Introduction to Glycosylation in Biomolecules
Glycosylation is a crucial post-translational modification impacting the structure, function, and biological activity of various biomolecules, including proteins, lipids, peptides, nucleic acids and small molecules like flavonoids and cannabinoids. For instance:
-
Glycosylated flavonoids (e.g., quercetin glycosides) exhibit improved water solubility and bioavailability compared to their aglycone forms, making them promising candidates for anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective therapies.
-
Glycosylated cannabinoids, such as cannabosides generated via enzymatic glycosylation, overcome the hydrophobicity of parent cannabinoids, enabling novel oral drug delivery strategies.
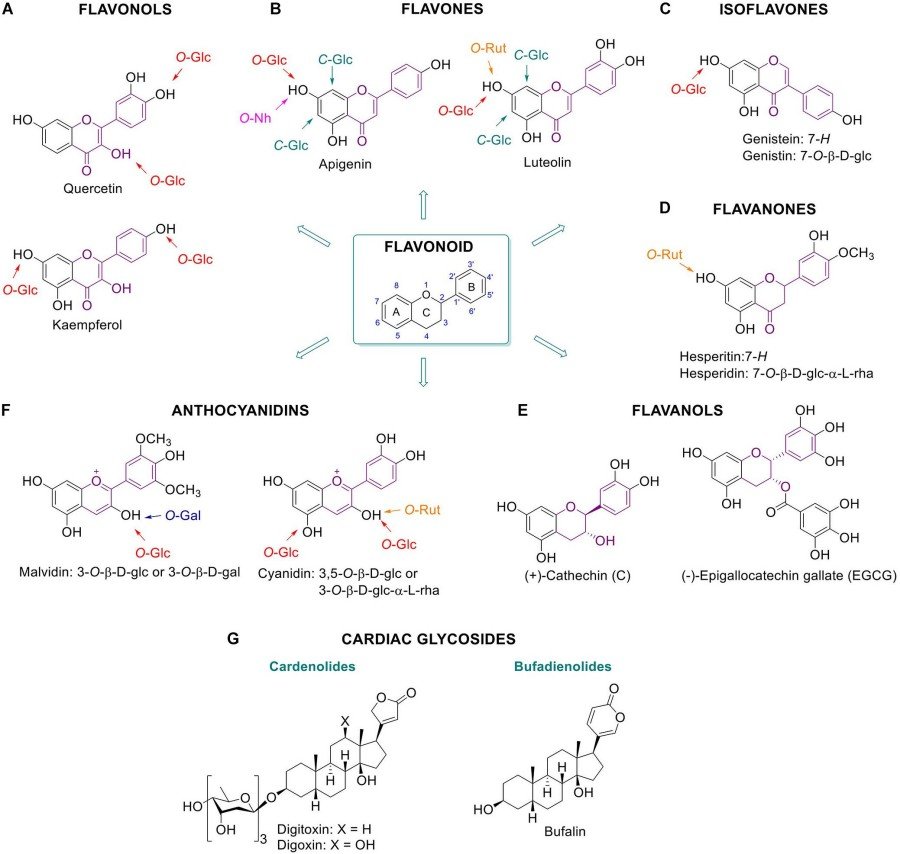 Fig.1 Beneficial glycosylated plant metabolites for humans.1
Fig.1 Beneficial glycosylated plant metabolites for humans.1
This process creates complex glycoconjugates like glycoproteins, glycolipids, and glycopeptides. Analyzing these molecules is challenging due to their diverse sugar compositions, linkage types, and structural arrangements. Accurately characterizing glycosylation requires specialized expertise to understand structural variations, identify modification sites, and quantify interactions between glycans and proteins. At Creative Biolabs, we offer specialized glycoconjugate analysis services designed to tackle these complexities. We recognize that each type of biomolecule needs a specific approach to fully understand its glycosylation patterns. Whether you're working with N-glycosylated therapeutic proteins, O-glycosylated cell surface receptors, or glycolipids involved in cell signaling, our comprehensive services utilize advanced technologies to provide precise, useful data. By combining our expertise in molecular diversity with analytical excellence, we empower researchers and biotech partners to navigate the complex field of glycoconjugates, accelerating breakthroughs in glycobiology, disease research, and the development of therapeutics.
Comprehensive Glycosylation Analysis Methods
Glycosylation is a complex post-translational modification that requires careful, specialized techniques to analyze. The variety of glycan structures and glycoprotein differences make this challenging. To understand glycosylation fully, we use a mix of methods. Each method offers unique insights into different aspects, such as glycan composition or modification sites. At Creative Biolabs, our specialized glycoconjugate analysis services combine these techniques to deliver accurate, detailed results for your research needs.
MS is a key tool for glycosylation analysis. It offers high sensitivity and accuracy, essential for studying complex glycans. These methods provide both qualitative and quantitative data, helping identify glycan types, modification sites, and protein interactions.
-
HILIC-MS is ideal for analyzing polar glycans in glycosylated flavonoids, such as the sialylated or fucosylated derivatives of quercetin. This method, combined with our high-throughput screening platforms, enables rapid profiling of complex samples like plant extracts or microbial fermentation broths.
-
MALDI-MS and ESI-MS are used to characterize intact glycoproteins and glycopeptides. For example, alpha glycosyl isoquercitrin, a glycosylated flavonol, can be analyzed via ESI-MS to determine its glycan composition and linkage patterns.
Enzymatic Techniques
Enzymes play a key role in releasing and modifying glycans for analysis. They allow specific cleavage of glycosylation sites, separating glycans from protein backbones.
PNGase F Digestion
-
Specifically removes N-linked glycans from asparagine residues in glycoproteins.
-
Enables free glycan analysis, especially useful for complex structures with sialic acid or fucose.
O-Glycan Release
-
O-glycans attach to serine or threonine residues and are harder to release due to enzymatic resistance.
-
Uses O-glycosidases or chemical treatments (e.g., reductive β-elimination) to cleave and isolate O-glycans.
-
Follow-up MS or HPLC analysis determines their composition and structure.
Lectin arrays are used to study glycan-protein interactions in glycosylated quercetin and alpha glycosyl isoquercitrin, uncovering their binding specificities to immune receptors or microbial lectins. This is invaluable for optimizing drug-targeting strategies. The high-throughput tool study glycan-protein interactions by immobilizing glycans on a solid surface. Our glycobiology microarray services help uncover glycan-binding specificities for the development of novel biomarkers or therapeutics.
-
Immobilize lectins (glycan-binding proteins) to identify specific glycan structures they recognize.
-
Screen glycan profiles in samples like serum or cell surfaces, valuable for cancer, immune, and pathogen research.
Automated systems process hundreds of samples quickly, integrating techniques like HILIC-MS and glycan microarrays.
-
Ideal for large-scale datasets to profile glycosylation patterns efficiently.
-
Provides comprehensive results in less time than traditional methods.
Structural Glycomics and Computational Tools
Advanced computational tools and databases predict glycosylation sites and structures using molecular modeling. We use complement experimental methods to offer a complete view of glycosylation's role in cells and disease. Our team combines computational predictions with wet-lab analysis for robust, multi-faceted glycoconjugate characterization.
Glycosylation and Disease: Understanding the Connections
Glycosylation, the enzymatic attachment of sugar molecules to proteins, lipids, and other biomolecules, is a fundamental process in cellular biology. Aberrant glycosylation patterns have been linked to diverse pathological conditions, with specific glycoconjugates playing critical roles in disease progression, diagnosis, and therapy. Below is a disease-specific analysis of glycoconjugates.
|
Disease
|
Glycoconjugate Type
|
Case/Application
|
Significance
|
|
Cancer
|
Sialylated Glycoproteins (e.g., CA19-9)
|
CA19-9, a sialylated mucin-type glycoprotein, as a biomarker for pancreatic cancer
|
Sialylation masks tumor antigens, promoting immune evasion. Targeting sialic acid residues in cancer immunotherapy.
|
|
Glycolipids (e.g., Globo H)
|
Globo H in ovarian and breast cancers, under investigation in a vaccine (GM2-KLH) for tumor targeting
|
Glycolipids like Globo H promote tumor adhesion and metastasis, with vaccine-based cancer treatments being explored.
|
|
Autoimmune Diseases
|
Glycosylated Autoantibodies (e.g., IgG)
|
In rheumatoid arthritis, altered IgG glycosylation with reduced galactosylation and increased fucosylation
|
Altered IgG glycosylation correlates with disease severity. Potential for glycoengineered antibodies as therapy.
|
|
Glycosylated Cytokines (e.g., IL-6)
|
O-glycosylation of IL-6 in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) enhances leukocyte infiltration
|
Glycosylation of cytokines influences immune responses, with IL-6 glycosylation inhibition as a potential treatment.
|
|
Infectious Diseases
|
Viral Glycoproteins (e.g., Influenza HA)
|
Influenza hemagglutinin (HA) glycosylation facilitates viral entry, targeted by oseltamivir
|
Glycosylation of viral glycoproteins helps evade immune detection, and targeted antivirals (e.g., oseltamivir) control infection.
|
|
Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
|
LPS in Gram-negative bacteria triggers sepsis, neutralized by polymyxin B
|
LPS glycosylation affects bacterial virulence, with antibiotics or TLR4 antagonists mitigating sepsis and infections.
|
|
Emerging Glycobiology
|
Glycosylated RNA (GlycoRNA)
|
Small RNAs modified with N-glycans, bound to Siglec receptors on cell surfaces
|
Discovery of glycoRNAs as glycan-modified RNAs offers new insight into glycan-protein interactions, impacting immune responses.
|
|
Metabolic Disorders
|
N-Glycosylated Proteins (e.g., Transferrin)
|
Congenital disorders of glycosylation (e.g., CDG-Ia) affect transferrin and coagulation factors
|
CDGs highlight the essential role of glycosylation in protein secretion and folding. Glycosylation rescue therapies in development.
|
|
O-Glycosylated Proteins (e.g., Mucins)
|
O-glycosylation defects in mucins cause gastrointestinal dysfunction in CDG-IIc (COG5-CDG)
|
O-glycosylation defects disrupt mucosal barriers, with targeted treatments for mucin-related CDGs being developed.
|
|
Cardiovascular Diseases
|
Glycosylated Selectins (e.g., E-Selectin)
|
E-selectin in atherosclerosis mediates leukocyte recruitment, influenced by statins
|
Selectin glycosylation plays a key role in inflammation; inhibition may reduce atherosclerotic plaque formation.
|
|
Glycosylated Platelet Proteins (e.g., GPIb-IX)
|
O-glycosylation in diabetes enhances platelet aggregation, affecting thrombosis risk
|
Glycosylation regulates platelet function; targeting glycoproteins could prevent cardiovascular events in diabetic patients.
|
|
Neurological Disorders
|
Glycosylated Synaptic Proteins (e.g., NCAM)
|
NCAM polysialylation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is reduced; supplementation improves synaptic plasticity
|
Glycosylation of synaptic proteins is crucial for neuronal communication, with potential for slowing cognitive decline in AD.
|
|
Glycosylated Tau Protein
|
O-GlcNAc glycosylation of tau in AD promotes neurofibrillary tangle formation
|
Tau glycosylation contributes to neurodegeneration; targeting O-GlcNAcylation may offer therapeutic benefits.
|
|
Diabetes
|
Glycosylated Insulin Receptors
|
N-glycosylation defects in insulin receptors impair signaling in type 2 diabetes
|
Glycosylation defects in insulin receptors contribute to insulin resistance; restoring glycosylation enhances sensitivity.
|
|
Glycosylated Collagen (e.g., in Diabetic Complications)
|
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) form on collagen, contributing to vascular stiffness
|
Glycation of extracellular matrix proteins drives diabetic complications; targeting AGEs may prevent microvascular damage.
|
|
Know More ↓
|
Why Choose Us?
-
Our experienced team specializes in complex glycosylation analysis of proteins, antibodies, lipids, and small molecules.
-
We use the latest mass spectrometry, glycan arrays, and enzymatic tools for precise glycosylation profiling.
-
Our services are tailored to meet the unique needs of your research, whether for basic or biopharmaceutical studies.
-
We offer high-throughput analysis, ensuring fast processing and efficient research for large-scale studies and drug development.
Glycosylation plays a crucial role in a wide variety of biological processes and is integral to the development and efficacy of many biopharmaceuticals. Our specialized glycoconjugate analysis service offers the expertise and advanced tools necessary to navigate the complexities of glycosylation, ensuring that your research is built on the most reliable data available. Whether you're studying disease mechanisms, developing new therapeutics, or optimizing glycoprotein-based drugs, Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner in glycoscience.
References
-
Kytidou, Kassiani, et al. "Plant glycosides and glycosidases: a treasure-trove for therapeutics." Frontiers in plant science 11 (2020): 357. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00357
-
Khodzhaieva, Ruslana S., et al. "Progress and achievements in glycosylation of flavonoids." Frontiers in Chemistry 9 (2021): 637994. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2021.637994
-
Sordon, Sandra, Jarosław Popłoński, and E. W. A. Huszcza. "Microbial glycosylation of flavonoids." Polish journal of microbiology 65.2 (2016): 7. https://doi.org/10.5604/17331331.1204473
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Beneficial glycosylated plant metabolites for humans.1
Fig.1 Beneficial glycosylated plant metabolites for humans.1

