Chemoselective and Site-Specific Glycosylation
Introduction and Necessity for Protein Glycosylation
Protein glycosylation also refers to the covalent attachment of carbohydrates to the side chains of proteins, is one of the most common co- and posttranslational modifications for proteins. The carbohydrate portions play important roles in a series of biological processes, such as host-pathogen interaction, host immune responses, and cell adhesion. In this case, correct glycosylation is critical for normal protein expression and folding. To better understand the properties and functions of glycoproteins, the biosynthesis of complex glycoproteins is necessary. In general, natural and recombinant glycoproteins share the same peptide backbone but differ in the carbohydrate portions and the sites of the linkage which makes it extremely difficult to obtain a pure, homogeneous glycoprotein.
Multiple Approaches for Chemoselective and Site-Specific Glycosylation
To better understand the molecular basis of the oligosaccharides for drug discovery application, a series of nonnative chemoselective ligation approaches have been developed to introduce carbohydrate moieties at specific sites of peptides and proteins.
For example, iodoacetamide-containing mono- and oligosaccharides have been used for site-specific glycosylation of cysteine-containing peptides/proteins. The glyco-methanethiosulfonates have been developed for proteins’ site-selective glycosylation. Combined with the introduction of cysteine residue via sited-directed mutagenesis, glycan-specific glycosylation for a series of biological proteins is allowed. In summary, these chemoselective ligation methods allow us to design and synthesize novel glycoproteins for various biological research and applications.
In addition, multiple approaches have been developed to increase the selectivity and predictability of protein glycosylation. It has been reported that an aldehyde tag can be introduced onto the C-6 of a GalNAc residue in the antimicrobial 19- residue peptide drosocin under the specific action of galactose oxidase. And then this aldehyde allows the introduction of more oligosaccharides by combining with aminooxy glycosides.
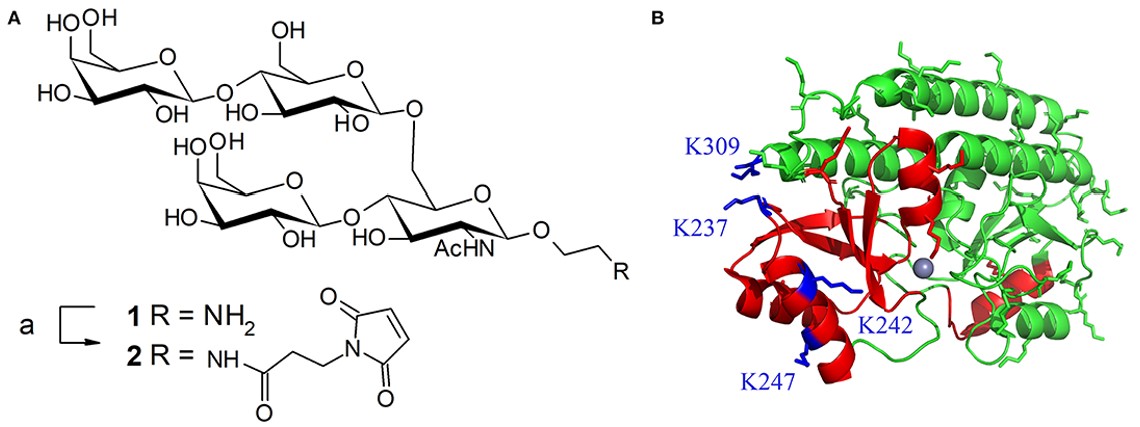 Fig.1 Preparation of glycoconjugate vaccines using thiol/maleimide coupling chemistry.1, 2
Fig.1 Preparation of glycoconjugate vaccines using thiol/maleimide coupling chemistry.1, 2
Maleimide-based Site-specific Glycosylation
There are a series of maleimide-activated mono- and oligosaccharides for site-specific glycosylation of cysteine-containing peptides and proteins. Combined with site-specific mutagenesis, site-specific glycosylation of proteins can be achieved by efficient maleimide-thiol linkage reaction. Under physiological conditions, this reaction is rapid, essentially quantitative, and highly selective. Multivalent HIV-1 peptides have been synthesized successfully using this highly chemoselective ligation.
Creative Biolabs has been a long-term expert in the field of glycomics. As a pioneer and the undisrupted global leader in glycan research, we offer a variety of products and services including custom glycoprotein synthesis. If you are interested in our products or services, please do not hesitate to contact us for more detailed information.
References
-
Pillot, Aline, et al. "Site-specific conjugation for fully controlled glycoconjugate vaccine preparation." Frontiers in Chemistry 7 (2019): 726.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Preparation of glycoconjugate vaccines using thiol/maleimide coupling chemistry.1, 2
Fig.1 Preparation of glycoconjugate vaccines using thiol/maleimide coupling chemistry.1, 2

