In today's fast-moving landscape of functional foods, few ingredients bridge the gap between scientific rigor and consumer demand as elegantly as isomaltooligosaccharides (IMOs). These α-(1,6)-linked glucose oligosaccharides offer more than prebiotic potential—they exemplify the power of enzymatic design and microbial biosynthesis. At Creative Biolabs, with over 20 years of hands-on experience in carbohydrate biology, we're not just following the trend—we're helping shape it. Our tailored custom oligosaccharide synthesis services and robust IMO analysis platforms are designed to support every step of your research, from strain engineering to purity validation.
What Are Isomaltooligosaccharides?
IMOs are composed of 2 to 10 glucose units, primarily joined by α-(1,6)-glycosidic bonds—a feature that makes them structurally and functionally distinct from more familiar oligosaccharides like FOS or GOS. Key components such as isomaltose (DP2) and panose (DP3) resist digestion in the upper GI tract, instead serving as fermentable substrates for beneficial gut microbiota.
|
Feature
|
Fructooligosaccharides (FOS)
|
Galactooligosaccharides (GOS)
|
Isomaltooligosaccharides (IMO)
|
|
Monomer Units
|
Fructose & Glucose
|
Galactose & Glucose
|
Glucose
|
|
Main Linkage
|
β-(2,1)
|
β-(1,4)
|
α-(1,6)
|
|
DP Range
|
2–10
|
2–10
|
2–10
|
|
Source
|
Chicory root, sugarcane
|
Lactose
|
Starch
|
|
Prebiotic Effect
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
From Starch to IMO: Biosynthesis of IMOs
The biosynthesis of IMOs is a choreography of enzymatic transformations:
-
Liquefaction: Starch is gelatinized and broken down by α-amylase.
-
Saccharification: Glucoamylase releases glucose and maltose.
-
Transglycosylation: Transglucosidase (TGase) creates new α-(1,6)-bonds, shifting the structure toward IMOs.
|
Enzyme
|
Source
|
Role
|
pH
|
Temp (°C)
|
|
α-Amylase
|
Bacillus subtilis
|
Starch liquefaction
|
6.0–6.5
|
90–105
|
|
Glucoamylase
|
Aspergillus niger
|
Glucose release
|
4.0–5.0
|
55–60
|
|
Transglucosidase
|
A. oryzae
|
α(1→6) linkage formation
|
5.0–6.0
|
55–60
|
After enzymatic synthesis, IMOs are purified through activated carbon, ion-exchange resins, and vacuum concentration, yielding a clean syrup suitable for food-grade applications.
Tailored Tools for IMO Characterization
Thorough analytical profiling is key to understanding IMO functionality. At Creative Biolabs, we offer high-resolution analytical tools to guide and validate your process:
|
Analytical Technique
|
Application in IMO Characterization
|
Sensitivity
|
Industrial Use Case
|
|
HPLC-RID / ELSD
|
Quantitative determination of IMO composition, including glucose, isomaltose, isomaltotriose, and higher-DP isomaltooligosaccharides.
|
High
|
Batch release testing, regulatory compliance for labeling, quantification of total IMO content.
|
|
TLC
|
Rapid visualization of IMO conversion during enzymatic transglycosylation; distinguishes between unreacted sugars and α(1→6)-linked oligosaccharides.
|
Medium
|
Enzyme screening, real-time monitoring of fermentation or enzymatic synthesis.
|
|
NMR
|
Structural elucidation of IMO linkages, especially confirmation of α(1→6)-glycosidic bonds between glucose units.
|
Very High
|
R&D validation of product structure, patent support, regulatory submission packages.
|
|
MALDI-TOF MS
|
Profiling the degree of polymerization (DP) of IMO molecules; detects individual isomaltooligosaccharide species (DP2–DP9+).
|
High
|
Product fingerprinting, purity assessment, and higher-DP IMO identification.
|
|
HPAEC-PAD
|
High-resolution separation of IMO isomers and mono-/di-saccharides; differentiates isomaltose from maltose.
|
Very High
|
Critical for high-purity IMO production, structural isomer separation in QA/QC workflows.
|
|
Optical Rotation & Viscosity
|
Evaluation of global carbohydrate characteristics, indicative of IMO concentration and molecular weight distribution.
|
Low
|
Supplementary QC tool in routine batch comparison and historical trend analysis.
|
Isomaltooligosaccharides Uses
The versatility of isomaltooligosaccharides has led to their widespread adoption across various industries:
-
Food Industry: IMO are used as a prebiotic ingredient to enhance the gut health benefits of various food products, including yogurts, granola bars, cereals, and baked goods. They can also function as a low-calorie sweetener and a bulking agent.
-
Beverage Industry: IMO are incorporated into functional beverages, such as prebiotic drinks, sports drinks, and fruit juices, to provide added health benefits.
-
Dietary Supplements: Imoisomalto-oligosaccharides are commonly found in prebiotic supplements, often in combination with probiotics, to support digestive health.
-
Animal Feed: IMO are also being explored for their potential benefits in animal feed, promoting gut health and overall well-being in livestock and pets.
Case Study: A Microbial Platform for IMO Innovation
This study established an efficient method to produce long-chain IMOs (up to DP14) from maltose using Bacillus subtilis AP-1, without residual glucose or maltose. The IMOs exhibited strong digestive resistance, selective support of probiotic growth, favorable fermentation into SCFAs, and excellent cellular safety, offering a practical and scalable solution for functional food and nutraceutical development.
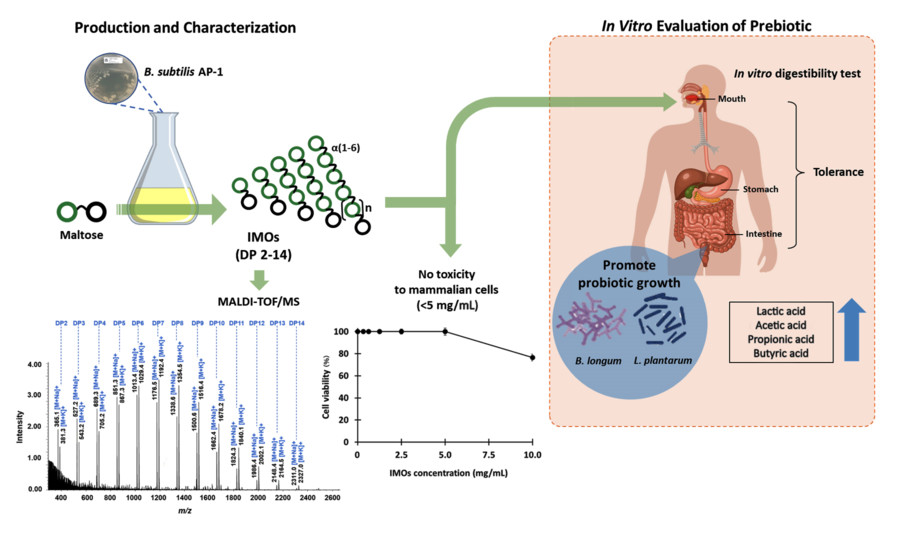 Fig.1 Microbial Production and Prebiotic Evaluation of IMOs.1
Fig.1 Microbial Production and Prebiotic Evaluation of IMOs.1
Key Analytical Methods
-
α-Glucosidase Activity Assay: Measured in the culture supernatant using maltose to confirm enzyme function in IMO synthesis.
-
TLC Analysis: Used to track oligosaccharide formation and assess purification quality.
-
MALDI-TOF/MS: Confirmed the molecular weight and degree of polymerization (up to DP14) of the IMOs.
-
Enzymatic Digestion: α-Amylase and oligosaccharide α-1,6-glucosidase were used to confirm the α-(1→6)-linkages characteristic of IMOs.
Functional Evaluation
-
Simulated Digestion: IMOs resisted enzymatic breakdown under simulated oral, gastric, and intestinal conditions.
-
Microbial Growth Assays: Promoted the growth of probiotics while showing minimal support for pathogenic strains.
-
SCFA Analysis: GC and HPLC confirmed SCFA production from IMO fermentation by beneficial microbes.
-
MTT Cytotoxicity Assay: Demonstrated excellent biocompatibility with L929 fibroblasts.
Why Work with Creative Biolabs?
Whether you're optimizing microbial biosynthesis or validating the functional impact of IMO formulations, Creative Biolabs offers one-stop expertise:
As oligosaccharide-based ingredients continue reshaping the landscape of functional food and gut health, IMOs offer a compelling model of how enzymatic design meets nutritional relevance. Whether you're modifying α-glucosidic bonds or navigating the maze of isomeric analysis, Creative Biolabs is here to streamline your journey. Explore more at Creative Biolabs and let's bring your carbohydrate innovation to life.
References
-
Tiangpook, Suratsawadee, et al. "Production of a series of long-chain isomaltooligosaccharides from maltose by Bacillus subtilis AP-1 and associated prebiotic properties." Foods 12.7 (2023): 1499. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071499
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Microbial Production and Prebiotic Evaluation of IMOs.1
Fig.1 Microbial Production and Prebiotic Evaluation of IMOs.1

