As one of the most structurally complex and functionally diverse classes of bioactive carbohydrates, Human Milk Oligosaccharides (HMOs) have emerged as essential components in infant nutrition, microbiome development, and immunomodulation. With over 200 unique structures identified to date, HMOs—especially fucosylated oligosaccharides—have garnered significant interest from both the scientific and industrial communities. Today, advancements in human milk oligosaccharides synthesis, enabled by chemoenzymatic strategies, metabolic engineering, and next-generation enzyme technologies, are fueling the rise of novel human milk oligosaccharides manufacturers and suppliers. At Creative Biolabs, we bring not only deep scientific insight but also tailored, reliable solutions in custom milk oligosaccharide synthesis and analytical services, supporting the entire journey from molecule design to functional application.
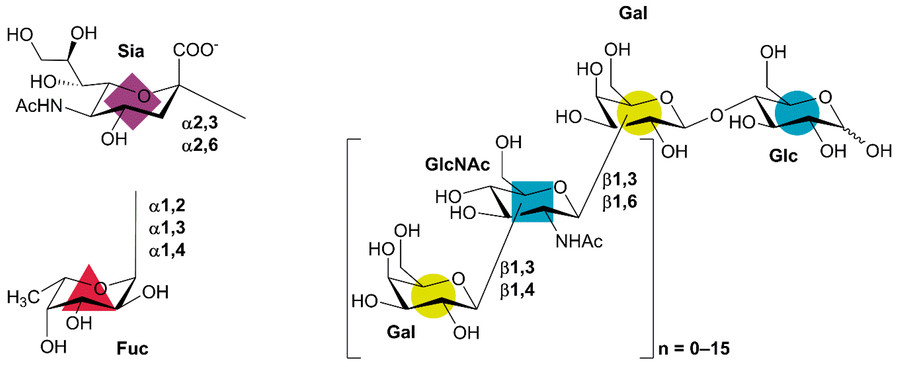 Fig.1 Human milk oligosaccharide (HMO) structure basis.1
Fig.1 Human milk oligosaccharide (HMO) structure basis.1
Chemoenzymatic Synthesis
Chemoenzymatic synthesis has become the cornerstone method for constructing structurally complex HMOs. By combining the flexibility of chemical synthesis with the regio- and stereoselectivity of enzymatic catalysis, this approach facilitates high-yield, scalable production of diverse HMO structures, including fucosylated and sialylated oligosaccharides. Key strategies include:
-
Core Scaffold Construction: Lactose-derived core structures such as Lacto-N-tetraose (LNT) and Lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT) are synthesized via CSEE-based convergent coupling, using thioglycoside or halide glycosyl donors.
-
Enzymatic Extension: Bacterial glycosyltransferases (GTs) are employed to decorate these cores:
-
LgtB from Neisseria meningitidis adds Galβ1-4GlcNAc,
-
Hpα1,3FT and Hmα1,2FT insert fucose in α1,3 and α1,2 linkages, respectively,
-
Pd2,6ST introduces α2,6-linked sialic acid (Neu5Ac).
-
One-Pot Multienzyme (OPME) Systems: These systems streamline reactions and reduce purification steps. For example, LgtB and BiGalK can sequentially generate Galβ1-4GlcNAc from simple monosaccharides in a single reaction vessel.
We are proud of our flexible chemoenzymatic synthesis technologies with lots of advantages, while there are still challenges that need to be address:
|
Advantages
|
-
Capable of producing over 30 structurally diverse HMOs, including asymmetric and multi-antennary types.
-
High regio- and stereoselectivity.
|
|
Challenges
|
-
Substrate specificity of glycosyltransferases (e.g., Hmα1,2FT's terminal Gal preference).
-
High cost of nucleotide-sugar donors like GDP-Fuc and CMP-Neu5Ac.
|
Metabolic Engineering & Cell Factories
Metabolic engineering leverages genetically modified microbial systems to enable cost-effective, scalable human milk oligosaccharides production, particularly for relatively simple structures such as 2'-fucosyllactose (2'-FL) and 3-FL.
-
Fucosylation Pathway Engineering:
-
Genes such as futC (α1,2-fucosyltransferase), manC, and gmd (for GDP-Fuc biosynthesis) are introduced into E. coli or Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
-
Achieved 2.5 g/L of LNFP I in engineered E. coli strains.
-
Yeast Platforms:
-
Yeasts offer endotoxin-free environments and facilitate extracellular secretion of HMOs.
-
Modular "Plug-and-Play" Circuit Design:
-
AI-guided optimization of promoters and ribosome binding sites (RBS) enhances expression efficiency.
-
Cross-species expression of mammalian GTs allows synthesis of branched or more complex HMOs.
Next-Generation Enzyme Engineering
To overcome the limitations of natural enzymes, next-generation enzyme engineering focuses on expanding substrate ranges, improving thermostability, and enabling non-natural oligosaccharide construction. Recent research found that, a bifunctional enzyme was developed (LgtB-Pd2,6ST fusion) for one-pot synthesis of sialylated LNT. Innovations include:
-
Transglycosylation-Enabling Mutations: Engineered GH29 α-L-fucosidases now perform transglycosylation for constructing α1,2-linked fucosylated structures.
-
Non-Canonical Donor Substrate Utilization: Modified enzymes utilize GDP-6-deoxyfucose and other analogs for tailored oligosaccharide derivatization.
-
Extremophile-Derived Enzymes: Thermostable glycosyltransferases from Thermotoga maritima are optimized for high-temperature fermentation.
Need Support in Oligosaccharide Design or Manufacturing?
At Creative Biolabs, we offer a full suite of solutions for oligosaccharide synthesis and analysis, tailored for researchers and product developers across biotech, nutrition, and pharma sectors. We've got the tools and expertise to accelerate your innovation.
We also offer a series of high- quality oligosaccharide products that may be suitable for your research
New Breakthroughs in Human Milk Oligosaccharides Synthesis
Biotech-Driven Enzymatic Synthesis
-
Multi-omics approaches have led to the development of enzyme libraries including GH29 α-L-fucosidases and β3GalTs with broadened substrate scope.
Microbial Fermentation & Whole-Cell Biotransformation
-
Engineered strains of E. coli and S. cerevisiae are achieving high titers of LNT and fucosylated variants.
-
Use α-L-fucosidase from wheat microbial strains to enhance reaction efficiency.
Plant Synthetic Biology
-
Nicotiana benthamiana and other plant platforms are now viable for low-cost HMO production.
Hybrid Chemical-Enzymatic Systems
-
Solid-phase synthesis coupled with OPME catalysis allows for precise HMO architecture control.
Expanding Structural & Functional Diversity
-
Studies continue to reveal specific roles of 2'-FL and 6'-SL in pathogen resistance, gut health, and neural development.
Industrial Advancement
-
Human milk oligosaccharides suppliers are leveraging integrated production platforms for scalable manufacturing and reduced cost.
Applications
HMOs in Gut Microbiota Modulation
-
2'-FL acts as a decoy receptor, neutralizing E. coli, Norovirus, and more.
-
Selectively promotes Bifidobacterium colonization, reducing NEC in neonates.
Neurodevelopmental and Immunomodulatory Roles
-
Sialylated HMOs like 3'-SL and 6'-SL modulate Notch signaling and improve cognitive flexibility.
-
Regulate T cell responses and cytokine profiles in preclinical models.
As consumer demand for infant nutrition products with enhanced functional properties continues to rise, human milk oligosaccharides manufacturers are at the forefront of innovation. Technologies such as chemoenzymatic synthesis, metabolic engineering, and enzyme evolution are collectively transforming how human milk oligosaccharides are made and applied. At Creative Biolabs, we don't just follow these innovations—we help build them. From custom HMO synthesis to in-depth glycan profiling, we offer end-to-end services tailored to your product pipeline. Whether you're optimizing a formulation or launching a new oligosaccharide-based therapeutic, partner with us—your expert HMO supplier in the science of sugar.
FAQs
Q: What is the biosynthesis of HMOs?
A: HMOs are biosynthesized in mammary epithelial cells via glycosyltransferases that sequentially add fucose, sialic acid, and other sugars to lactose. This genetically regulated process yields diverse structures, influenced by maternal FUT2/FUT3 genotypes.
Q: How are HMOs produced?
A: HMOs are produced using chemoenzymatic synthesis or engineered microbial fermentation. These technologies mimic natural biosynthesis, enabling scalable production of specific structures like 2'-FL and LNnT, followed by purification to meet nutritional or pharmaceutical-grade standards.
Reference
-
Zeuner, Birgitte, et al. "Synthesis of human milk oligosaccharides: Protein engineering strategies for improved enzymatic transglycosylation." Molecules 24.11 (2019): 2033. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112033
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Human milk oligosaccharide (HMO) structure basis.1
Fig.1 Human milk oligosaccharide (HMO) structure basis.1

