Enzymatic Formation of the Glycan-Protein/Peptide Link
Glycoproteins are widespread in organisms and are closely related to various life activities. The formation of glycan-protein / peptide chains plays an important role in glycoprotein synthesis. Enzymatic glycoprotein synthesis has always received extensive attention due to its wide application in the process of protein research. As an expert in the glycoprotein field, we can provide the best enzymatic services to obtain the glycan-protein / peptide link required in your projects.
Enzymatic synthesis of glycoproteins usually requires the participation of multiple enzymes. Frequently used enzymes include endoglycosidases, proteases, and glycosyltransferases. These enzymes are used to synthesize glycoproteins in different ways. There are two common methods used in the synthesis of glycoproteins: one is to use endoglycosidase to remove the heterogeneous carbohydrates of glycoproteins, and then use glycosyltransferase to add the required carbohydrates; the second is to use protease to connect synthetic peptides and glycopeptides followed by enzymatic glycosylation.
Enzymes for Glycan-Protein / Peptide Link Synthesis
Protease is a vital catalyst for peptide synthesis. Although proteases hydrolyze peptide bonds in vivo, these enzymes can be induced to act as catalysts for the formation of amide bonds or ester bonds under certain conditions in vitro. At present, many chemical and genetic methods have been applied to modify the specificity of proteases. It is worth mentioning that the method of attaching specific functional groups to the acylation donor substrate allows the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids other than those commonly accepted by proteases. The amidase and esterase activities of serine proteases can be adjusted by using chemical methods in conjunction with site-directed mutagenesis to modify the active site residues. Similar to proteases, endoglycosidases usually cleave internal glycosidic bonds in oligosaccharide chains but can be used as synthesis catalysts under kinetic control conditions. In addition to glycosyltransferase and endoglycosidase, various exoglycosidase enzymes have been applied to the formation of glycosidic bonds.
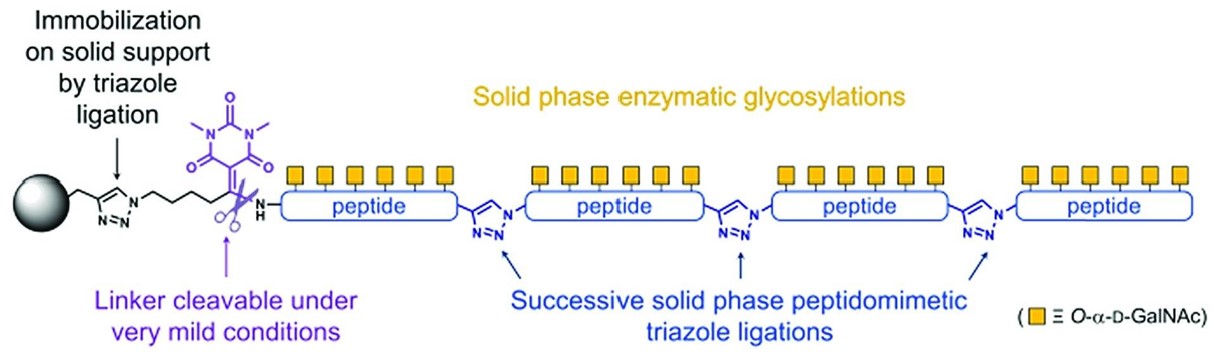 Fig.1 Solid-phase enzymatic formation of glycopeptide linkages.1, 2
Fig.1 Solid-phase enzymatic formation of glycopeptide linkages.1, 2
The Role of Enzymes in Formation of Glycans
-
Elaboration and trimming of glycans
The enzyme-catalyzed technology of glycans has been successfully applied to the processing of glycosyl amino acids, peptides and proteins. In addition, enzymatic methods have even been used to directly modify cell surface proteins. A typical example is a milk fucosyltransferase that allows modification of glycans by adding fucose residues with a series of substituents at specific sites. In fact, glycosyltransferase-mediated fine processing is particularly useful as a chemoselective technique for challenging, function-rich structures. Another enzymatic method is to purify sugar mixtures by selectively enzymatically degrading unwanted sugar types. Furthermore, endoglycosidase-mediated glycan structure trimming plays a key role in glycoprotein remodeling technology.
-
Enzymatic formation of the glycan-protein / peptide link
An effective strategy of enzymatic glycoprotein synthesis is to directly utilize the enzymes responsible for the formation of glycoprotein linkages. Interestingly, recent studies have found that certain specific groups can be transferred to the side chain hydroxyl group of seryl residues in the hexapeptide by using endogalactosaminidase. Moreover, microbial transglutaminase is used to transfer the side chain γ-carboxamide group to the hexapeptide. Both methods suggest that the general enzymatic catalytic strategy used to form key glycan-protein linkages will become a reality.
After decades of research, we have established a collection of multiple enzymes for the synthesis and modification of different glycoproteins or peptide chains. Based on our professional knowledge and advanced platform, Creative Biolabs is committed to providing custom glycoprotein synthesis services. Please contact us for more details.
References
-
Galibert, Mathieu, et al. "Combining triazole ligation and enzymatic glycosylation on solid phase simplifies the synthesis of very long glycoprotein analogues." Chemical Science 6.6 (2015): 3617-3623.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 3.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Solid-phase enzymatic formation of glycopeptide linkages.1, 2
Fig.1 Solid-phase enzymatic formation of glycopeptide linkages.1, 2

