Introduction
Glycosylation is one of the most critical post-translational modifications (PTMs), intricately shaping protein folding, stability, immunogenicity, and therapeutic efficacy. In the production of recombinant proteins and peptides, controlling glycosylation is essential to mimic native forms, optimize pharmacokinetics, and achieve regulatory compliance.
At Creative Biolabs, we provide custom glycosylation services to precisely tailor N- and O-linked glycan structures on expressed proteins and peptides. Our platforms integrate cell line engineering, enzymatic remodeling, and advanced glycoanalysis to produce defined glycoforms tailored for your research.
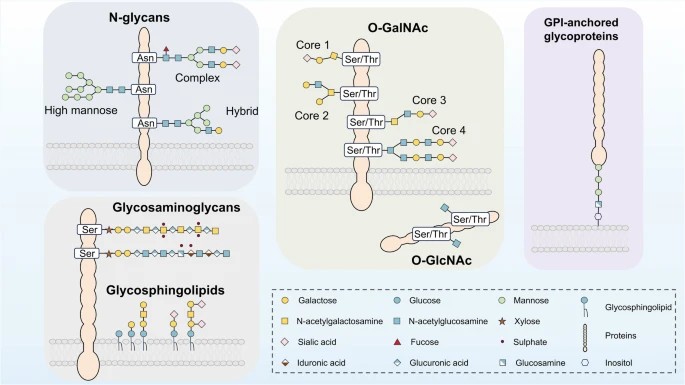 Fig.1 Major glycosylation on proteins.1
Fig.1 Major glycosylation on proteins.1
Why Custom Glycosylation Matters
-
Custom sialylation or polysialylation reduces renal clearance, extending serum half-life for therapeutic proteins like EPO and interferons.
-
Afucosylated IgG1 exhibits enhanced FcγRIIIa binding, boosting antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) in cancer immunotherapy.
-
Defined glycoforms influence PD-L1/PD-1 interactions, ACE2-spike binding, and integrin-mediated adhesion—critical for checkpoint blockade, antiviral design, and metastasis research.
-
Controlled glycosylation eliminates variability caused by host- or batch-specific glycan processing, improving reproducibility in preclinical and clinical batches.
-
N-glycans aid folding of complex proteins such as Fc-fusion constructs and enzymes, improving expression yields and reducing aggregation.
Glycosylation Targets We Serve
|
Molecule Type
|
Application Example
|
Representative Protein(s)
|
|
Monoclonal Antibodies
|
Fc glycan engineering to enhance ADCC
|
Rituximab, Obinutuzumab
|
|
Fc-Fusion Proteins
|
Half-life tuning or receptor affinity optimization
|
Etanercept, Aflibercept, CTLA4-Fc
|
|
Recombinant Enzymes
|
Lysosomal targeting via M6P or core trimming
|
α-Glucosidase, β-Galactosidase, GAA
|
|
Cytokines & Hormones
|
Sialylation for reduced hepatic clearance
|
Erythropoietin, IFN-α2b, G-CSF
|
|
Neoantigenic Peptides
|
O-glycan mimicry for immune response enhancement
|
MUC1 peptide, MAGE-A1
|
|
Checkpoint Ligands
|
Glycoform modulation to study or enhance interaction
|
PD-L1, PD-1, ACE2
|
|
Receptor Proteins
|
Glycosylation for trafficking or function studies
|
EGFR, Integrin β1, CD98
|
Service Workflow: From Design to Delivery
We provide an end-to-end solution, integrating bioinformatics, cell engineering, and structural analysis into one streamlined service. Key enabling technologies are integrated at each step.
Step 1: Consultation & Feasibility
-
Identify client's goals (e.g., reduce heterogeneity, enhance ADCC)
-
Evaluate protein structure and potential glycosylation sites
-
Recommend host system and modification strategy
Step 2: Glycoengineering Strategy Design
-
Select suitable expression system (mammalian cells such as CHO and HEK293, bacteria, plant, yeast, insect, with tags)
-
Choose glycan type (e.g., afucosylated, bisected, sialylated)
-
Edit gene or design in vitro enzyme panel
Step 3: Cell Line Construction or In Vitro Remodeling
-
Generate stable or transient expression lines
-
For cell-free pathways: perform enzymatic trimming & rebuilding
-
Optimize folding, secretion, and yield
Step 4: Protein Production & Purification
-
Expression scale-up (milligram to gram scale)
-
Affinity or HIC-based purification
-
Stability and purity QC
Step 5: Glycosylation Analysis
-
Confirm glycan structure and site occupancy
-
Quantify glycoform heterogeneity
-
Compare to reference or biosimilar standards
Step 6: Reporting & Delivery
-
Full analytical report (glycopeptide maps, spectra, site coverage)
-
Annotated sequence with glycan occupancy
-
Final deliverables: purified protein, QC report, optional validation data
Why Choose Creative Biolabs?
-
Full-spectrum platform for glycoengineering, from sequence to purified glycoprotein
-
Flexible production hosts: CHO, HEK293, yeast, insect (with synthetic tags)
-
Advanced analytical pipelines: PGC-LC-MS/MS, MALDI-TOF, lectin profiling
-
Regulatory experience: Glycosylation profiles designed to support IND/BLA submissions
-
Fast turnaround: 4–8 weeks for most projects, including analytics
-
Customized solutions: Site-specific, structure-defined, application-oriented
Our Related Custom Glycosylation Services
For instance, CHO cell line knockout of FUT8 to generate afucosylated IgG1 with enhanced FcγRIIIa binding. We design and engineer glycosylation pathways in common production hosts (CHO, HEK293, yeast, plants) using:
-
Multiple gene-editing methods
-
Overexpression or knockout of specific glycosyltransferases or sialyltransferases
-
Metabolic pathway rewiring to boost glycosylation precursors
-
Glycosylation pathway humanization in yeast or plant cells
This glycan remodeling technique is ideal for antibody glycoform standardization or Fc glycan modifications. We offer precise remodeling of glycoproteins via chemoenzymatic steps:
-
Endoglycosidase-assisted glycan trimming
-
Site-specific rebuilding using defined glycosyltransferase panels
-
Tailored addition of sialic acid, fucose, GalNAc, or bisecting GlcNAc
-
GlycoPEGylation for improved solubility or half-life
Our analytics team provides full structural elucidation and quantification using:
-
LC-MS/MS, HILIC
-
Workflows for deep profiling (>100,000 glycopeptides/sample)
-
Glycoform mapping and site occupancy calculation
-
O- and N-linked glycan subclass distribution
-
Solubility and charge variant correlations with glycan heterogeneity
FAQs
Do you offer glycosylation services for non-antibody proteins like EPO, PD-L1, or enzymes?
Absolutely. We routinely glycoengineer a wide range of proteins, including:
-
Erythropoietin (EPO): Sialylation for half-life extension, glycosite insertion for DARBEPOETIN-like design
-
PD-L1/PD-1: Removal or modification of N-glycans to study checkpoint pathway sensitivity or improve detection
-
Enzymes (e.g., GAA, α-Gal): Addition of M6P tags or hybrid structures to facilitate lysosomal uptake
-
MUC1 peptides: Truncated O-GalNAc glycans for cancer vaccine mimicry
-
Receptors (ACE2, EGFR, Integrin β1): Custom glycoform libraries for interaction screening
If needed, we can design glycosylation-null mutants or glycoform variants for comparative functional assays.
Why should I consider customizing glycosylation for my expressed protein or peptide?
Glycosylation plays a crucial role in protein folding, stability, receptor binding, immunogenicity, and serum half-life. However, default glycosylation patterns in conventional expression systems (e.g., CHO, HEK293, yeast) often lead to heterogeneous or non-human glycoforms. By customizing glycosylation, you gain control over:
-
Glycoform homogeneity
-
Functional enhancement (e.g., afucosylated IgG for increased ADCC)
-
Improved pharmacokinetics (e.g., sialylation or polysialylation for extended half-life)
-
Regulatory consistency for IND/BLA submissions
Creative Biolabs provides tailored glycosylation solutions using cell engineering, enzymatic remodeling, and advanced glycoanalytics to match your molecule's biological goals.
Reference
-
He, Mengyuan, Xiangxiang Zhou, and Xin Wang. "Glycosylation: mechanisms, biological functions and clinical implications." Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 9.1 (2024): 194. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01886-1
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Major glycosylation on proteins.1
Fig.1 Major glycosylation on proteins.1

