microscope scanning
We use polarized light microscopy (PLM) to measure the birefringence phenomenon and the "Maltese cross" image of starch granules. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is used to visually observe the surface morphology, size, and interaction between starch granules, to help clients deeply understand the microscopic morphology of starch.
Creative Biolabs provides clients with the most comprehensive and accurate Starch Analysis services. Whether you are a food company, pharmaceutical company, or scientific research institution, we can meet your needs for starch physical property analysis and provide solid technical support for your product development, quality control, and technological innovation. Please contact us if you need more service information or have any questions. We look forward to working with you to jointly promote the development of starch products.
Published Data
This study investigated the physicochemical properties of green wheat starch, including its starch content, structural morphology, crystallinity, and thermal properties. The figure below illustrates the thermal behavior of green wheat starch and shows the thermogravimetric (TG) and derivative thermogravimetric (DTG) curves. These curves show that the thermal decomposition of green wheat starch occurs in three distinct stages. The initial stage is observed at temperatures below 225 °C, with a mass loss of approximately 6.615%, mainly due to the release of volatile compounds, especially water evaporation. The second stage, which ranges from 225 °C to 375 °C, corresponds to the decomposition of the starch component itself. The third and final stage occurs at temperatures above 375 °C and is characterized by the carbonization of the material. The data show that the decomposition of the starch occurs in the temperature range of 225 °C to 375 °C, with the maximum decomposition rate observed at 308 °C. In addition, the study showed that almost all (99.95%) of the starch was completely decomposed when the temperature reached 600 °C.
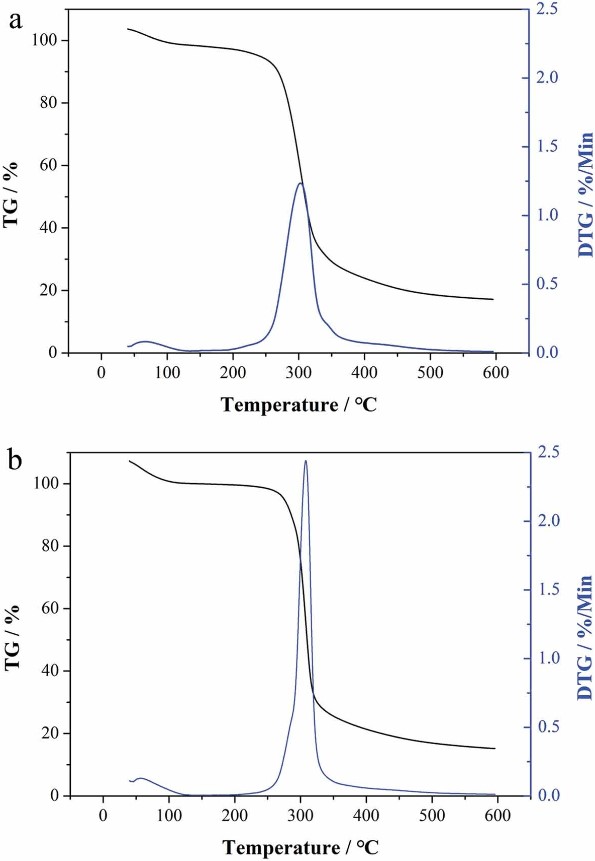 Fig.1 TG and DTG analysis results of green wheat.1
Fig.1 TG and DTG analysis results of green wheat.1
FAQs
Q1: Could you analyze modified starches, or are you limited to native starches?
A1: Our service scope includes both native starches and modified starches. For modified starches, such as hydroxypropyl starch and cross-linked starch, we have rich analysis experience and methods to evaluate the changes in physical properties after modification. This is of great significance for studying the effect of the modification process and guiding product application.
Q2: What sample size is required for starch physical property analysis?
A2: The amount of sample required depends on the specific analysis. Typically, we require about 3-5 g of starch for viscosity analysis and about 5-10 mg per sample for gelatinization temperature analysis. To ensure accuracy for all analyses and repeat tests, we recommend providing at least 50 g of starch sample.
Q3: Could you customize the analysis to target specific properties relevant to our applications?
A3: Yes, we tailor our analysis services to focus on the most relevant physical properties according to your specific application or industry needs. Whether you are interested in specific gelatinization behavior, thermal transitions, rheological profiles, or particle size distribution, we can design a custom testing program to meet your needs to ensure you get the most relevant information for your product development.
Customer Review
Comprehensive Physical Property Analysis to Improve Product R&D Quality
"Through the comprehensive physical property analysis provided by Creative Biolabs, we have a comprehensive understanding of the starch materials used. The report covers multiple aspects such as rheological properties, particle morphology, and crystal structure, laying a solid foundation for us to develop high-quality products."
Detailed and Accurate Analysis Reports Help Optimize Products
"We are very pleased with the starch physical property analysis service offered by Creative Biolabs. The report we received is detailed, and the data is accurate and reliable. In particular, the detailed analysis of the gelatinization characteristics and viscosity curve of starch enables us to have a deep understanding of the raw material characteristics, effectively optimize the product formula, and improve the quality and stability of the final product. The professional advice of the technical team also provides strong support for our R&D direction."
Reference
-
Zhang, Yu, and Guozhi Zhang. "Starch content and physicochemical properties of green wheat starch." International Journal of Food Properties 22.1 (2019): 1463-1474. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Services
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on


 Fig.1 TG and DTG analysis results of green wheat.1
Fig.1 TG and DTG analysis results of green wheat.1

