What is O-Linked Glycosylation?
Enzymes attach monosaccharides to oxygen atoms located in the side chains of serine or threonine during O-linked glycosylation. O-linked glycosylation takes place only in the Golgi apparatus where its activity is controlled by specific glycosyltransferases unlike N-linked glycosylation that starts in the endoplasmic reticulum. The initial sugar that starts this process is N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc). The glycosylation sequence continues with the addition of galactose, N-acetylglucosamine, sialic acid and fucose. O-linked glycans display structural differences that depend on the specific cellular environment and are shaped by enzyme expression profiles, protein structure configurations, and their subcellular positioning.
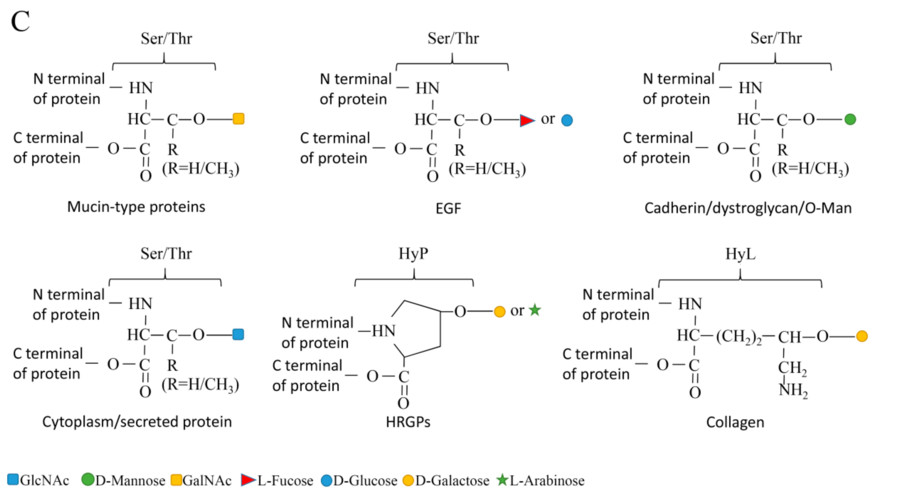 Fig.1 O-linked glycosylation types.1
Fig.1 O-linked glycosylation types.1
Creative Biolabs combines decades of glycoprotein engineering experience with advanced services for custom O-linked oligosaccharide synthesis and glycan analysis to enable glycoengineering that helps researchers explore new possibilities in glycobiology.
O-Linked Glycosylation Function
O-linked glycosylation performs numerous biological functions:
-
Glycans contribute to protein structural stability by protecting proteins from proteolysis and assisting in correct protein folding.
-
Glycosylation alters receptor function as seen in Notch signaling which determines cell destiny.
-
O-glycans operate as selectins and galectins ligands which direct immune cell movement and tissue formation.
-
O-linked glycosylation functions as a molecular address label which directs intracellular transport.
-
This biological process alters glycoprotein antigenicity and immune response capabilities.
-
Numerous pathogens exploit host O-glycan structures to gain entry or evade immune detection.
Alterations in O-glycosylation patterns show significant correlations with diseases including cancer, diabetes, and Alzheimer's disease. That's why robust analytical tools are indispensable. Our service provides complete mapping of glycosylation sites for analysis of your O-glycosylation patterns. Our O-linked glycosylation mapping technologies cover methods including but not limited to:
O-Linked Oligosaccharide Structure
O-linked oligosaccharides have core glycan motifs which begin with GalNAc linked to serine or threonine. These core structures include:
Core 1: GalNAc-α1-Ser/Thr linked to β1,3-galactose.
Core 2: The Core 2 structure builds upon Core 1 by adding a β1,6-linked N-acetylglucosamine.
Core 3: GalNAc-α1-Ser/Thr linked to β1,3-N-acetylglucosamine.
Core 4: Core 3 structure extends by adding β1,6-linked N-acetylglucosamine.
The different core types produce branched structures that perform distinct biological functions. The existence of molecular diversity serves as a foundation for precise molecular interactions and effective protein performance.
O-Linked Oligosaccharide Types and Examples
|
Type
|
Example Proteins
|
Biological Role
|
|
Mucins
|
MUC1, MUC2
|
Protect epithelial surfaces, form mucus gel layer
|
|
Glycophorin
|
Glycophorin A (erythrocyte membrane protein)
|
Determines blood group antigens, prevents cell aggregation
|
|
Notch
|
Notch receptors
|
Modulates cell differentiation and fate via ligand interactions
|
|
CD43
|
Leukosialin (on T cells)
|
Involved in cell migration and immune response
|
|
hCG
|
Human chorionic gonadotropin
|
Glycans extend serum half-life and bioactivity
|
|
IgA1
|
Immunoglobulin A1
|
Mucin-type O-glycans regulate immune effector functions
|
Creative Biolabs supplies researchers working with glycoconjugates with a comprehensive selection of superior oligosaccharide products suitable for analytical standards and assay development as well as glycoengineering applications.
O-Linked Oligosaccharide Function
O-linked oligosaccharides not only serve structural roles but also have distinct biological functions:
-
Enhancing Protein Half-Life: Glycans protect therapeutic proteins, extending their systemic circulation.
-
Regulating Enzymatic Activity: O-glycans can allosterically modulate catalytic domains or substrate accessibility.
-
Forming ABO Antigens: Blood group antigens are synthesized through O-linked glycosylation.
-
Building Mucosal Barriers: In mucins, they form dense glycan shields that block pathogen access.
-
Cell Development & Differentiation: Glycans shape developmental signaling cascades.
-
Disease Indicators: Aberrant O-glycosylation is a hallmark of multiple pathologies and serves as a biomarker.
Creative Biolabs Services Supporting O-Glycosylation Research
To help accelerate O-linked glycosylation studies, we offer a suite of tailored solutions that cover everything from synthesis to structural characterization:
Whether you're engineering glycoprotein therapeutics or exploring glycan biomarkers, we've got your O-glycan workflows covered—fast, flexible, and fully customized.
Difference Between N-Linked and O-Linked Oligosaccharides
N-linked and O-linked glycosylation share the common feature of glycan attachment to proteins but they exhibit distinct differences in multiple aspects. Recognizing these distinctions between glycosylation types enables researchers to understand the specific roles these biochemical processes serve in cellular functions while also revealing their relevance to health and disease.
-
N-linked glycans bind asparagine residues in an Asn-X-Ser/Thr motif while O-linked glycans connect to serine or threonine hydroxyl groups without requiring a specific sequence pattern.
-
The initiation of N-linked glycosylation involves N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) whereas O-linked glycosylation starts with N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc).
-
The conserved pentasaccharide core (GlcNAc₂Man₃) characterizes N-linked structures while O-linked cores present structural diversity as seen in Core 1 (GalNAc-α1-Ser/Thr extended by β1,3-galactose).
-
N-linked glycan formation begins in the endoplasmic reticulum during translation and extends into the Golgi apparatus while O-linked glycan synthesis occurs entirely within the Golgi after protein translation.
-
N-linked glycans usually display greater size and more complex branching patterns whereas O-linked glycans remain shorter with less branching but exhibit diverse structural forms.
-
N-linked modifications facilitate protein folding alongside ER quality control and stability maintenance while O-linked glycans principally regulate cell signaling processes, immune recognition mechanisms and mucosal protection functions.
-
N-linked glycosylation usually occurs on immunoglobulins and transmembrane receptors while O-linked glycans dominate mucins and blood group antigens.
O-linked oligosaccharides carry essential roles in biological systems through their regulation of immune responses and cell communication which affects disease progression and leads to therapeutic developments. Their structural diversity reflects their biological precision. Creative Biolabs offers continuous support to researchers at every stage during their glycosylation research projects. Our team delivers crucial assistance to convert glycobiology obstacles into valuable biomedical information for scientists conducting glycan function mapping or custom structure synthesis. Ready to accelerate your O-linked glycosylation research? Talk to our experts today.
Reference
-
Lin, Borong, et al. "Role of protein glycosylation in host-pathogen interaction." Cells 9.4 (2020): 1022. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, it was cropped to keep only part C. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9041022
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 O-linked glycosylation types.1
Fig.1 O-linked glycosylation types.1

