Oligosaccharides, with 2–10 monosaccharide units linked by glycosidic bonds, are nature's molecular multitaskers, driving processes from gut health to immune recognition. At Creative Biolabs, we deliver custom oligosaccharide synthesis solutions that bridge discovery and application, whether you're engineering prebiotic oligosaccharides or designing glycans for next-gen therapeutics. Explore our expertise to accelerate your project with precision and scalability.
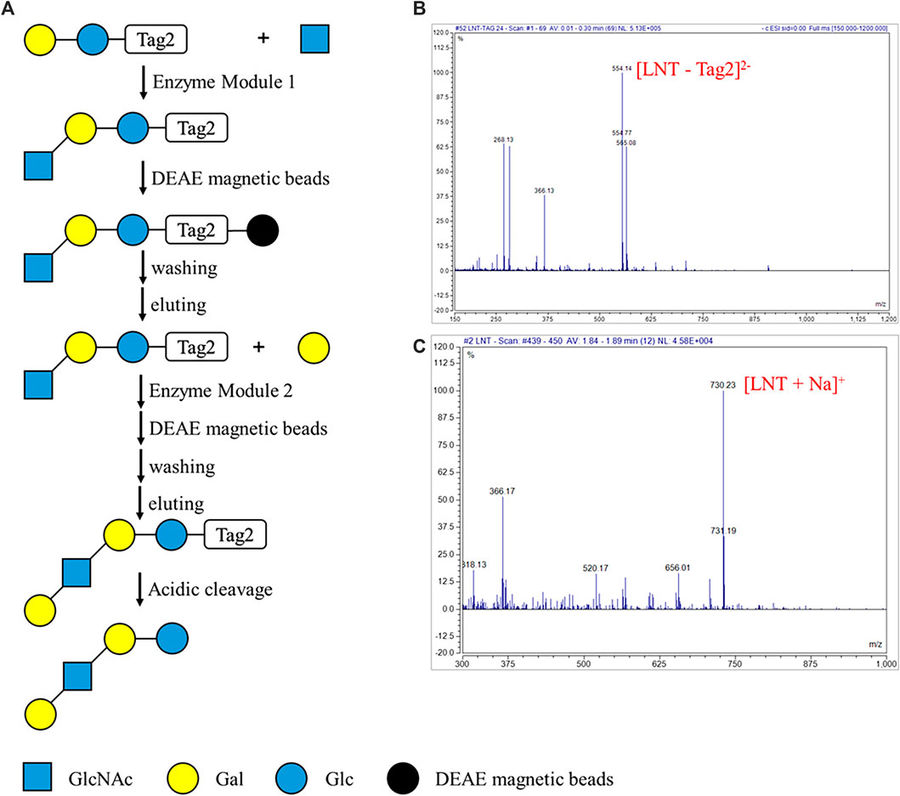 Fig.1 Automated enzymatic oligosaccharide synthesis on the DMF device.1
Fig.1 Automated enzymatic oligosaccharide synthesis on the DMF device.1
The Fundamentals of Oligosaccharide Biosynthesis
A series of enzyme-driven steps are included:
-
Nucleotide Sugar Activation
: Monosaccharides like glucose are activated into energy-rich nucleotide sugars (e.g., UDP-glucose), primed for glycosidic bond formation.
-
Enzymatic Sugar Transfer
: Glycosyltransferases catalyze the transfer of activated sugars to proteins or lipids, forming N-linked (asparagine-targeted) or O-linked (serine/threonine-targeted) oligosaccharides.
-
Structural Refinement
: Post-transfer modifications such as sialylation, fucosylation, or sulfation fine-tune oligosaccharide structures, enabling them to perform specialized roles—think of sialic acid on NK cell surfaces enhancing cancer cell recognition, as demonstrated in our NK cell glycoengineering services.
Advanced Strategies for Oligosaccharide Synthesis
Chemical Synthesis
Chemical methods offer unmatched control over oligosaccharide structure, leveraging techniques like click chemistry (e.g., DBCO-azide cycloadditions) for rapid, specific bond formation. Key steps include:
-
Protecting Group Manipulation: Temporarily blocking reactive groups to ensure regioselective glycosylation.
-
Activated Sugar Donors: Using halides or thioglycosides to enable efficient sugar transfer.
-
Solid-Phase Support: Immobilizing growing oligosaccharide chains on resin for easy purification and scale-up.
Enzymatic Synthesis
-
Glycosynthases: Engineered variants of glycosidases, designed to synthesize rather than degrade oligosaccharides, enabling the production of otherwise inaccessible glycan linkages.
-
One-Pot Glycosylation: Combining multiple enzymes in a single reaction to streamline chain elongation, a technique we employ for efficient synthesis of human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) like 2'-fucosyllactose.
Automated Synthesis
-
Solid-Phase Synthesis Robots: Automating repetitive steps like coupling, washing, and deprotection for large-scale production.
-
Real-Time Monitoring: Integrating HPLC or mass spectrometry to validate intermediate products, ensuring structural accuracy at every stage.
Chemoenzymatic Synthesis
-
Chemical Sugar Activation: Preparing monosaccharide building blocks with orthogonal protecting groups.
-
Enzymatic Bond Formation: Using glycosyltransferases to assemble these blocks into defined sequences, minimizing side reactions and maximizing yield.
Oligosaccharide Synthesis Steps
We employ click chemistry to synthesize oligosaccharides with different sequences and structures. The table below illustrates the general process of oligosaccharide synthesis:
|
Step
|
Description
|
|
Preparation of vector
|
Appropriate vectors are selected, such as alkynyl-modified molecules or solid-phase vectors. The alkynyl group on the vector undergoes a click reaction with the azide group.
|
|
Modification and synthesis of sugar monomers
|
Organic chemistry methods are used to synthesize desired sugar monomers containing functional groups that react with click reaction sites, such as sugar monomers containing an azide group.
|
|
Click reaction
|
A click reaction is performed between an alkynyl-modified vector and an azide donor of the first monosaccharide unit. The reaction is carried out with a suitable copper catalyst to attach the first monosaccharide unit to the vector.
|
|
Repeat click reaction
|
The click reaction steps are repeated, stepwise adding the required number of sugar monomers to build the oligosaccharide of the desired length. In each click reaction, a new monosaccharide unit of the azide donor is used to click with the oligosaccharide chain already attached to the vector, gradually constructing the target oligosaccharide sequence.
|
|
Deprotection
|
After the click reaction is completed, the appropriate deprotection method is selected, and the deprotection step is performed under suitable conditions.
|
Custom Solutions for Diverse Applications
-
Site-specific sulfation techniques: This method allows us to control the sulfation pattern at critical positions on the sugar chain, which is crucial for the oligosaccharide's biological activity.
-
Sulfotransferases for enzymatic sulfation: By using engineered sulfotransferase enzymes, we achieve high selectivity and efficiency in transferring sulfate groups to specific positions on the chondroitin sulfate oligosaccharide backbone.
-
HPLC-MS/MS confirmation: We utilize high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) to ensure accurate sulfation and verify the final structure of the chondroitin sulfate oligosaccharides.
HMOs are essential for infant immune development and gut colonization. We are expert in in synthesizing complex HMOs like lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT) and 6'-sialyllactose using:
-
Enzymatic galactosylation
-
Chemoenzymatic fucosylation
-
One-pot multi-enzyme cascades
Our services include:
-
Synthesis of high-mannose, hybrid, and complex-type N-glycans
-
Mimicking native O-glycosylation patterns (e.g., mucin-type O-glycans)
-
Customization for antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) and viral vectors
These glycans demand precise sulfation at specific positions—a challenge we tackle with:
-
Site-selective chemical sulfation: This ensures that sulfation is incorporated at desired positions, replicating the natural sulfation patterns found in biological systems.
-
Engineered sulfotransferases for enzymatic sulfation: We use advanced engineered enzymes that transfer sulfate groups to specific hydroxyl groups on the sugar backbone, ensuring highly controlled sulfation.
-
HPLC-MS/MS analysis to confirm sulfation patterns: This technology allows for detailed verification of sulfation locations, ensuring the correct structure and functionality of the synthesized heparan sulfate oligosaccharides.
Collaborate with Creative Biolabs
With over decades of experience in glycoengineering, we've supported hundreds of projects in unlocking the potential of oligosaccharides. Our strengths lie in:
-
Technical Expertise: A team of glycobiologists, chemists, and engineers proficient in both classical and cutting-edge synthesis methods.
-
Flexible Scaling: From milligram-scale research samples to gram-scale production, we adapt to your volume needs.
-
Collaborative Approach: Work directly with our scientists to refine your project requirements, ensuring alignment at every stage.
|
Service Feature
|
Technical Edge
|
|
Multi-Technology Platform
|
Choose from chemical, enzymatic, or chemoenzymatic workflows; we match the optimal method to your glycan's complexity.
|
|
End-to-End Customization
|
From monosaccharide selection (e.g., glucose, fructose, sialic acid) to final deprotection, every step is client-driven.
|
|
Rigorous Characterization
|
Confirm structure and purity using MS, NMR, and HPLC—critical for regulatory compliance in biopharmaceuticals.
|
|
Rapid Turnaround
|
Optimized protocols reduce lead times without compromising quality; ideal for time-sensitive drug discovery projects.
|
Are you prepared to translate your glycan research into practical applications? Discover how our custom oligosaccharide synthesis services can supply you with the exact oligosaccharides your project needs. Our team offers essential expertise and dependable support if you work on glycoengineered therapeutic development or other projects. Contact us now to begin our conversation about your project and together we will develop the ideal oligosaccharide for your objectives.
FAQs
Q: What techniques guarantee the structural correctness of synthesized oligosaccharides?
A: Our analysis of synthesized oligosaccharides uses HPLC-MS/MS technology to verify their structure and composition. Our engineered sulfotransferases together with site-selective sulfation methods enable accurate placement of sulfation groups at designated positions.
Q: Your company has the capability to synthesize complex milk oligosaccharides from human breast milk?
A: Our expertise lies in creating complex oligosaccharides such as HMOs. Our one-pot glycosylation approach along with automated synthesis platforms enables us to generate multiantennary branched structures critical for infant nutrition research and various applications.
Q: What methods do you use to synthesize branched oligosaccharides?
A: The production of branched oligosaccharides depends on sophisticated methods to achieve precise branching point formation. Our team at Creative Biolabs employs customized glycosylation methods and automated systems to build branched structures that replicate natural glycosylation patterns in glycoproteins and additional biomolecules.
Reference
-
Sun, Yunze, et al. "Digital microfluidics-engaged automated enzymatic degradation and synthesis of oligosaccharides." Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 11 (2023): 1201300. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2023.1201300
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Automated enzymatic oligosaccharide synthesis on the DMF device.1
Fig.1 Automated enzymatic oligosaccharide synthesis on the DMF device.1

