Medicine is constantly evolving, and one key challenge is ensuring therapeutic agents reach their intended biological targets effectively and safely. You often see that conventional drug delivery can lead to the drug circulating widely, causing side effects where it's not needed. That's why advanced drug delivery systems are so exciting – they're changing the game for treating diseases. Liposomes are a prime example. These versatile nanocarriers are proving incredibly useful in clinics, offering a reliable way to package and deliver all sorts of therapeutic molecules. At Creative Biolabs, we really understand this technology inside out. We're here to support you with innovative research ideas and dependable solutions, leveraging our expertise to help you turn therapeutic potential into tangible, high-quality products.
Liposomes are self-assembling spherical vesicles composed of one or more lipid bilayers enclosing an aqueous core. Their unique amphiphilic structure allows them to encapsulate both hydrophilic drugs within their aqueous lumen and hydrophobic drugs within their lipid bilayers. This inherent versatility, coupled with their excellent biocompatibility, biodegradability, and low immunogenicity, has made liposomes a cornerstone in the development of sophisticated drug delivery system. However, despite these advantages, native liposomes often face limitations such as rapid clearance by the reticuloendothelial system (RES) and a lack of specificity, leading to non-targeted distribution throughout the body. Overcoming these challenges is paramount to realizing the full therapeutic potential of liposome-based formulations. This is precisely where bioconjugation plays a transformative role.
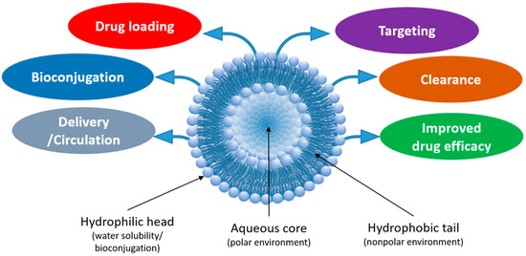 Fig. 1 Structural features of liposomes and their advantageous features.1
Fig. 1 Structural features of liposomes and their advantageous features.1
Bioconjugation, in the context of liposomes, involves the covalent or non-covalent attachment of biologically active molecules to the liposomal surface or within its lipid bilayer. This strategic modification confers enhanced functionalities, allowing liposomes to overcome biological barriers, achieve precise targeting, improve stability, enable controlled release, and facilitate imaging or diagnostic capabilities.
The molecules commonly conjugated to liposomes include:
| Ligand | Liposome Composition | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Hyaluronic acid, HA (polymer) | DPPC, DOPG, hydrazide-cholesterol, HA | Delivery of drug to CD44+ cells |
| Folate acid, FA (vitamin) | FA-PEG-DSPE, DSPC, chol, mPEG-DSPE | Treatment of FA receptor+ tumors |
| α-tocopherol (vitamin) | HSPC, PG, chol | Treatment of fungal infection |
| Porphyrins | DSPC, chol, DSPE-PEG, DOPC | Ultrasound-triggered drug release |
| HER2 (antibody) | ICG-ODA (photosensitizer), DSPE-PEG2000, SPC | Light-triggered drug release and ROS generation for chemotherapy |
| CD11c (antibody) | DOPE, EPC, chol, DBCO-PEG | Treatment of CD11c+ diseases |
The choice of bioconjugation strategy is critical, depending on the nature of the liposome, the molecule to be conjugated, and the desired application. These strategies aim for high efficiency, specificity, and preservation of the biological activity of the conjugated molecule.
The field of bioconjugated liposomes is continually evolving, driven by innovations in materials science, synthetic chemistry, and biotechnology.
Bioconjugation strategies have fundamentally transformed liposome-mediated drug delivery, enabling the development of highly precise, stable, and multifunctional nanocarriers. From enhancing targeted therapy and imaging to facilitating gene editing and immunotherapy, the power of attaching specific biomolecules to liposomes continues to unlock unprecedented therapeutic possibilities. As research progresses, the integration of novel chemistries and advanced engineering will further refine these systems, promising a future of more effective and safer treatments.
Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of this innovation, offering the scientific knowledge, technical expertise, and comprehensive services required to navigate the complexities of bioconjugated liposome development. Connect with us to explore how our capabilities can accelerate your research and bring your groundbreaking therapies to fruition.
Creative Biolabs offers specialized services to accelerate your research and development in bioconjugation strategies for liposome-mediated drug delivery across all applications. Our expertise ensures robust and scalable solutions.
| Service Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Conjugation Strategy Design | Expert design and optimization of bioconjugation chemistries (e.g., click chemistry, NHS, maleimide) for various ligands, including antibodies, peptides, polymers, and aptamers, ensuring high efficiency and preserved biological activity. |
| Stimuli-Responsive Liposome Development | Design and development of liposomes engineered to release payloads or expose ligands in response to specific stimuli (e.g., pH, temperature, light, enzymes), enhancing targeted delivery and controlled release. |
| Characterization |
Comprehensive analysis including size, polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential, drug loading, ligand density, and morphology to ensure product quality and consistency. We employ multiple methods to prove the successful conjugation of ligands, such as BCA, Bradford. |
| Validation | Rigorous testing of targeted liposomes for specific binding, cellular uptake, and therapeutic efficacy in relevant in vitro and in vivo models. This includes verifying the distribution of the drug in different tissues/cells to demonstrate successful targeting after coupling. |
Creative Biolabs provides essential products that facilitate cutting-edge research and development in lipid-based drug delivery systems and their applications. These high-quality components support the implementation and study of bioconjugation strategies and similar technologies.
| Product Category | Product Category |
|---|---|
| Pre-formulated Liposome | These pre-formulated liposomes are designed to be either easily functionalized or already possess features that make them amenable to bioconjugation with various ligands. |
| Lipid Components | A comprehensive selection of high-purity lipids, including phospholipids, cholesterol, and PEGylated lipids, essential for custom liposome formulation and functionalization. |
| Conjugation Reagents | A range of reactive molecules and kits specifically designed for efficient and reliable bioconjugation of targeting ligands to liposomes, including NHS esters, maleimides, and click chemistry reagents. |
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry