The increasing need for precise biotherapeutics underscores the essential role of understanding glycosylation mechanisms with a special emphasis on N-linked oligosaccharides. Glycosylated sugar structures extend beyond simple post-translational decorations to fulfill essential roles in protein folding and trafficking as well as immune recognition and pharmacokinetics. N-linked glycosylation determines biological performance across monoclonal antibodies and hormone therapies. Creative Biolabs delivers extensive specialized experience spanning decades in both glycoengineering and glycan analysis. Our flexible high-quality service solutions are available for both optimizing therapeutic antibody Fc-effector functions and high-resolution oligosaccharide structural analysis according to your needs. Our custom N-linked oligosaccharide synthesis service helps you drive your project forward with assured performance.
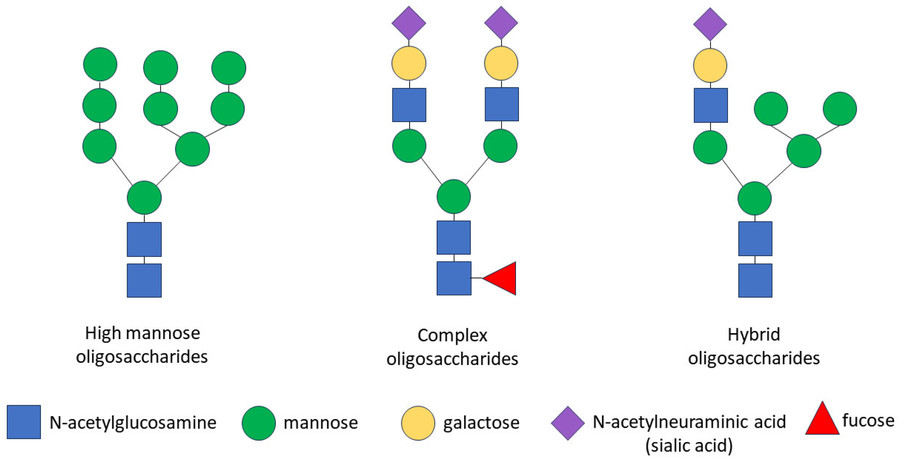 Fig.1 Three types of N-Linked oligosaccharides.1
Fig.1 Three types of N-Linked oligosaccharides.1
What is N-Linked Glycosylation?
N-linked glycosylation is the enzymatic addition of oligosaccharide chains to the nitrogen atom of an asparagine (Asn) residue, typically within the Asn-X-Ser/Thr consensus sequence (where X ≠ Proline). This modification begins co-translationally in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and continues in the Golgi apparatus, where oligosaccharide structures are further processed into diverse functional forms. N-linked glycosylation is not optional for most secreted and membrane-bound proteins—it is essential. It influences:
-
Proper folding and conformation of glycoproteins
-
Intracellular trafficking and secretion efficiency
-
Receptor interaction and signal modulation
-
Resistance to proteolytic degradation
-
Serum half-life and bioavailability
Mechanism of N-Linked Glycosylation
The N-linked glycosylation process involves a highly orchestrated pathway:
-
Synthesis of the lipid-linked oligosaccharide precursor (Glc₃Man₉GlcNAc₂) on the ER membrane.
-
Transfer of the glycan to a nascent polypeptide chain by oligosaccharyltransferase (OST).
-
Trimming of glucose and mannose residues in the ER for folding and quality control.
-
Remodeling in the Golgi apparatus, introducing branching sugars (e.g., GlcNAc, Gal, NeuAc).
-
Final targeting of mature glycoproteins to the cell surface or secretion pathways.
Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive glycosylation site mapping service for your N-linked glycosylation patterns analysis. Our technologies for N-linked glycosylation mapping including but not limited to:
Types of N-Linked Oligosaccharides
N-linked oligosaccharides fall into three types: high-mannose oligosaccharide, complex oligosaccharide, and hybrid oligosaccharide, all sharing a conserved Man₃GlcNAc₂ core, but diverge significantly in structure and function based on further enzymatic modifications.
|
Type
|
Structure
|
Biological Relevance
|
|
High Mannose
|
Core + 2–9 mannose units
|
Early ER forms; involved in folding and ER-associated degradation
|
|
Complex
|
Core + GlcNAc, Gal, Fuc, NeuAc on branched antennas
|
Terminal structures; modulate immune recognition and cell signaling
|
|
Hybrid
|
One branch remains mannose-rich, other undergoes processing
|
Transitional forms; seen in therapeutic glycoproteins (e.g., EPO)
|
N-Linked Oligosaccharides & Glycoproteins Examples
-
Ribonuclease B carries high mannose glycans and is widely used in folding studies and ER retention models.
-
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) contains complex-type N-glycans that modulate Fc-mediated effector functions such as ADCC.
-
Erythropoietin (EPO) features hybrid or complex glycans that extend serum half-life and boost biological activity.
N-Linked Oligosaccharides on Secreted Glycoproteins
Secreted proteins rely heavily on N-linked oligosaccharides for structural integrity and functional performance. Without proper glycosylation, many biologics fail to fold correctly or exhibit undesirable immunogenicity.
|
Role
|
Protein Example
|
Glycosylation Impact
|
|
Enhancing stability
|
Erythropoietin (EPO)
|
Complex-type glycans increase solubility and in vivo persistence
|
|
Modulating immune function
|
IgG Fc Region
|
Specific glycoforms alter receptor binding and inflammatory responses
|
|
Enabling receptor interaction
|
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone
|
Glycan pattern controls signal transduction
|
|
Protecting against degradation
|
Alpha-1-antitrypsin
|
Sugar shields prevent proteolysis
|
Our therapeutic protein glycoengineering services can help optimize glycosylation to improve pharmacological properties and reduce production variability.
N-Linked vs O-Linked Oligosaccharides
Understanding how N-linked and O-linked glycosylation differ is critical when selecting expression platforms or engineering cell lines for biotherapeutic production.
|
Feature
|
N-Linked
|
O-Linked
|
|
Attachment Site
|
Asparagine (Asn)
|
Serine or Threonine (Ser/Thr)
|
|
Core Structure
|
Conserved GlcNAc₂Man₃
|
Typically starts with GalNAc
|
|
Initiation Site
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
|
Golgi apparatus
|
|
Synthesis Pattern
|
En bloc transfer
|
Stepwise monosaccharide addition
|
|
Timing
|
Co-translational
|
Post-translational
|
|
Functional Role
|
Folding, immune modulation
|
Mucosal protection, signaling
|
Analytical and Synthetic Support from Creative Biolabs
Whether you're working on glycoprotein-based vaccines, diagnostic markers, or next-generation biologics, Creative Biolabs offers a full suite of services to advance your oligosaccharide-related projects:
Engineering Support from Creative Biolabs
If your goal is to control or customize N-linked oligosaccharides in recombinant proteins, you'll need a system that delivers both consistency and flexibility. That's where our cell line glycoengineering platform comes in. Whether you're working on antibody therapeutics, recombinant enzymes, or novel fusion proteins, we'll help you fine-tune your glycosylation profiles—right down to the oligosaccharide branch. Let us know your target, and we'll engineer the right cell line to get you there.
N-linked glycosylation represents a molecular control layer that ensures proteins not only fold properly but also interact correctly with the cellular environment. From high mannose intermediates involved in ER quality control to complex-type glycans driving immunomodulation, N-linked oligosaccharides are deeply integrated into nearly every aspect of protein biology. At Creative Biolabs, we understand the challenges and opportunities glycosylation brings to therapeutic development. With years of dedicated experience in glycoengineering and glycobiology, we are proud to partner with clients across academia and industry to design, analyze, and produce glycosylated biomolecules that meet the highest scientific and regulatory standards. Contact us now and let us help you navigate glycosylation complexities.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between N-linked vs O-linked oligosaccharides?
A: N-linked oligosaccharides are attached to asparagine residues within a specific sequence motif and begin assembly in the endoplasmic reticulum. In contrast, O-linked oligosaccharides are linked to serine or threonine residues and are synthesized later in the Golgi, without a conserved attachment sequence.
Q: What is an example of an N-linked glycan?
A: The high mannose-type glycan Man₅GlcNAc₂ is a typical N-linked structure. It is commonly found on glycoproteins such as RNase B and plays a key role during early-stage folding and ER quality control.
Q: What is the purpose of N-linked glycosylation?
A: One major purpose of N-linked glycosylation is to assist newly synthesized proteins in achieving correct three-dimensional folding. Without this modification, many glycoproteins cannot pass ER quality control and are targeted for degradation.
Q: What are the two physiological roles of the N-linked oligosaccharide?
A: First, N-linked oligosaccharides act as molecular tags that guide protein folding and ER retention. Second, they influence glycoprotein recognition on the cell surface, affecting immune responses and receptor interactions.
Reference
-
Gisina, Alisa, Konstantin Yarygin, and Alexey Lupatov. "The Impact of Glycosylation on the Functional Activity of CD133 and the Accuracy of Its Immunodetection." Biology 13.6 (2024): 449. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060449
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Three types of N-Linked oligosaccharides.1
Fig.1 Three types of N-Linked oligosaccharides.1

