Advanced mRNA-LNP Vaccine Research for Viral Infections
mRNA-LNP Vaccines mRNA-LNP for Lassa Fever Research Insights Case Study Products & Services Resources
In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern medicine, mRNA-lipid nanoparticle (mRNA-LNP) technology has truly stepped into the spotlight as a groundbreaking platform, especially when it comes to creating vaccines. This innovative approach gives us a level of speed and flexibility we've never had before in tackling global health issues – whether it's new viruses popping up or even tailoring treatments just for individual patients. At Creative Biolabs, we are at the forefront of this innovation, providing comprehensive services that span IVT mRNA synthesis, LNP preparation and characterization, and rigorous validation. This page delves into the scientific underpinnings and practical applications of advanced mRNA-LNP vaccine research for viral infections, showcasing how our expertise can accelerate your journey from concept to clinic.
The Power of mRNA-LNP Vaccines in Combating Viral Infections
The rapid development and deployment of mRNA vaccines during global health crises have unequivocally demonstrated their transformative potential. Unlike traditional vaccines that introduce weakened or inactivated viruses, or viral proteins, mRNA vaccines deliver genetic instructions (mRNA) to our cells. These instructions guide the cellular machinery to produce specific viral proteins, which then trigger a robust immune response without causing disease.
The true enabler of this revolutionary technology lies in the LNP delivery system. mRNA molecules are inherently fragile and susceptible to degradation in the body. LNPs serve as sophisticated, nanoscale vehicles that encapsulate and protect the mRNA, facilitating its safe and efficient transport into target cells. This synergistic combination of mRNA and LNPs is pivotal, allowing for precise delivery, enhanced stability, and potent immunogenicity.
The Threat of Lassa Fever and the Promise of mRNA-LNP Vaccines
Lassa fever, a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever, is caused by the mammarenavirus Lassa virus (LASV). Endemic in parts of West Africa, LASV poses a significant public health threat due to its high morbidity and mortality rates, especially in regions with limited healthcare infrastructure. The virus is primarily transmitted to humans through contact with food or household items contaminated with the urine or feces of persistently infected rodents, Mastomys natalensis. Clinical manifestations range from mild, non-specific symptoms to severe multi-organ failure, hemorrhagic manifestations, and neurological complications. The urgent need for effective preventive and therapeutic strategies against Lassa fever has driven intensive research efforts.
In response to this critical need, researchers have explored innovative vaccine platforms, including those based on mRNA-LNP technology. A promising approach involves utilizing the expression of specific viral components as antigens to elicit a protective immune response. Notably, studies have focused on the Lassa virus glycoprotein precursor (LASgpc) and the nucleoprotein (LCMnp) of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV). LCMV, a related mammarenavirus, is often used as a surrogate model for LASV in preclinical studies due to its shared genetic and pathogenic characteristics, allowing for safer and more controlled research environments. mRNA-LNP vaccines designed to express these specific antigens aim to prepare the immune system to recognize and combat LASV infection, offering a targeted strategy for Lassa fever prevention.
Experimental Insights into mRNA-LNP Vaccine Development
The journey from concept to a protective mRNA-LNP vaccine involves a series of meticulously designed experimental stages. The foundational research by Pallasch et al. (2024) provides a clear illustration of these critical steps and their outcomes, echoing the comprehensive services Creative Biolabs offers.
-
mRNA Synthesis, LNP Formulation, and In Vitro Expression Validation
This initial phase is critical for establishing the foundational components of an mRNA-LNP vaccine. It involves the meticulous design and synthesis of optimized mRNA constructs encoding target antigens, followed by their encapsulation within precisely engineered LNP. In the context of Lassa fever vaccine research, studies like Pallasch et al. (2024) initiated their work by synthesizing mRNA encoding LASgpc or LCMnp. These mRNAs were then formulated into LNP. A crucial early step involved in vitro assessment of antigen expression. Researchers confirmed that cells transfected with LASgpc-mRNA or LCMnp-mRNA successfully expressed the respective proteins, validating the functionality of the mRNA and its efficient delivery by the LNPs. This initial validation is paramount to ensure the vaccine candidate's potential before proceeding with more complex in vivo studies.
 Fig. 2 Generation of IVT mRNAs expressing the LASV glycoprotein precursor (LASgpc-mRNA) and LCMV nucleoprotein (LCMnp-mRNA).1
Fig. 2 Generation of IVT mRNAs expressing the LASV glycoprotein precursor (LASgpc-mRNA) and LCMV nucleoprotein (LCMnp-mRNA).1
-
Comprehensive In Vivo Immunization and Challenge Studies
Evaluating the protective efficacy of vaccine candidates requires rigorous in vivo studies across relevant animal models. This involves administering the mRNA-LNP formulations via appropriate routes and subsequently challenging the immunized subjects with the target pathogen or a suitable surrogate. They conducted extensive immunization and challenge studies across different mouse strains to assess the protective capacity of their mRNA-LNP vaccine candidates:
Protection in C57BL/6 Mice
Immunization with either LASgpc-mRNA-LNP or LCMnp-mRNA-LNP, followed by a lethal challenge with recombinant LCMV expressing a modified LASgpc (rLCMV/LASgpc2m), demonstrated significant protective immunity. Two doses of these vaccines were sufficient to protect C57BL/6 mice from lethal infection, highlighting the vaccine's ability to prevent severe disease outcomes.
 Fig. 3 Intravenous immunization of C57BL/6 mice with LASgpc- and LCMnp-mRNA-LNP provides protection against rLCMV/LASgpc2m.1
Fig. 3 Intravenous immunization of C57BL/6 mice with LASgpc- and LCMnp-mRNA-LNP provides protection against rLCMV/LASgpc2m.1
Protection in FVB/N Mice
The study also included immunization with LCMnp-mRNA-LNP and challenge with wild-type rLCMV in FVB/N mice, expanding the scope of the protective assessment and demonstrating broader applicability.
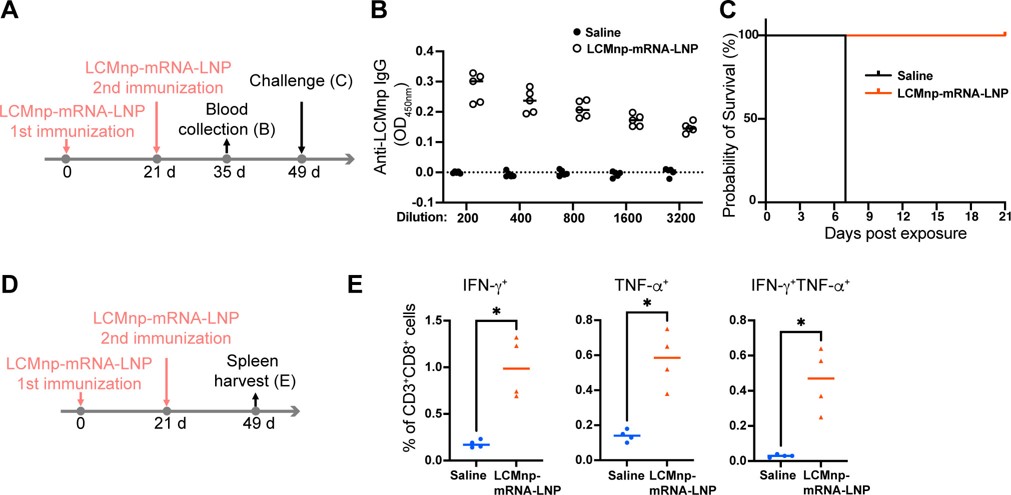 Fig. 4 LCMnp-mRNA-LNP immunization provides protection in hemorrhagic disease mouse model (FVB mouse).1
Fig. 4 LCMnp-mRNA-LNP immunization provides protection in hemorrhagic disease mouse model (FVB mouse).1
Significant Viral Load Reduction
Intramuscular administration of LASgpc-mRNA-LNP and LCMnp-mRNA-LNP vaccines also significantly lowered rLCMV/LASgpc2m replication levels in C57BL/6 mice, beyond improving survival. This reduction in viral load is a critical indicator of vaccine-induced protection and disease attenuation, demonstrating the vaccine's capacity to control viral proliferation within the host.
 Fig. 5 Intramuscular immunization with LASgpc- or LCMnp-mRNA-LNP reduces the viral load in C57BL/6 mice.1
Fig. 5 Intramuscular immunization with LASgpc- or LCMnp-mRNA-LNP reduces the viral load in C57BL/6 mice.1
-
Detailed Humoral and Cellular Immune Response Characterization
A thorough understanding of the immune mechanisms elicited by a vaccine is essential for its development and optimization. This involves characterizing both the antibody (humoral) and T-cell (cellular) responses to identify the key mediators of protection.
Detection of Specific Antibodies
The study rigorously assessed antibody responses, specifically detecting LCMnp- and LASgpc-specific antibodies by ELISA. While these antibodies were present, the researchers noted that no virus-neutralizing activity was observed in the immunized mice. This finding suggests that, in this specific model, protection was not primarily mediated by conventional neutralizing antibodies.
Robust CD8+ T Cell Responses and Correlation with Protection
The research revealed robust specific CD8+ T cell responses to LCMnp and LASgpc immunodominant peptides in the immunized mice. Furthermore, the observed protection against lethal rLCMV/LASgpc2m infection in CBA mice immunized with LASgpc-mRNA-LNP was found to correlate strongly with these LASgpc-specific CD8+ T cell responses. This observation underscores the indispensable contribution of cellular immunity, specifically cytotoxic T lymphocytes, to the protective efficacy conferred by these mRNA-LNP vaccines against surrogates of Lassa virus, thereby illuminating a key determinant of vaccine potency.
Case Study
A typical dynamic light scattering (DLS) image of our prepared LNPs would demonstrate a narrow size distribution, indicative of a homogenous and stable formulation, a testament to our robust process development capabilities.
This hands-on experience and our ability to achieve such critical quality attributes underscore our rich expertise and capabilities in the complex field of mRNA-LNP development, positioning us as a reliable partner for your research and development needs.
Creative Biolabs stands as a leading expert in the field of lipid-based drug delivery systems, offering unparalleled scientific knowledge and practical capabilities in advanced mRNA-LNP vaccine research. Our comprehensive suite of services, from precise IVT mRNA synthesis and optimized LNP formulation to rigorous characterization and validation, ensures that your projects are supported by the highest standards of scientific excellence and industrial experience. Contact us today to learn how our specialized services can empower your next breakthrough in viral infection prevention and treatment.
Related Products & Services
At Creative Biolabs, we understand that translating groundbreaking scientific research into viable therapeutic and prophylactic solutions requires specialized expertise and state-of-the-art capabilities. Our comprehensive services are designed to bridge the gap between academic insights, such as those found in the Journal of Virology regarding mRNA-LNP vaccines, and industrial application.
|
Service
|
Description
|
Inquire
|
|
mRNA Encapsulation and Process Optimization
|
We provide expertise in scalable manufacturing processes to ensure efficient and consistent mRNA encapsulation within LNPs, critical for vaccine potency.
|
Inquire
|
|
LNP Formulation Development
|
Leveraging our deep understanding of lipid chemistry and nanoparticle engineering, we assist clients in designing and optimizing LNP formulations for enhanced mRNA encapsulation, stability, and targeted delivery.
|
Inquire
|
|
In Vitro and In Vivo Validation Support
|
We offer robust testing services to validate the immunological responses and protective efficacy of mRNA-LNP vaccine candidates, guiding clients through critical preclinical stages.
|
Inquire
|
|
We have some ready-to-use mRNA-LNP products that can serve as references for your mRNA-LNP research. If you have specific needs, please contact us.
|
Resources
Reference
-
Hashizume, Mei, Ayako Takashima, and Masaharu Iwasaki. "An mRNA-LNP-based Lassa virus vaccine induces protective immunity in mice." Journal of Virology 98.6 (2024): e00578-24. doi:10.1128/jvi.00578-24. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
 Fig. 3 Intravenous immunization of C57BL/6 mice with LASgpc- and LCMnp-mRNA-LNP provides protection against rLCMV/LASgpc2m.1
Fig. 3 Intravenous immunization of C57BL/6 mice with LASgpc- and LCMnp-mRNA-LNP provides protection against rLCMV/LASgpc2m.1
 Fig. 4 LCMnp-mRNA-LNP immunization provides protection in hemorrhagic disease mouse model (FVB mouse).1
Fig. 4 LCMnp-mRNA-LNP immunization provides protection in hemorrhagic disease mouse model (FVB mouse).1
 Fig. 5 Intramuscular immunization with LASgpc- or LCMnp-mRNA-LNP reduces the viral load in C57BL/6 mice.1
Fig. 5 Intramuscular immunization with LASgpc- or LCMnp-mRNA-LNP reduces the viral load in C57BL/6 mice.1


 Fig. 2 Generation of IVT mRNAs expressing the LASV glycoprotein precursor (LASgpc-mRNA) and LCMV nucleoprotein (LCMnp-mRNA).1
Fig. 2 Generation of IVT mRNAs expressing the LASV glycoprotein precursor (LASgpc-mRNA) and LCMV nucleoprotein (LCMnp-mRNA).1



 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use