Oligosaccharides which consist of short monosaccharide chains (typically 2–10 units) seem simple but show immense biological significance. Found freely or as glycoconjugates in glycoproteins and glycolipids, these carbohydrate structures regulate essential cellular activities: These carbohydrate structures regulate crucial cellular processes including immune signaling molecular recognition inflammation and host-pathogen communication among others. The real complexity of these molecules emerges from their structural design. Oligosaccharides demonstrate substantial structural diversity through diverse branching patterns and linkages along with extensive modifications unlike proteins or DNA. While structural complexity in oligosaccharides results in functional diversity it presents a significant challenge for analytical methods.
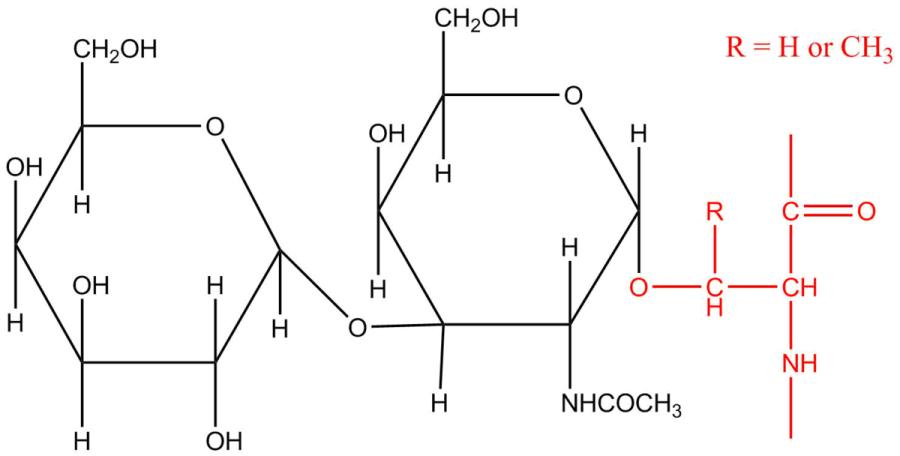 Fig.1 O-linked oligosaccharide structure. Distributed under Public Domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.1 O-linked oligosaccharide structure. Distributed under Public Domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Our team at Creative Biolabs recognizes that characterizing oligosaccharide structures exceeds technical necessity and serves as the key to accessing their biomedical capabilities. The first step to discovery in developing glycoengineered antibodies or studying human milk oligosaccharides involves accurate structure elucidation. Our comprehensive oligosaccharide services deliver precision while maintaining flexibility and integration across multiple platforms.
Oligosaccharides Structure
Every oligosaccharide is a unique combination of six fundamental features:
-
Monosaccharide Composition: Common units include glucose, galactose, mannose, fucose, and sialic acid.
-
Sequence: The linear order of sugars influences function dramatically.
-
Linkage Position: Glycosidic bonds can form between various carbon atoms (e.g., 1→3 or 1→6), shaping the molecule's topology.
-
Anomeric Configuration: α or β configurations affect binding and recognition.
-
Branching: Unlike linear peptides, oligosaccharides form tree-like architectures.
-
Chemical Modifications: Sulfation, acetylation, and methylation add further nuance, critical for specialized functions (e.g., in heparin or glycosaminoglycans).
These structural features generate an exponential number of permutations—even a trisaccharide can exist in dozens of isomeric forms. That's why a complete topological map is essential—not just the formula, but the full 3D context. Oligosaccharides are rarely standalone. N-linked glycans, for example, profoundly influence protein stability, folding, and trafficking. Similarly, glycolipids on cell membranes serve as ligands for immune receptors. Structural precision matters, especially when even minor modifications can alter bioactivity or receptor affinity.
Biophysical and Biochemical Properties
Physical Characteristics
Most oligosaccharides are water-soluble, though solubility depends on molecular weight and chemical modifications. Their osmotic behavior (e.g., in sports nutrition formulations like oligomaltose) and viscosity properties influence their roles in formulations and physiological interactions.
Chemical Properties
Glycosidic bonds are hydrolyzable—enzymatically or chemically—and the presence of a reducing end allows redox-based detection. Some oligosaccharides resist enzymatic degradation (a basis for prebiotic function), while others possess antioxidant properties. Chemical and enzymatic depolymerization (like free radical cleavage used in fucosylated glycosaminoglycans) is not only a method for analysis but also for generating bioactive fragments.
Methods for Structural Characterization
Defining oligosaccharide structure requires more than a single method—it demands a hybrid, orthogonal approach. Each glycan analysis technology answers a different part of the structural puzzle:
|
Technique
|
Role in Oligosaccharide Characterization
|
|
HPLC/CE/SEC/SAX
|
Separates oligosaccharides by size, charge, or hydrophilicity. Ideal for purification and profiling.
|
|
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
|
Determines molecular weight, sequence, and branching. MS/MS fragmentation aids linkage analysis.
|
|
NMR Spectroscopy
|
Reveals fine details like anomeric configuration and linkage position. Requires pure and ample sample.
|
|
Enzymatic & Chemical Cleavage
|
Glycosidases or methylation methods simplify structural determination by breaking complex molecules apart.
|
At Creative Biolabs, our analytical service suite for oligosaccharides is designed for flexibility. Whether your target is a rare sulfated oligosaccharide or a therapeutic glycan analog, we integrate these technologies for complete characterization.
Biological Relevance and Applications
The relationship between structure and function becomes apparent when studying oligosaccharides. For instance:
-
Human Milk Oligosaccharides (HMOs): Complex sugars found only in breast milk help establish the neonatal microbiome while shaping immune system development.
-
Fucosylated Glycosaminoglycans (FGs): The sulfation of their branches generates anticoagulant properties which leads to development of synthetic heparin mimetics.
-
Immune Modulation: Some oligosaccharides connect with immune system receptors including galectins or siglecs to control inflammation or establish tolerance.
-
Cancer Targeting: Aberrant glycosylation is a cancer hallmark. Designer oligosaccharides provide precise biomarkers and therapeutic options.
Industries utilize these applications from functional food supplements with GOS and FOS to advanced glycoengineered biopharmaceuticals. We serve laboratories focused on fundamental glycoscience research together with biotech companies working on therapeutic glycoprotein optimization.
Why Choose Creative Biolabs?
We don't just analyze oligosaccharides—we build, modify, and validate them for real-world applications. Our integrated custom oligosaccharide synthesis services allow us to synthesize and characterize complex glycans, from human milk oligosaccharides to anticoagulant mimetics. From raw synthesis to final quality control, we help researchers generate glycans with confidence—backed by high-resolution MS, advanced HPLC platforms, and decades of glycoscience experience. We offer a suite of customized services tailored to oligosaccharide projects, including but not limited to:
Nature uses oligosaccharides as its most complex chemical codes which demonstrate subtle power alongside their diverse specificity. The structural complexity of these molecules supports numerous biological functions yet creates distinctive challenges for analysis. Appropriate tools transform this complexity into a manageable asset that offers practical benefits. Creative Biolabs proudly works with scientists and developers from around the globe who strive to decode these molecular structures. Our oligosaccharide structure characterization and synthesis expertise enable scientists to achieve their goals in both prebiotic HMO exploration and glycosylated drug delivery system engineering. Our team specializes in decoding and designing glycomolecules before deploying them for future applications. Start your project with us today!
FAQs
Q: What is the structure of oligosaccharides?
A: Oligosaccharides are composed of 2 to 10 monosaccharide units linked via glycosidic bonds. Their structure is defined by monosaccharide type, sequence, linkage position (e.g., 1→3, 1→6), branching patterns, and anomeric configuration (α or β). Chemical modifications such as sulfation or acetylation further enhance their diversity and biological specificity. At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in decoding this complexity to support advanced glycomics and therapeutic development.
Q: How do you identify oligosaccharides?
A: Identifying oligosaccharides requires a multifaceted analytical approach. We combine high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), capillary electrophoresis (CE), mass spectrometry (MS/MS), and NMR spectroscopy to resolve isomers, determine linkages, and characterize branching. At Creative Biolabs, our integrated platform ensures accurate and reproducible oligosaccharide profiling—essential for functional glycomics, drug design, and glycoengineering research.
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 O-linked oligosaccharide structure.
Fig.1 O-linked oligosaccharide structure. 
