Chemical Deglycosylation
Overview of Chemical Deglycosylation
The chemical method is to use chemical reagents to effectively release the glycan chain without destroying the integrity of the glycan chain and protein structure, such as hydrazinolysis, periodate oxidation-β elimination method, trifluoroacetic acid method, trifluoromethanesulfonic acid method, etc. For N-linked glycopeptides, hydrazinolysis can effectively release N-glycan chains. For O-linked glycopeptides, the periodate oxidation-β elimination method and trifluoroacetic acid method can effectively release O-linked glycan chains. O-linked glycosidic bonds are sensitive to alkalis. Under alkaline conditions, the O-glycosylated groups of Ser/Thr undergo β- elimination to form unsaturated bonds, and the double bonds are easily added by nucleophile attack. Trifluoroacetic acid breaks the peptide chain by transamination, thereby releasing the glycan chain. The trifluoromethanesulfonic acid method is suitable for all glycan chains, but the glycan chain removal is not thorough enough.
Chemical Deglycosylation Strategies
The hydrazinolysis method can deglycosylate N-glycan chains. Glycoproteins are deacetylated after hydrazinolysis and then release glycan chains. To avoid the hydrolysis and deacetylation of glycan chains by hydrazine, the glycan chains need to be reduced and acetylated after hydrazinolysis. The disadvantages of this method are: firstly, the acetyl group of N-acetylamino glycan, the acetyl group of sialic acid, and glycolyl group will be hydrolyzed under the conditions of hydrazinolysis; secondly, the remaining hydrazine or amino acids will bind to the ends of reducing glycan; thirdly, the high reaction temperature will cause the loss of GlcNAc; finally, this process must strictly maintain anhydrous conditions, and the hydrazinolysis conditions are severe, which will cause protein denaturation, and it is only used for obtaining glycan chains for structural analysis. However, if used with caution, hydrazinolysis can be applied commercially in large quantities.
-
Periodate oxidation-β elimination
The key to the sodium periodate oxidation-β elimination method is that the C3 position of the side chain glycan group should be no substituents. If there is a substituent on the C3 position, the sulfonic trifluoromethane (TFMSA) treatment is required. The first step of the periodate oxidation-β elimination method is to form dialdehydes at the C3 and C4 positions of N-acetylgalactosamine, and then under alkaline conditions, the dialdehyde derivatives undergo β-elimination reaction. O-linked glycosidic bonds are sensitive to alkali. This method can completely remove O-linked glycans under alkaline conditions. For N-linked glycans, GlcNAc residues will remain on Asn after removal.
The trifluoroacetic acid method (TFA) breaks the peptide chain by transamination, and the N-trifluoroacetate group replaces the N-acetyl group in the amino glycan. The disadvantage of this reaction is that the O-glycosidic bond between serine and threonine as well as the N-acetylgalactosamine bond will be broken, and the galactosamine residue will be partially cleaved. Thus the oligosaccharides released by this reaction cannot be recovered quantitatively and the reducing end of the chain will be partially degraded.
-
Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid
The trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (TFMS) method can remove all glycan groups except the monosaccharide directly connected to the peptide chain. The disadvantage of this method is that if sialic acid exists at the end of the glycan chain, the efficiency of the reaction will be affected, and the structure of the glycan chain will be destroyed, resulting in incomplete and inaccurate information. In addition, the process of this method must be kept strictly anhydrous.
Services at Creative Biolabs
The importance of chemical deglycosylation is partly reflected in the potential to realize commercial deglycosylation in large quantities. As an industry-leading glycoprotein-based services provider, Creative Biolabs has established a comprehensive technology platform providing reliable glycoprotein analysis services:
If you are interested in our services or you have any other questions, please feel free to contact us for more information.
Published data
Glycan analysis helps develop glycan biomarkers and evaluate the diversity of glycosylation of biopharmaceuticals. Glycans are unstable under alkaline conditions, and chemical deglycosylation of N-linked glycans may increase the yield of released glycans. In this study, the authors explored a new method for chemical deglycosylation of N-linked glycans. The authors placed N-linked glycans with hydroxylamine under alkaline conditions to react with the reducing end of hydroxylamine to form a mixture of oximes, free glycans, and glycosylamines, thereby completing the deglycosylation process. N-linked glycans were released within 1 hour at 50°C or 80°C. The authors then labeled the released glycans and the corresponding oximes with a fluorescent tag (2-aminobenzamide), and then sensitively analyzed the glycan structure by high-performance liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Compared with the traditional hydrazinolysis method, the use of hydroxylamine for deglycosylation had simple reaction conditions and simple operation and did not require acetylation and anhydrous conditions. In addition, the authors compared the glycan recovery rates of traditional enzymatic methods and this deglycosylation method, and the results showed that increasing the temperature and time led to the degradation of glycans while reducing these parameters resulted in a decrease in the release of glycans. Therefore, the authors recommend deglycosylation at 80°C for 1 hour for mammalian sialoglycoproteins and 50°C for 1 hour for sialoglycoproteins. The authors believed that this chemical deglycosylation method could be used to quickly and easily evaluate the glycosylation status of therapeutic antibodies.
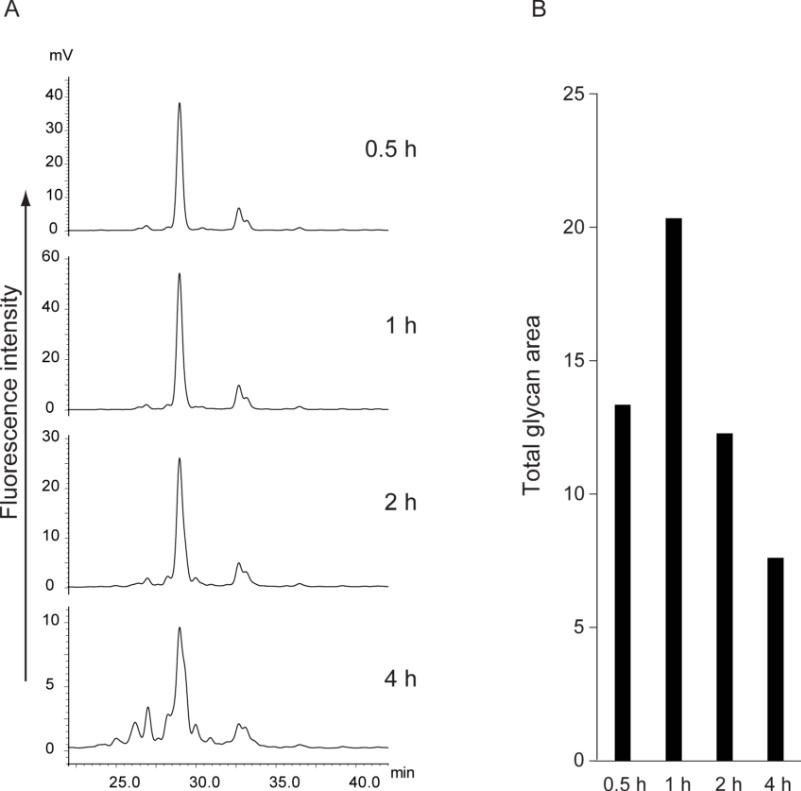 Fig.1 Deglycosylation process at different time points.1
Fig.1 Deglycosylation process at different time points.1
FAQs
Q1: How do you ensure the accuracy and integrity of glycan chain analysis after deglycosylation?
A1: We use a combination of optimized deglycosylation techniques and subsequent analysis methods such as mass spectrometry, HPLC, and glycan labeling technologies. Our platform is designed to ensure that even delicate structures are maximally preserved for accurate and complete analysis.
Q2: How do you handle proteins that are sensitive to the conditions required by some chemical deglycosylation techniques?
A2: We use tailored methods according to the type of glycoprotein and the specific glycan structure. In some cases, milder conditions or enzymatic methods are used as an alternative to avoid damaging sensitive proteins. Our extensive experience and comprehensive technology platform allow us to select the best method for each specific case.
Q3: What are the quality control measures during the deglycosylation process?
A3: We implement stringent quality control measures at every stage of the deglycosylation process, including monitoring reaction conditions, verifying the integrity of glycan removal, and analyzing the structural integrity of glycans and proteins using advanced analytical techniques such as mass spectrometry and chromatography.
Customer Review
Thorough Deglycosylation
"I was impressed by the excellent execution of the hydrazinolysis by Creative Biolabs. Their method maintained the integrity of our glycan chains while ensuring thorough deglycosylation. We were particularly pleased with the high purity of the glycan chains obtained, which was ideal for our structural analysis needs."
Providing Sufficient Quantities of Oligosaccharides to Clients
"I appreciate that Creative Biolabs used the trifluoroacetic acid method to process our complex O-linked glycopeptides. Their systematic approach minimized the cleavage of O-linked sugar bonds and N-acetylgalactosamine, providing sufficient quantities of oligosaccharides for our high-throughput sugar screening."
References
-
Kameyama, Akihiko, Santha Kumara Dissanayake, and Wai Wai Thet Tin. "Rapid chemical de-N-glycosylation and derivatization for liquid chromatography of immunoglobulin N-linked glycans." PLoS One 13.5 (2018): e0196800. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Deglycosylation process at different time points.1
Fig.1 Deglycosylation process at different time points.1

