The cell membrane functions as a dynamic biological landscape consisting of lipid bilayers and oligosaccharides that regulate almost every aspect of cellular communication. These molecules perform essential roles that include molecular recognition and immune modulation as well as signal transduction. Creative Biolabs has spent more than twenty years at the vanguard of glycoscience to provide comprehensive solutions that reveal the structure and function of plasma membrane oligosaccharides. Our custom oligosaccharide synthesis and oligosaccharides analysis service provide comprehensive support throughout your discovery pipeline whether you study glycosylation patterns in diseases or develop glycan-based therapies.
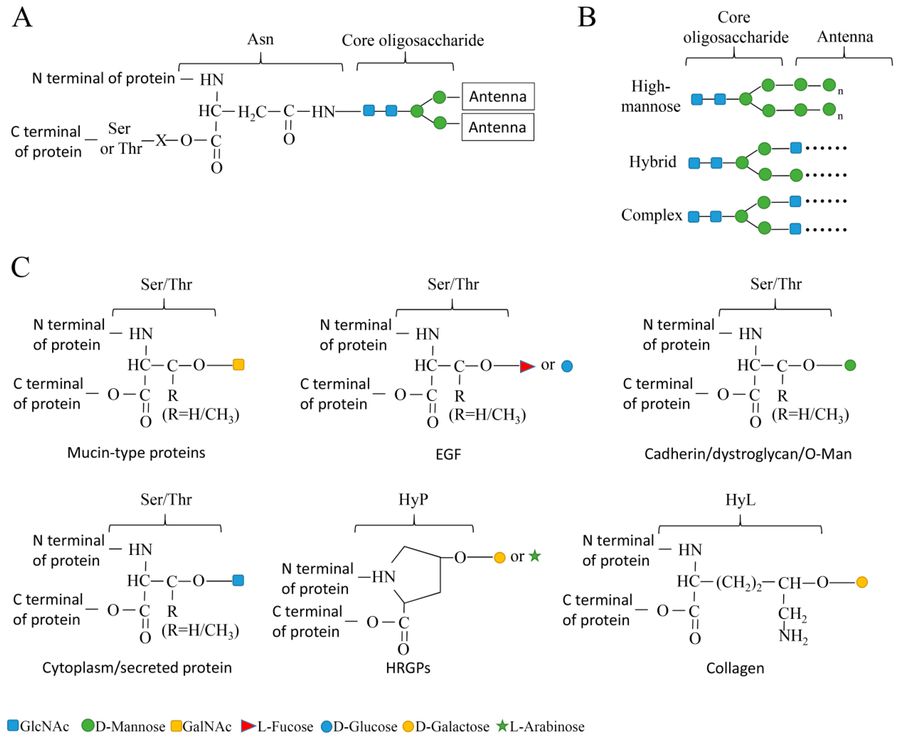 Fig.1 N-Linked and O-Linked oligosaccharides with different glycosylation types.1
Fig.1 N-Linked and O-Linked oligosaccharides with different glycosylation types.1
N-linked oligosaccharides are attached to asparagine residues within the consensus motif Asn-X-Ser/Thr, a process initiated in the endoplasmic reticulum and further refined in the Golgi apparatus. Their biosynthesis starts with the transfer of a pre-built glycan core, yielding three structural subtypes:
-
High-Mannose N-Glycans: Composed primarily of mannose residues, these are typical of early glycoproteins.
-
Hybrid N-Glycans: A transitional form combining mannose cores with complex outer branches.
-
Complex N-Glycans: Branched chains containing GlcNAc, fucose, galactose, and sialic acid—crucial for cell signaling.
A classic example is the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), where N-glycosylation modulates ligand binding and downstream signaling. Aberrant N-linked glycosylation has been implicated in tumorigenesis and immune evasion.
O-linked glycans, in contrast, are added post-translationally to serine or threonine residues. Initiated by GalNAc transfer, they are pivotal in mucosal immunity and membrane protein function. Mucins in the intestinal barrier are prime examples, showcasing O-linked oligosaccharides' protective roles against pathogens.
Another intriguing case involves CD36, a glycoprotein whose O-linked glycosylation status influences lipid uptake and has been tied to pancreatic cancer metastasis through crosstalk with palmitoylation pathways.
N-Linked vs. O-Linked Oligosaccharides
|
|
N-Linked
|
O-Linked
|
|
Residue Target
|
Asparagine (Asn)
|
Serine (Ser) / Threonine (Thr)
|
|
Linkage Type
|
β-N-glycosidic bond
|
α-O-glycosidic bond
|
|
Initiation Site
|
Endoplasmic reticulum (co-translational)
|
Golgi apparatus (post-translational)
|
|
Structural Forms
|
High-mannose, hybrid, complex
|
Core 1–4, often linear but diverse
|
|
Function
|
Protein folding, immune signaling
|
Barrier function, cell adhesion
|
Why It Matters: Functional Roles in Health and Disease
Membrane-bound oligosaccharides aren't passive decorations—they actively mediate:
-
Immune Evasion: Viruses like HIV exploit "glycan shields"(e.g., gp120) to escape host immunity.
-
Immune Checkpoints: Sialylated glycans interact with Siglec receptors, suppressing immune activation.
-
Neurodegeneration: In Alzheimer's, faulty glycosylation of HSP90β impairs Aβ clearance.
-
Cancer Progression: Aberrant glycosylation of CD36 and other membrane proteins enhances metastasis.
Advanced Tools for Cell Membrane Oligosaccharide Discovery
To uncover these complex glycosylation landscapes, Creative Biolabs offers a full suite of glycomics technologies:
Our team combines expert glycoengineering with analytical precision to provide robust, scalable solutions across research and therapeutic pipelines.
From Cell Membranes to Applications
At Creative Biolabs, we don't just analyze glycan structures—we help translate them into tangible solutions. Whether you're building a next-gen vaccine or deconstructing glycan-pathogen interactions, our custom oligosaccharides synthesis solutions and oligosaccharides analysis service delivers the precision you need, backed by our scientific expertise. We're also witnessing breakthroughs in glyco-based medicine:
-
Serum Glycomics: Markers like CA19-9 serve in early cancer diagnostics, especially for pancreatic and gastrointestinal tumors.
-
CAR-T Optimization: Engineered glycosylation patterns on CAR constructs can enhance immune activation or tumor specificity.
-
Glycan Vaccines: Cancer-specific carbohydrate antigens are being harnessed to stimulate targeted immunity.
-
Neurodegeneration Targets: HSP90β's impaired glycan-binding is linked to faulty Aβ clearance in Alzheimer's—a possible therapeutic entry point.
The role of oligosaccharides in the plasma membrane has evolved beyond structural support to becoming essential regulators that influence human health and disease. Knowledge of oligosaccharide biosynthesis and diversity together with their interactive behavior enables breakthroughs in both diagnostic and therapeutic fields. Creative Biolabs combines its extensive glycoscience knowledge with modern technology to enable the transformation of glycan structure understanding into biological insights. We provide synthetic oligosaccharides and customized glycoanalysis along with full-service glycan profiling for your cell membrane projects. Contact us now to learn how our custom synthesis and advanced analytics capabilities will help achieve the success of your project. Contact us to start a conversation!
FAQs
Q: What do oligosaccharides do in the cell membrane?
A: At Creative Biolabs, we understand that oligosaccharides on the cell membrane are far more than structural add-ons—they serve as dynamic biological interfaces. These glycans mediate essential processes such as cell–cell recognition, immune modulation, and signal transduction. Both N-linked and O-linked oligosaccharides on glycoproteins help regulate protein folding, stability, and receptor activity, playing pivotal roles in maintaining cellular communication and response.
Q: What are membrane derived oligosaccharides?
A: Membrane-derived oligosaccharides refer to carbohydrate chains that are either cleaved from or associated with membrane glycoproteins and glycolipids. These glycans, often liberated during cellular remodeling, signaling, or pathological events, can retain bioactivity and participate in intercellular signaling or immune recognition. At Creative Biolabs, we study these oligosaccharides to better understand disease mechanisms and explore their potential as diagnostic biomarkers or therapeutic targets.
Q: How are oligosaccharides linked to membrane proteins?
A: Oligosaccharides are covalently attached to membrane proteins through two primary types of glycosidic linkages: N-linked glycans attach to the amide nitrogen of asparagine residues, while O-linked glycans bind to the hydroxyl groups of serine or threonine residues. These post-translational modifications occur in the ER and Golgi apparatus and are critical for membrane protein folding, trafficking, and function. At Creative Biolabs, we offer advanced services to synthesize, analyze, and engineer these glycosylation patterns for both basic research and translational applications.
Reference
-
Lin, Borong, et al. "Role of protein glycosylation in host-pathogen interaction." Cells 9.4 (2020): 1022. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9041022
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 N-Linked and O-Linked oligosaccharides with different glycosylation types.1
Fig.1 N-Linked and O-Linked oligosaccharides with different glycosylation types.1

