Background of Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Research related to Glycosylation Analysis
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a global health challenge, necessitating advanced diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic strategies. Beyond genetics and proteomics, the emerging field of glycomics reveals that aberrant glycosylation—the modification of proteins and lipids with complex sugar chains—is a universal hallmark of cancer. These altered glycan structures play pivotal roles in tumor initiation, progression, metastasis, immune evasion, and drug resistance. Understanding these intricate glycosylation changes is crucial for uncovering novel biomarkers and identifying new therapeutic targets, paving the way for a new era of precision oncology in CRC. Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of glycosylation analysis, driven by specialized expertise and a relentless commitment to scientific excellence. We provide a comprehensive suite of solutions specifically designed to unravel the intricate roles of glycosylation in CRC. Our service offers precise insights into aberrant glycan structures, their expression patterns, and their association with key biological processes, including metastasis, immune evasion, and drug resistance. Clients can expect robust data, in-depth interpretation, and actionable intelligence to drive their research forward.
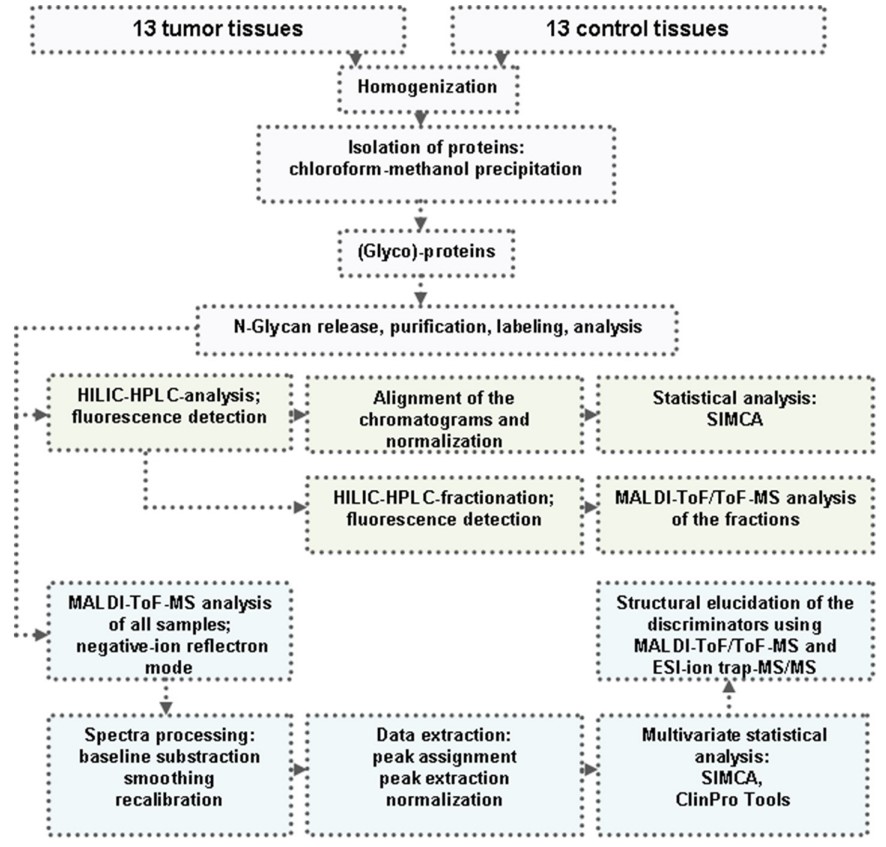 Fig.1 Schematic overview of N-glycosylation analysis in CRC vs. normal colorectal tissues.1
Fig.1 Schematic overview of N-glycosylation analysis in CRC vs. normal colorectal tissues.1
Workflow of CRC Glycosylation Analysis
Our streamlined workflow ensures a meticulous and efficient analysis of your samples, providing high-quality, interpretable results.
-
Required Starting Materials
-
Tissue samples: Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) or fresh-frozen CRC tumor tissues, alongside matched normal adjacent tissues (if available).
-
Biological fluids: Plasma or serum samples from CRC patients and control cohorts.
-
Cell lines: Specific CRC cell lines.
-
Key Steps Involved
Sample preparation & extraction
This initial phase involves meticulous preparation of your provided biological materials. For tissues, this includes homogenization or microdissection, followed by optimized protein and glycan extraction protocols to preserve structural integrity. For fluid samples, this may involve enrichment steps. The expected outcome is purified protein or glycan samples ready for downstream analysis.
Glycan release & labeling
N-Glycans are enzymatically released from glycoproteins using PNGase F, and O-glycans may be released through reductive β-elimination. Released glycans are then precisely labeled with fluorescent tags or derivatized. This step prepares glycans for high-resolution separation and detection.
High-resolution separation
Labeled glycans are separated using advanced chromatographic techniques. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC-UPLC) provides highly reproducible separation based on glycan polarity, crucial for resolving complex mixtures. This step yields separated glycan peaks for subsequent mass spectrometry.
Mass spectrometry analysis
This is the core of our characterization. We employ cutting-edge mass spectrometry platforms such as MALDI-TOF-MS for high-throughput profiling and LC-MS/MS for in-depth structural elucidation. This stage generates raw mass spectral data and fragmentation patterns.
Bioinformatics & data interpretation
Raw MS data undergoes rigorous processing, including peak picking, baseline correction, normalization, and structural annotation using specialized glycoinformatics tools. This is followed by advanced multivariate statistical analysis and machine learning algorithms to identify statistically significant differences in glycan profiles between sample groups. This step transforms complex data into interpretable biological insights, identifying differentially expressed glycans and potential biomarkers.
-
Final Deliverables
-
Comprehensive data reports: Detailed reports summarizing identified glycan structures, their relative abundances, and statistically significant changes.
-
Bioinformatics analysis summaries: Visualizations and interpretations of multivariate statistical analyses, including heatmaps, volcano plots, and pathway enrichment analyses.
-
Candidate biomarker lists: A prioritized list of glycan features with high discriminatory power, accompanied by their potential clinical significance.
Main Glycosylation Changes in CRC
-
Altered sialylation: Often increased, particularly α2,6-sialylation, which is linked to enhanced cell recognition, adhesion, and signaling, promoting metastasis and protection against apoptosis. Conversely, α2,3-sialylation might be downregulated in specific contexts.
-
Changes in fucosylation: Highly variable, but core-fucosylated high mannose N-glycans, and specific fucosylated Lewis epitopes (e.g., Sialyl Lewis X, Lewis Y), are frequently upregulated in tumors and associated with metastatic potential and poor prognosis.
-
Antennarity changes: Alterations in the branching of N-glycans (e.g., increased diantennary and monoantennary, decreased triantennary) are observed, impacting cell adhesion and migration.
-
Sulfated N-glycans: Increased levels of sulfated N-glycans are found in tumors, contributing to negative charge and interactions that may facilitate adhesion and metastasis.
-
IgG glycosylation: Systemic changes in plasma IgG glycosylation, such as decreased galactosylation and sialylation, and increased bisecting GlcNAc, are associated with a pro-inflammatory IgG phenotype and poorer prognosis, especially in late-stage CRC.
Why We Need to Analyze These Glycosylation Patterns?
Glycosylation is one of the most abundant and functionally diverse post-translational modifications, directly impacting protein function, cell-cell recognition, and interactions with the extracellular matrix. In CRC, these modifications are frequently dysregulated, leading to "aberrant glycosylation." Analyzing these changes is critical for several reasons:
-
Novel biomarker discovery
-
Understanding Disease Mechanisms
-
Identifying therapeutic targets
-
Predicting drug resistance
-
Prognostic stratification
Creative Biolabs is committed to empowering your CRC research with unparalleled insights into the glycobiology of the disease. Our comprehensive glycosylation analysis services are designed to accelerate your discoveries, identify novel biomarkers, and pave the way for more effective therapeutic strategies. Partner with us to transform complex glycomic data into actionable scientific solutions.
Published Data
This study delves into the alterations in N-glycosylation patterns observed in CRC tissues compared to healthy colon tissues, seeking to identify potential new biomarkers for early detection. The researchers employed a comprehensive approach, combining HILIC with fluorescence detection and MALDI-TOF-MS to analyze N-glycan profiles. Through the application of multivariate statistical analysis, they demonstrated excellent discriminatory power between cancer and control samples using both analytical techniques. Figure 2 visually illustrates the distinct N-glycan profiles obtained from a CRC tissue and its corresponding healthy control tissue using negative mode MALDI-TOF-MS. The graph presents two overlaid mass spectra, one representing the tumor sample and the other the control. While both spectra exhibit a variety of N-glycan types, subtle yet crucial differences in their relative peak intensities are discernible. These variations in peak heights across the mass-to-charge (m/z) range highlight the quantitative shifts in specific N-glycan abundances between the diseased and healthy states, underscoring the potential of these molecular changes as diagnostic indicators. This visual comparison directly supports the study's aim to identify altered glycosylation patterns in CRC.
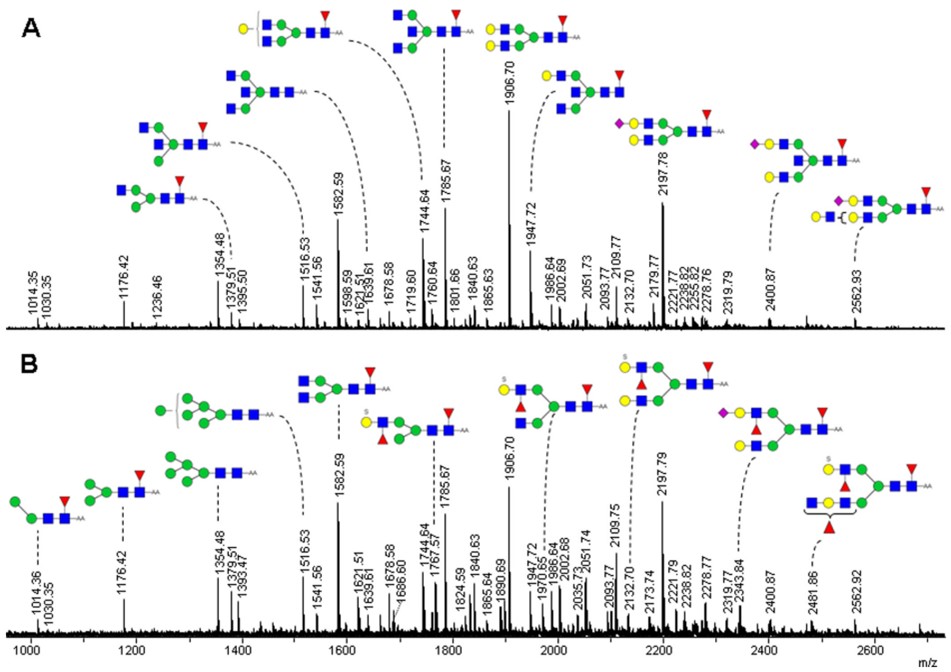 Fig.2 MS fingerprints of AA-labeled N-glycans from tumor (B) and control (A) colorectal samples.1
Fig.2 MS fingerprints of AA-labeled N-glycans from tumor (B) and control (A) colorectal samples.1
FAQs
Q1: How can Creative Biolabs' service help me find new biomarkers for CRC?
A1: Our service provides an in-depth analysis of glycan changes in CRC tissues and biofluids, which are often altered early in disease development. By identifying unique glycan patterns specific to cancer, particularly those associated with early stages or recurrence risk, we can uncover novel and highly specific biomarker candidates that traditional methods might miss. This significantly accelerates your biomarker discovery pipeline.
Q2: What type of samples do I need to provide for the analysis, and what is the typical turnaround time?
A2: We accept various sample types, including fresh-frozen or FFPE colorectal cancer tissues, plasma, serum, and CRC cell lines. The typical timeframe for a comprehensive analysis ranges from 6 to 12 weeks, depending on the sample complexity and the depth of analysis required. We prioritize efficiency without compromising data quality.
Q3: How does Creative Biolabs's approach differ from standard proteomic or genomic analyses for CRC?
A3: While proteomics and genomics are vital, they often miss crucial functional information encoded by glycans. Our specialized glycomics and glycoproteomics approach focuses on the "glyco-code," revealing post-translational modifications that directly impact protein function, cell-cell interactions, and tumor biology. This provides a complementary and often more nuanced understanding of disease mechanisms and biomarker potential, offering insights not achievable through DNA or protein expression alone.
Customer Review
Robust Analytical Methods and Comprehensive Data Interpretation
"Using Creative Biolabs's IgG glycome profiling service in our clinical cohort has significantly improved our ability to stratify CRC patients by prognosis. Their robust analytical methods and comprehensive data interpretation allowed us to identify critical pro-inflammatory glycan patterns linked to poor outcomes, which was impossible with standard clinical markers alone." - Ms. R. Moo***e.
Truly Exceptional Support
"The unprecedented clarity on N-glycan changes using Creative Biolabs's platform in our colorectal tissue analysis has significantly improved our understanding of early progression markers. The detailed structural elucidation facilitated targeted validation efforts." - Dr. D. Tay***r.
Reference
-
Balog, Crina IA, et al. "N-glycosylation of colorectal cancer tissues: a liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry-based investigation." Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 11.9 (2012): 571-585. DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M111.011601. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Services
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Schematic overview of N-glycosylation analysis in CRC vs. normal colorectal tissues.1
Fig.1 Schematic overview of N-glycosylation analysis in CRC vs. normal colorectal tissues.1
 Fig.2 MS fingerprints of AA-labeled N-glycans from tumor (B) and control (A) colorectal samples.1
Fig.2 MS fingerprints of AA-labeled N-glycans from tumor (B) and control (A) colorectal samples.1

