Our Products Overview Product Types Highlights Publication Customer Reviews FAQs Related Services
Glycoengineering Viral Particles, Build Consistent Glycoforms Fast.
Facing batch-to-batch glycoform variability, uncertain enzyme localization, or low transduction in primary and in vivo models? Creative Biolabs offers glycoengineering viral particles, such as recombinant lentivirus, MMLV/MSCV retrovirus, adenovirus, and adeno-associated virus, to establish defined glycosylation states and reproducible phenotypes by matching vector class/serotype to your cells, tuning promoters, and ensuring ER/Golgi targeting. Choose targeted overexpression (e.g., glycosyltransferases, chaperones) or gene silencing primarily via shRNA (with CRISPR/Cas9 knockout available on request) to modulate pathway nodes precisely—delivered as documented, QC-validated, ready-to-use lots for seamless adoption.
Product Types
Recombinant Lentivirus
Genome-integrating, high-titer particles for durable glycoenzyme expression in dividing and quiescent cells, delivered with annotated maps, sterility/mycoplasma QC, and MOI guidance for long-term, assay-ready use.
Recombinant MMLV Retrovirus
Integration restricted to actively dividing cells for clean stable clones; functional titer verified, packaging optimized for medium-to-large inserts, and documentation supporting scalable glyco-pathway studies.
Recombinant MSCV Retrovirus
Stem-cell–optimized architecture that minimizes silencing in hematopoietic/pluripotent models; ready-to-use lots with identity/purity data and transduction performance records for consistent glycoengineering.
Recombinant AAV1-AAV9
In vivo–ready capsids with tissue-tropic options (e.g., liver, heart, CNS, retina, inner ear); compact payload and optional scAAV formats, supplied with endotoxin screening and dosing guidance for targeted glycan modulation.
Recombinant Adenovirus
Non-integrating, high-transduction vectors suited for rapid, transient expression or shRNA-mediated silencing; larger payload capacity than AAV, broad cell-type compatibility, and delivery with sterility/mycoplasma QC plus dosing guidance for fast pathway interrogation.
Highlights
 Producer cell optimization
Producer cell optimization
Tune glycosyltransferase levels to achieve the desired Fc or receptor glycoforms before scale-up.
 Cancer model engineering
Cancer model engineering
Modulate pathway enzymes to interrogate invasion, signaling, or immune interactions tied to glycan patterns.
 shRNA-first silencing
shRNA-first silencing
Deploy single or pooled shRNA constructs for rapid pathway deconvolution; transition to stable lines with lentivirus or MMLV/MSCV when needed.
Discover the Creative Biolabs Advantage – Inquire with Us for a Customized Quote.
Publication
In the working model, hepatic glycogen acts as a metabolic rheostat that gates gluconeogenesis via an AMPK/CRTC2 signaling axis. Elevating AA8-PPP1R3C (PTG) targets PP1 to glycogen particles, expands glycogen reserves, and consequently dampens the CREB/CRTC2 transcriptional program that drives Pck1, G6pc, and other gluconeogenic genes; conversely, reducing AA8-PPP1R3C lowers glycogen and amplifies gluconeogenic tone. This glycogen→AMPK→CRTC2 pathway positions AA8-PPP1R3C as a proximal lever linking glycogen architecture to nuclear control of glucose output. Conceptually, the model reframes glycogen from a passive store to an active signal that tunes hepatic glucose production across fasting–feeding and hormonal states, illuminating why perturbations in glycogen handling reshape systemic glucose homeostasis.
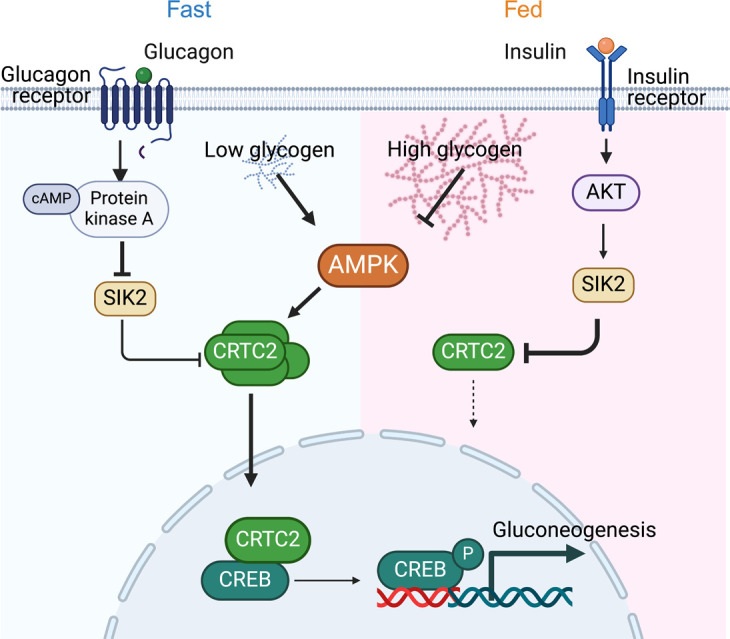 Fig.1 Hepatic glycogen controls the expression of gluconeogenic genes via the newly identified glycogen/AMPK/CRTC2 signaling pathway.1
Fig.1 Hepatic glycogen controls the expression of gluconeogenic genes via the newly identified glycogen/AMPK/CRTC2 signaling pathway.1
Customer Reviews
Robust Glycoform Control
Using Creative Biolabs' glycoengineering viral particles in our hepatocyte model has significantly improved quantitation of N-glycan branching and clarified dose–response behavior, enabling a clean link between enzyme expression and secretion quality. Dr. Mar*** Klein
Clearer MOA In Vivo
Using Creative Biolabs' AAV-based constructs in our cardiac study has significantly facilitated tissue-restricted expression and reduced background, letting us attribute functional changes to defined glyco-modulation with fewer animals. Prof. Lin*** Ortega
Faster Assay Turnaround
Using Creative Biolabs' integrating vectors in primary neural cultures has significantly improved transduction consistency and stabilized enzyme levels, cutting our assay cycle from weeks to days without compromising data integrity. C. Gar*** Patel
FAQs
Q: How do I choose between integrating vectors and AAV for my use case?
A: Select integrating vectors when you need durable expression in dividing or quiescent cells in vitro; choose AAV1–AAV9 for tissue-directed in vivo studies or where lower genomic disruption risk is preferred. Ask us for a matrix matched to your model.
Q: What insert size can you accommodate?
A: Compact payloads are ideal. We routinely engineer constructs to fit within common packaging limits and offer design strategies (minimal UTRs, shorter tags) to keep function intact. Share your ORF length and we will propose options.
Q: How is subcellular localization ensured?
A: We incorporate signal peptides, transmembrane domains, and retention motifs validated for ER/Golgi targeting so enzymes access the correct substrates. Localization can be confirmed with tags and co-staining if needed.
Q: Can you help with analytics to verify glycoengineering effects?
A: Yes. We offer glycomics (LC–MS), lectin arrays, Western blots, and activity assays, and we align them with your phenotypic readouts to link glycan shifts to function.
Q: What if my tissue target is challenging?
A: We optimize serotype, promoter, and dosing, and can test small panels to identify the best-performing configuration in your system before scaling.
Related Services
Accelerate your research endeavors with our glycoengineering solutions. Contact us for a consultation now.
Reference
-
Zhang, Bichen et al. "Hepatic glycogen directly regulates gluconeogenesis through an AMPK/CRTC2 axis in mice." The Journal of clinical investigation vol. 135,11 e188363. 2 Jun. 2025. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci188363




 Fig.1 Hepatic glycogen controls the expression of gluconeogenic genes via the newly identified glycogen/AMPK/CRTC2 signaling pathway.1
Fig.1 Hepatic glycogen controls the expression of gluconeogenic genes via the newly identified glycogen/AMPK/CRTC2 signaling pathway.1

