What Defines Alginate Oligosaccharides?
Low-molecular-weight sugars called Alginate oligosaccharides (AOS) originate from alginate which serves as a polysaccharide biopolymer in brown seaweed cell walls. Produced through physical, chemical, or enzymatic degradation, AOS (molecular weight: Alginate oligosaccharides with molecular weights between 400 and 5000 Da demonstrate superior performance through their lower viscosity alongside better water solubility and enhanced stability and bioavailability compared to their larger molecular weight equivalents. Their unique characteristics make AOS desirable across food and pharmaceutical sectors as well as agricultural industries because their bioactivity and adaptability foster innovation. As AOS decomposes it results not only in structural changes but also in improved functional properties. The resulting oligosaccharides demonstrate high solubility which enables easy dissolution and improves biological system interactions thus delivering strong performance in applications because of their exceptional solubility and bioactivity.
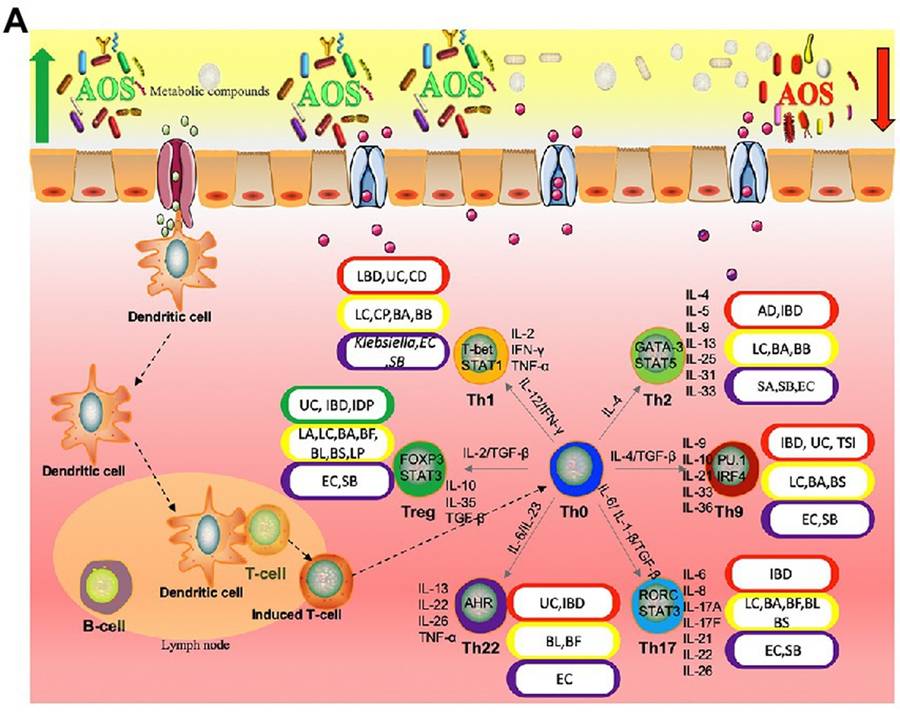 Fig.1 AOS in the inflammatory immunology process of intestine.1
Fig.1 AOS in the inflammatory immunology process of intestine.1
Structure Determines Function
AOS are built from two monomers: β-D-mannuronic acid (M) and α-L-guluronic acid (G), linked by 1,4-glycosidic bonds. Their magic lies in two key features:
-
M/G Ratio: Higher M content ramps up antioxidant activity, while more G units boost antimicrobial power.
-
Degree of Polymerization (DP): Short chains (DP2–4) nourish gut bacteria, while longer chains (DP5+) excel in anti-inflammatory and anticancer roles.
|
AOS Structure Feature
|
Biological Impact
|
|
High M/G Ratio
|
Enhanced antioxidant activity, combating oxidative damage
|
|
High G Content (>85%)
|
Potent antimicrobial effects against bacterial pathogens
|
|
Low DP (2–4)
|
Prebiotic action: fosters growth of beneficial gut microbiota
|
|
Unsaturated End Groups
|
Stronger anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating properties
|
This structural diversity gives AOS a toolkit of biological activities:
-
Antioxidant: Scavenge free radicals, protecting cells from oxidative stress.
-
Antimicrobial: Target pathogens like Staphylococcus aureus, ideal for infection control.
-
Anti-inflammatory: Dampen NF-κB and MAPK pathways, reducing cytokine release in conditions like arthritis.
-
Immunomodulatory: Activate defense pathways in plants and animals, enhancing disease resistance.
-
Metabolic Regulation: Improve blood sugar, lipid levels, and insulin sensitivity—promising for diabetes management.
AOS Production: Methods and Precision
Producing AOS requires precision, and there's no one-size-fits-all approach:
Physical Methods
Ultrasound, microwaves, or γ-radiation degrade alginate quickly, but control over molecular weight distribution can be tricky.
Chemical Methods
Acid hydrolysis (e.g., hydrochloric acid) or oxidative degradation (e.g., hydrogen peroxide) are straightforward, though chemical residues and inconsistent polymerization degrees (DP) can pose challenges.
Enzymatic Degradation
The gold standard for control: Alginate lyases—either endo-type (cleaving internal bonds for varied oligosaccharide lengths) or exo-type (trimming units from chain ends)—offer specificity and consistency.
Biological Synthesis
Genetically engineered microorganisms churn out AOS sustainably, ideal for scalable, eco-friendly production.
How AOS Work
Signaling Pathways
In plants, AOS trigger salicylic and jasmonic acid pathways, ramping up immune responses. In animals, they calm inflammation by regulating NF-κB and MAPK pathways, making them valuable in inflammatory disease therapies.
Metabolic Fine-Tuning
By adjusting enzyme activity and signaling molecules in lipid and glucose metabolism, AOS lower pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6, TNF-α), tackling root causes of metabolic disorders like obesity and diabetes.
AOS in Action: Diverse Applications
Cancer Therapy
Low-molecular-weight AOS (e.g., DP5) inhibit cancer cell growth and induce apoptosis, showing promise against osteosarcoma and breast cancer in preclinical studies.
Antioxidant & Anti-Inflammatory Support
Neutralize free radicals to fight atherosclerosis, arthritis, and neurodegenerative diseases. Their anti-inflammatory effects offer relief for chronic conditions.
Diabetes & Metabolic Health
Improve insulin sensitivity, regulate blood sugar and lipids—key for managing diabetes and related disorders.
Gut Health Optimization
Through their role as prebiotics, AOS provide essential nourishment to Bifidobacteria along with other helpful gut bacteria which helps maintain microbiome equilibrium while supporting digestive health.
How can AOS improve your project's potential? Creative Biolabs supports you in unlocking their full potential. Our team offers support whether you require custom synthesis services or need detailed analysis and application development guidance. Our commitment extends to delivering various services that include but are not limited to:
Analyzing AOS: Ensuring Quality and Precision
To unlock AOS potential, accurate characterization is key. Here's how we decode their structure and activity:
|
Technique
|
What It Reveals
|
|
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
|
Molecular weight and structural motifs (LC-ESI-MS, MALDI-TOF-MS)
|
|
NMR (¹H, ¹³C)
|
High-resolution sugar linkages and stereochemistry
|
|
HPLC
|
Separation and quantification of AOS mixtures (HPAEC-PAD, RP-HPLC)
|
|
TLC
|
Preliminary screening for purity and composition
|
|
FTIR & CD
|
Chemical bonds and stereochemical properties
|
Why Partner with Creative Biolabs for AOS Solutions?
At Creative Biolabs, we understand that every AOS project is unique. Whether you're exploring their bioactivity, optimizing synthesis, or scaling up for commercial use, our services are tailored to your goals:
Custom Glycan Synthesis
Leverage our expertise in enzymatic, chemical, and biological methods to create AOS with precise M/G ratios and DP values. We handle everything from small-scale research batches to large-scale production, ensuring consistency and purity.
Comprehensive Glycan Analysis
Our advanced platforms—including HPLC, MS, and NMR—deliver detailed insights into AOS structure, purity, and functional groups. We help you validate bioactivity and meet regulatory standards with confidence.
End-to-End Support
Our glycobiology experts will guide you through every stage from sequence design to process optimization to ensure your workflow remains efficient. Our cost-effective solutions deliver consistent quality so you can concentrate on driving innovation in your projects.
Reach out to us now to begin transforming your AOS vision into reality through our customizable services.
Reference
-
Zhang, Zhikai, Xuejiang Wang, and Feng Li. "An exploration of alginate oligosaccharides modulating intestinal inflammatory networks via gut microbiota." Frontiers in microbiology 14 (2023): 1072151. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1072151
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 AOS in the inflammatory immunology process of intestine.1
Fig.1 AOS in the inflammatory immunology process of intestine.1

