Small molecule drugs—like aspirin, morphine, and dexamethasone—are valued for their low molecular weight and ability to reach intracellular targets. However, many suffer from poor solubility, limited bioavailability, or off-target effects. At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in small molecule glycoengineering, combining enzymatic precision with scalable platforms to enhance performance and discover new delivery strategies.
Why and How We Glycosylate Small Molecule Drugs?
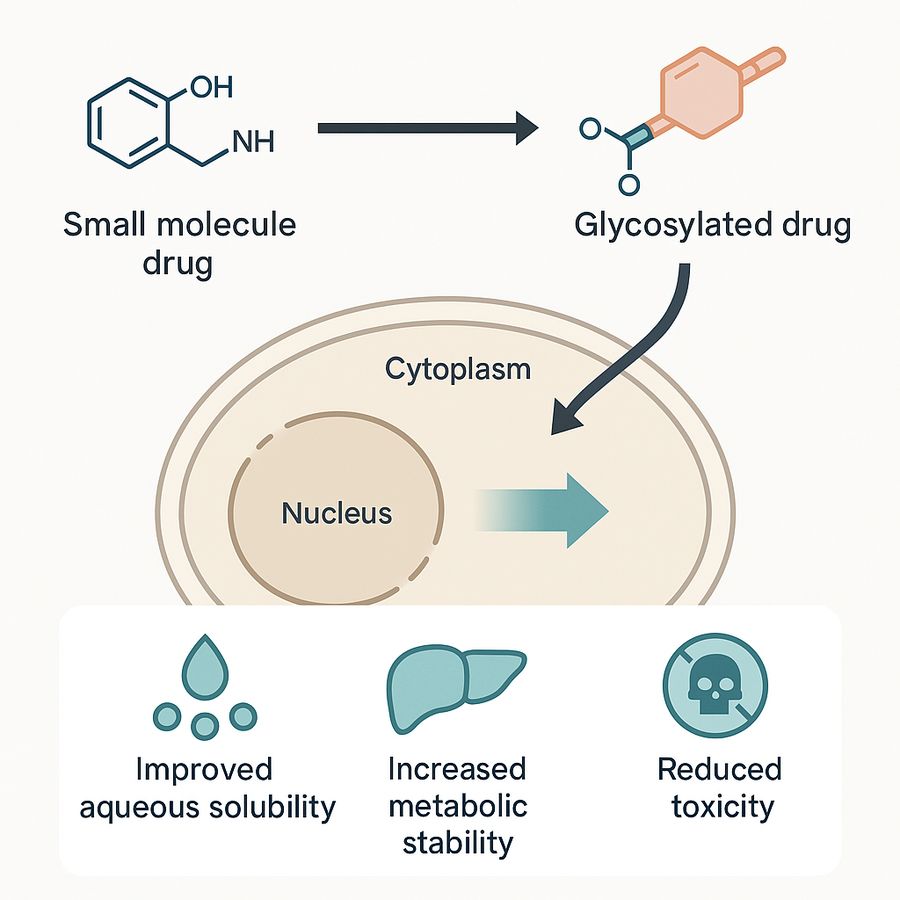 Fig.1 Enhancement of small molecule
Fig.1 Enhancement of small molecule
drugs via glycosylation.
Small molecule glycosylation involves covalently attaching carbohydrate moieties (e.g., glucose, galactose) to accessible functional groups such as hydroxyl, amine, or carboxyl. This modification can be performed chemically or enzymatically—with enzymatic methods offering higher regioselectivity and stereocontrol via specific glycosyltransferases. Why glycosylate? Because introducing a glycosyl moiety can dramatically enhance a drug's physicochemical and biological behavior. Glycosylated molecules often show improved aqueous solubility, increased metabolic stability and reduced toxicity. Nature already employs glycosylation in many potent therapeutics—from cardiac glycosides to macrolide antibiotics—making glyco-drugs a rational evolution in modern drug design.
Custom Glycosylation Workflow for Small Molecule Conjugation
At Creative Biolabs, we provide a robust and modular platform for glycosylation-based modification of small molecules, tailored for antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs), glycoprotein engineering, and site-specific bioconjugation. Our workflow ensures precise site accessibility, enzymatic precision, and biorthogonal compatibility to support both preclinical research and translational development.
1. Glycosylation Site Preparation
We begin by exposing specific glycosylation anchors on the target biomolecule. For antibodies, conserved N-glycosylation sites like Asn297 in the Fc region are commonly selected to avoid interference with antigen binding. In cases where native glycans obscure access, selective endoglycosidases (e.g., Endo-S, Endo-F2) are applied to trim complex glycans and reveal a single GlcNAc residue as the functional handle.
2. Enzymatic Functionalization
Next, we introduce chemically reactive sugar moieties via glycosyltransferase-catalyzed reactions. In optimized buffer systems, specific enzymes such as β1,4-galactosyltransferase or fucosyltransferase transfer modified monosaccharides onto exposed GlcNAc residues. These donor sugars are pre-functionalized with azide, alkyne, or DBCO groups to facilitate downstream click chemistry. Reactions proceed under mild agitation at 25–37°C, for several hours depending on the system.
3. Bioorthogonal Conjugation
Following glycofunctionalization, the reactive sugar handles enable high-efficiency coupling to payloads under physiological conditions. Using strain-promoted or copper-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition, we link azide- or alkyne-bearing payloads (drugs, probes, imaging agents) to the modified glycan. These reactions typically require no catalyst, proceed under ambient temperatures, and preserve the structural integrity of the protein or antibody.
4. Purification & Quality Control
Post-conjugation, we apply a combination of size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC), or tangential flow filtration (TFF) to remove excess reactants and enzymes. Our QC analytics include:
-
Assessing drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) via LC-MS.
-
Glycan modification efficiency is evaluated by HPLC or fluorescent tagging assays.
-
Antigen-binding activity is validated by ELISA or SPR, with retention typically above 90%.
This flexible glyco-conjugation strategy enables precise control over site and stoichiometry, making it ideal for developing next-generation bioconjugates. Creative Biolabs offers full-service support from design consultation to analytical validation, ensuring your glycosylated drugs or probes meet the highest standards of reproducibility, stability, and functional performance.
Our Capabilities in Drug Glycosylation Analysis
Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive drug glycosylation analysis tools to support every step of your development pipeline. Whether you're developing glycosylated drug analogs or functionalizing lead compounds for targeted delivery, we provide end-to-end analytical support.
-
Site-specific glycan mapping via LC-MS/MS
-
Sugar chain composition profiling
-
Conjugation efficiency testing
-
Functional bioassays for target validation
Applications of Glycosylated Small Molecules
Glycosylated small molecules have opened new avenues in drug design across multiple domains. In oncology, glycosylated prodrugs can be selectively activated in the tumor microenvironment by glycosidases, improving both efficacy and safety. Glycosylation has also enabled the oral delivery of poorly soluble steroids like dexamethasone by increasing gastrointestinal absorption. In CNS therapeutics, adding glucose moieties facilitates brain penetration via GLUT1-mediated transport. Similarly, topical and transdermal products, such as glycosylated vitamin E derivatives, demonstrate enhanced diffusion and local bioavailability. Glycosylation is also gaining ground in antiviral drug design, where solubility and pharmacokinetic limitations are common obstacles. Finally, in the nutraceutical and cosmetic industries, glycosylated flavonoids, polyphenols, and plant-based compounds offer better taste, absorption, and bioactivity.
Advantages of Our Small Molecule Glycosylation Services
-
Custom Design: Tailored strategies based on scaffold, application, and delivery goals
-
Modular Scalability: Process development from early discovery to preclinical scale-up
-
Enzymatic Precision: High stereoselectivity and functional group tolerance
-
Integrated Analytics: In-house NMR, LC-MS/MS, and biological testing
Related Services at Creative Biolabs
Reference
-
He, Mengyuan, Xiangxiang Zhou, and Xin Wang. "Glycosylation: mechanisms, biological functions and clinical implications." Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 9.1 (2024): 194. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01886-1
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Enhancement of small molecule
Fig.1 Enhancement of small molecule 
