GPI-anchored Glycoprotein
Introduction of GPI-anchored Glycoprotein
GPI, also known as glycosylphosphatidylinositol or glycophosphatidylinositol, is a phosphoglyceride that consists of a phosphatidylinositol group connected to the C-terminal amino acid of the mature protein through a carbohydrate-containing linker and a phosphoethanolamine (EtNP) bridge.
As an ancient glycoprotein modification, GPI-anchored glycoproteins have been identified in multiple eukaryotic species, such as humans, yeasts, insects, bacteria, as well as fungi. In humans, there are more than 150 GPI-anchored glycoproteins that function in a variety of roles serving as adhesion molecules, enzymes, receptors, transporters, transcytotic receptors, and protease inhibitors. In fungi, GPI-anchored glycoproteins are components of the cell wall and play important roles in cellular integrity. In protozoa, GPI-anchored glycoproteins are the major form of cell-surface proteins.
Biosynthesis and Degradation of GPI-anchored Glycoprotein
Through a series of enzymatic reactions, GPI anchors can be assembled on the phosphatidylinositol lipid in the endoplasmic reticulum and covalently attached to the carboxyl-terminal of the protein.
After it is assembled, it is transferred to the lumen, and the carboxyl end of the protein is connected to the GPI anchor. The release of GPI-anchored protein can be achieved by treatment with phospholipase C, phosphatidylinositol-specific (PLC-PI). The enzymatic release of the GPI anchor from the cell membrane may trigger the second messenger to perform signal transduction. In addition, there is a hydrophobic signal sequence at the carboxyl terminus of all GPI-anchored glycoproteins to trigger the addition of the GPI anchor.
 Fig.1 Maturation of GPI-anchored glycoproteins in mammals.1, 3
Fig.1 Maturation of GPI-anchored glycoproteins in mammals.1, 3
Hallmark Features of GPI-anchored Glycoprotein
-
Related to membrane microdomains (rafts) rich in sphingolipids and cholesterol
-
Exists on the cell surface as a transient homodimer
-
Internalized through a specific route
-
Transduction of signals for proliferation or cell movement during connection and aggregation
-
Can be detached from the plasma membrane after GPI anchor cleavage
Associated Diseases of GPI-anchored Glycoprotein
The latest research showed that genes mutation involved in the assembly, protein attachment, and remodeling of GPI-anchored glycoproteins may result in a series of genetic diseases. For example, defects in the fatty acid remodeling of GPI-anchored glycoproteins in the Golgi result in Mabry syndrome.
Creative Biolabs is a long-term expert in the field of glycomics. As a pioneer and the undisrupted global leader in glycan research, we offer a variety of products and services including custom glycan synthesis. If you are interested in our products or services, please do not hesitate to contact us for more detailed information.
Published data
Multiple GPI-anchored proteins are expressed on the surface of mammalian cells. Multiple genes are involved in the biosynthesis of GPI-anchored proteins in cells. GPI-anchored proteins have been found to play important roles in various biological processes, with unique properties in binding to lipid rafts and intracellular transport. In this study, researchers constructed a cell library and knocked out 32 genes involved in GPI biosynthesis. The knockdowns resulted in the production of GPIs with unique structures and functions. Using the constructed cell library, they systematically analyzed the sensitivity of GPI-anchored proteins to phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C and its surface expression. Also, the GPI structural motifs recognized by aerolysin were identified by these GPI knockdown libraries. This study demonstrates that cell-based GPI knockdown libraries are suitable for basic and applied research on GPI-anchored proteins. It not only provides insights into the genetic and biosynthetic regulation of GPI but also lays the foundation for us to produce GPI-anchored proteins with specific structures.
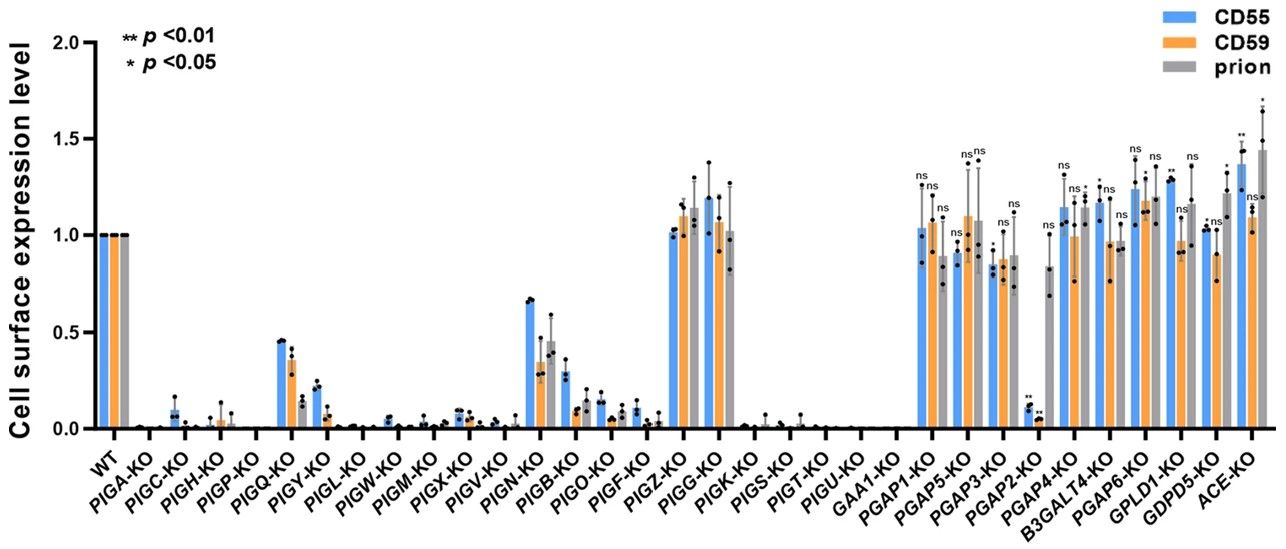 Fig.2 GPI-anchored glycoproteins expression in knockdown cell library.2, 3
Fig.2 GPI-anchored glycoproteins expression in knockdown cell library.2, 3
FAQs
Q1: What is the biological significance of the GPI anchor glycoprotein?
A1: GPI anchor glycoprotein has a variety of functions and is involved in some biological processes, such as signal transduction, participation in cell-to-cell contact and adhesion, and regulation of the complement cascade. In addition, it is shown to protect organisms from foreign invaders and pathogens. In addition to the above functions, GPI anchor glycoproteins are also shown to play a role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Several in vitro GPI anchor glycoprotein synthesis studies have been conducted to explore the functions of GPI and GPI anchor glycoproteins.
Q2: Can GPI anchor glycoproteins be synthesized in vitro?
A2: Of course, it can be synthesized in vitro. To explore the functions of GPI and GPI-anchored glycoproteins, researchers have tried to synthesize homogeneous and structurally well-defined GPI-anchored peptides, GPI-anchored glycoproteins, etc., by chemical and chemoenzymatic methods. For example, Many GPIs have been successfully synthesized by highly convergent GPI synthesis strategies, among which GPIs carrying azide and alkyne groups can be further site-specifically modified by click chemistry. GPI-anchored glycopeptides, glycoproteins, etc., are synthesized by site-specific linkage of GPI and glycopeptides or proteins.
Customer Review
Facilitated Research on GPI-anchored Glycoprotein
"Our research group conducted extensive research on the structure and functions of GPI-anchored glycoprotein and turned to Creative Biolabs to help us synthesize GPI-anchored glycoprotein with a specific structure. We had to say that the quality of the product they provided was very good, and it helped us a lot in our research."
Precise Fulfillment of Research Needs on GPI-anchored Glycoprotein
"Creative Biolabs has demonstrated exceptional expertise in the synthesis of GPI-anchored glycoprotein and other research. Not only did they provide a high-quality product, but they were communicative and precise in meeting all of our requirements. This professional and reliable service was recommendable."
References
-
Kinoshita, Taroh. "Biosynthesis and biology of mammalian GPI-anchored proteins." Open biology 10.3 (2020): 190290.
-
Liu, Si-Si, et al. "A knockout cell library of GPI biosynthetic genes for functional studies of GPI-anchored proteins." Communications biology 4.1 (2021): 777.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
无标题文档
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Maturation of GPI-anchored glycoproteins in mammals.1, 3
Fig.1 Maturation of GPI-anchored glycoproteins in mammals.1, 3
 Fig.2 GPI-anchored glycoproteins expression in knockdown cell library.2, 3
Fig.2 GPI-anchored glycoproteins expression in knockdown cell library.2, 3

