Background of Antibody Glycosylation
Monoclonal antibody glycosylation is a critical quality attribute that directly affects therapeutic efficacy, safety, and regulatory compliance. Glycans—particularly N-linked glycans at Asn 297 of the Fc region—govern key functions such as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), serum half-life, and immunogenicity. Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive glycosylation engineering services through our proprietary GlycoOptimize™ platform, enabling precise and reproducible tailoring of glycosylation profiles across diverse production systems and scales.
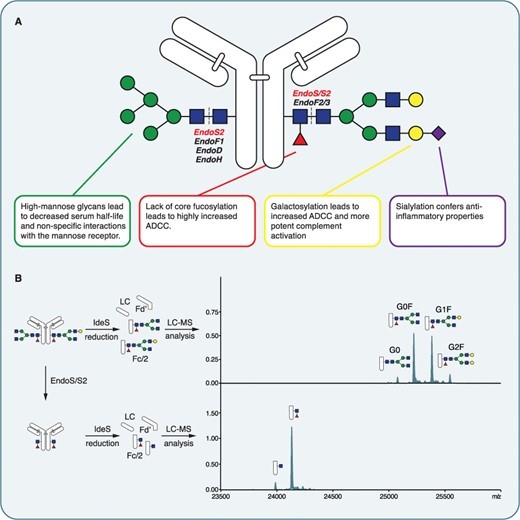 Fig.1 IgG Fc glycosylation and their potential effects.1
Fig.1 IgG Fc glycosylation and their potential effects.1
Why Glycosylation Matters
Antibodies with controlled glycosylation profiles are essential for meeting performance and regulatory demands in therapeutic development. Modifications to Fc glycosylation influence receptor interactions, immune modulation, and pharmacokinetics. For instance:
-
Fucosylation reduces FcγRIIIa binding; defucosylation enhances ADCC.
-
Sialylation promotes anti-inflammatory functions and extends serum half-life.
-
Galactosylation modulates CDC and complement activation.
-
Variability in glycosylation patterns introduces challenges in manufacturing consistency and bioactivity prediction.
Creative Biolabs' GlycoOptimize™ Platform
Our GlycoOptimize™ platform integrates genetic, cell-based, and metabolic strategies to modulate glycan structures precisely and predictably. It enables customization of N-glycans for research, preclinical, and commercial applications.
-
Genetic GlycoOptimization
Through rational design of glycosylation motifs, we can:
-
Introduce or enhance glycosylation sites to increase galactosylation or sialylation.
-
Modify amino acid sequences near Asn 297 to enhance glycosyltransferase access.
-
Engineer hyper-glycosylated variants to improve half-life (e.g., in EPO analogs).
-
Cell-Based GlycoOptimization
By engineering host cell lines, we can:
-
Knock out fucosyltransferase (FUT8) to generate afucosylated antibodies with significantly enhanced ADCC.
-
Knock in human α2,6-sialyltransferase (ST6Gal1) to achieve terminal α2,6 sialylation for anti-inflammatory function.
-
Screen and select clones with optimal glycosylation machinery for consistent performance.
-
Metabolic GlycoOptimization
Supplementing culture media with specific monosaccharide analogs allows us to:
-
Enrich glycoproteins with targeted sugar residues.
-
Alter linkage specificity (e.g., α2,3 vs. α2,6 sialic acids).
-
Increase structural uniformity and reduce unwanted heterogeneity.
How We Help with Antibody Glycosylation?
At Creative Biolabs, we recognize that glycosylation is not limited to the Fc Asn 297 site—it is a spatially distributed, functionally integrated modification that shapes antibody behavior. Our antibody glycoengineering services focus on both canonical and non-canonical glycosylation sites, tailoring each project to client-specific goals. Our flexible and iterative approach enables us to transform antibody glycosylation into a programmable feature.
-
Starting with the Fc region, we help modulate glycan structures to enhance effector functions such as ADCC and CDC by removing core fucose or enriching galactose content. For antibodies targeting inflammatory or autoimmune conditions, we increase sialylation—particularly α2,6 linkages—to dampen immune activation and prolong serum half-life.
-
When clients wish to explore the Fab region, we assist in introducing or eliminating glycosylation motifs in the variable domains to fine-tune antigen binding or minimize immunogenicity, ensuring that added glycans do not compromise structural integrity or epitope accessibility.
-
We also engineer glycosylation within hinge regions and glycine-serine linkers, especially for Fc-fusion formats, to improve protease resistance and in vivo stability.
-
For more advanced applications, we support the insertion of new glycosylation motifs or reprogram host cell glycosyltransferase expression to favor specific structures, such as bisected or hybrid glycans. Throughout the process, we provide detailed glycopeptide mapping, glycoform distribution analysis, and functional validation.
Glycosylation Profiling and Analysis
We provide comprehensive glycoprofiling using:
-
LC-MS/MS and MALDI-TOF for glycopeptide identification.
-
HILIC-UPLC for released glycan quantification.
-
Capillary electrophoresis and lectin arrays for structural validation.
Each project is supported with detailed reports outlining:
-
Glycoform distribution (G0, G1, G2, sialylated, fucosylated).
-
Glycosylation site occupancy and microheterogeneity.
-
Linkage-specific information (α2,3 vs. α2,6 sialylation).
Service Advantages
-
Customizable glycan profiles (fucosylation, sialylation, galactosylation)
-
Multiple expression hosts: mammalian cells, bacteria, plant, yeast, insect systems
-
Scalable production: from micrograms to multigram batches
-
Regulatory-aligned analytical packages
-
End-to-end workflow: from sequence design to validated biologic
Applications
-
Therapeutic antibodies requiring enhanced ADCC (e.g., anti-CD20, anti-HER2)
-
Anti-inflammatory IgG for autoimmune or infectious disease treatment
-
Bispecifics and antibody-drug conjugates with optimized Fc interaction
-
Biosimilars with matched glycan profiles to originator drugs
One Case: Enhancing ADCC via Fc Glycoengineering
Using CHO cell lines engineered through our platform, researchers developed four antibody variants:
-
Wild-type IgG1: standard fucosylated Fc glycoform.
-
FUT8 knockout: afucosylated IgG1 with enhanced ADCC.
-
ST6Gal1 knock-in: increased terminal α2,6-sialylation, enhancing anti-inflammatory effects.
-
Combined FUT8 KO + ST6Gal1 KI: balance of enhanced ADCC and immunomodulation.
Results demonstrated that afucosylation provided the highest gain in ADCC activity, while additional sialylation offered control over inflammatory response without sacrificing binding affinity.
Glycosylated antibody engineering is essential for next-generation therapeutics. Creative Biolabs' GlycoOptimize™ platform offers unmatched control, flexibility, and reproducibility in tailoring glycosylation for specific functional needs. By combining molecular biology, cell engineering, and analytical precision, we ensure that each antibody produced aligns with your functional goals and regulatory requirements. To initiate your glycosylation-related glycoengineering project, or learn more about our capabilities, visit our glycosylation engineering platform or contact our scientific team directly.
FAQs
Do you provide analytical support to characterize the glycosylation profile of our existing antibodies?
Yes, we provide standalone glycosylation profiling services for both client-derived antibodies and those produced through our platform. Our analytical suite includes glycoprotein detection, glycoprotein structure analysis, glycoprotein quantification, high-throughput glycan screening, and antibody glycoprofiling to support comprehensive evaluation of antibody glycosylation. We utilize a combination of MALDI-TOF MS, LC-MS/MS, HILIC-UPLC, and capillary electrophoresis to generate comprehensive glycan maps, including quantification of core fucosylation, sialylation (α2,3 vs. α2,6), galactosylation, bisecting GlcNAc, and high-mannose content. We also assess glycosylation site occupancy and heterogeneity. This data is crucial not only for regulatory documentation (e.g., biosimilarity assessment, comparability studies) but also for rational antibody optimization.
Can you help us generate antibodies with human-like glycosylation if we work with non-mammalian systems like yeast or insect cells?
Yes, Creative Biolabs offers tailored glycoengineering solutions for clients working in non-mammalian systems, or insect cells. These expression systems naturally produce glycans that differ significantly from human N-glycans—often lacking sialylation and containing non-human epitopes (e.g., high mannose, α-1,3-linked fucose). To address this, we offer glycoengineered strains or co-expression of key human glycosylation enzymes, such as β1,4-galactosyltransferase, ST6Gal1 (for α2,6 sialylation), and GlcNAc transferases, to reconstitute a human-like glycosylation pathway in these hosts. We also provide in vitro glycan remodeling post-expression when in vivo engineering is not feasible.
Reference
-
Sjögren, Jonathan, Rolf Lood, and Andreas Nägeli. "On enzymatic remodeling of IgG glycosylation; unique tools with broad applications." Glycobiology 30.4 (2020): 254-267. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwz085
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 IgG Fc glycosylation and their potential effects.1
Fig.1 IgG Fc glycosylation and their potential effects.1

