While lipid nanoparticle (LNP)-based gene therapy has achieved monumental success with mRNA vaccines, the field faces a new and complex set of challenges in developing durable, long-term therapeutic solutions. Prolonged gene expression with DNA LNPs offers a promising path forward, but requires navigating significant hurdles related to molecule size, cellular barriers, and formulation stability. Creative Biolabs can help customers overcome these challenges by providing innovative research ideas and a comprehensive platform for the development of advanced lipid-based drug delivery systems.
Traditional gene delivery often relies on viral vectors, which, while highly effective, can pose significant safety concerns, including immunogenicity and potential for genomic integration. LNPs have emerged as a powerful non-viral alternative, offering a safer and more scalable platform for encapsulating and delivering nucleic acids. Their self-assembling nature, biocompatibility, and ability to be finely tuned for specific applications make them an attractive choice for next-generation gene therapies, avoiding many of the limitations associated with viral systems.
A fundamental difference between nucleic acid types dictates the duration of their therapeutic effect. As an intermediate molecule, mRNA is designed to be transient; once it has been translated into a protein, it is rapidly degraded by the cell. While this is ideal for applications like vaccines where a short-lived burst of protein production is desired, it presents a challenge for treating chronic conditions that require sustained therapeutic protein levels. Plasmid DNA (pDNA), by contrast, can exist as a stable episome within the cell's nucleus for extended periods. This stability allows for continuous transcription into mRNA, leading to durable and prolonged expression of the therapeutic protein, potentially for months or even years from a single dose. This is a critical advantage for managing diseases like heart disease, diabetes, or certain cancers, where frequent redosing is a major barrier to patient adherence and treatment efficacy.
Delivering DNA using LNPs presents a unique set of challenges compared to delivering mRNA. Plasmid DNA is a substantially larger and more rigid molecule, which complicates its efficient encapsulation and release. Furthermore, for a pDNA therapeutic to be effective, the LNP must not only successfully deliver its payload into the cell's cytoplasm but also facilitate the difficult process of nuclear entry. This additional barrier is a key reason why pDNA LNPs have lagged behind their mRNA counterparts, and overcoming it is a critical step for unlocking their therapeutic potential.
Drawing from a recent landmark study published in Nature Communications, we highlight the key experimental strategies that are driving innovation in DNA LNP development. The research provides a blueprint for a systematic approach to overcoming the inherent challenges of plasmid DNA delivery.
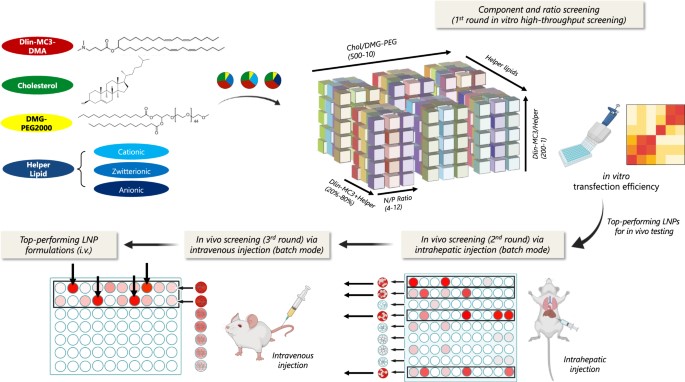 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of multi-step composition screening for LNPs delivering pDNA. 1
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of multi-step composition screening for LNPs delivering pDNA. 1
This study introduced a multi-step screening platform to efficiently identify optimal LNP formulations from a library of over 1000 candidates. The approach methodically evaluates the impact of different helper lipids and component ratios on gene delivery in vitro and in vivo, providing a data-driven path to down-select the most effective formulations and overcome physiological barriers.
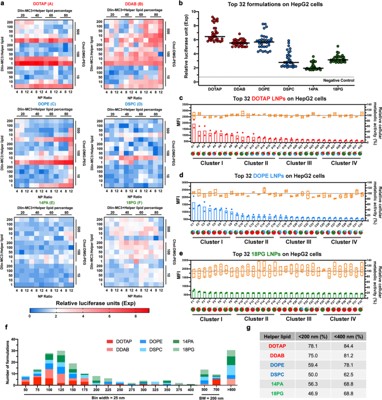 Fig. 2 LNP-mediated in vitro transmission of pDNA. 1
Fig. 2 LNP-mediated in vitro transmission of pDNA. 1
The research analyzed the efficacy of different LNP formulations for pDNA delivery. It demonstrated successful transgene delivery and prolonged expression in the liver of mice following intravenous administration. This work provides crucial data on how a systematically screened LNP can outperform both mRNA LNPs and a traditional commercial DNA transfection agent (in vivo-jetPEI/DNA).
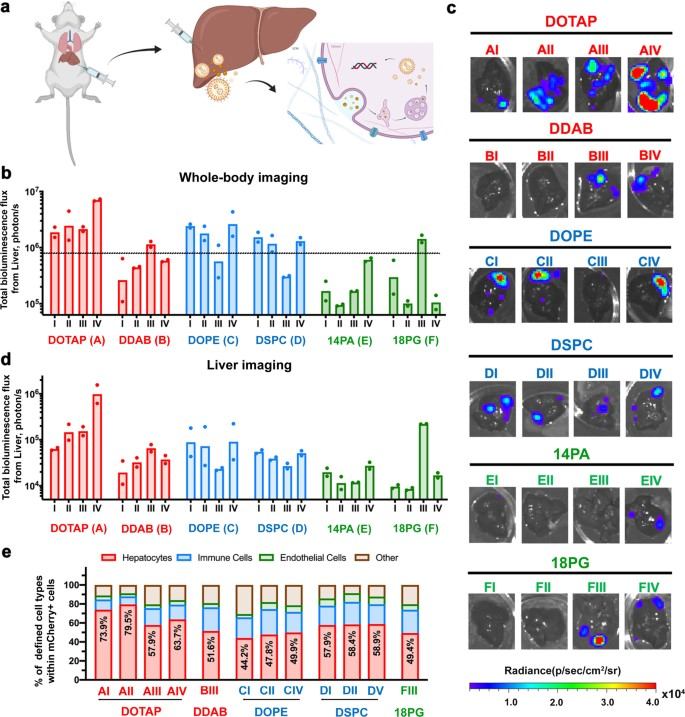 Fig. 3 LNP-mediated intrahepatic pDNA delivery. 1
Fig. 3 LNP-mediated intrahepatic pDNA delivery. 1
A significant innovation was the demonstration of a co-delivery strategy to further extend transgene expression. By co-encapsulating pDNA and siRNA that targets inflammatory response pathways, the research successfully addressed a key barrier to long-term expression. This approach highlights a novel method for enhancing the safety and duration of DNA-based gene medicine applications.
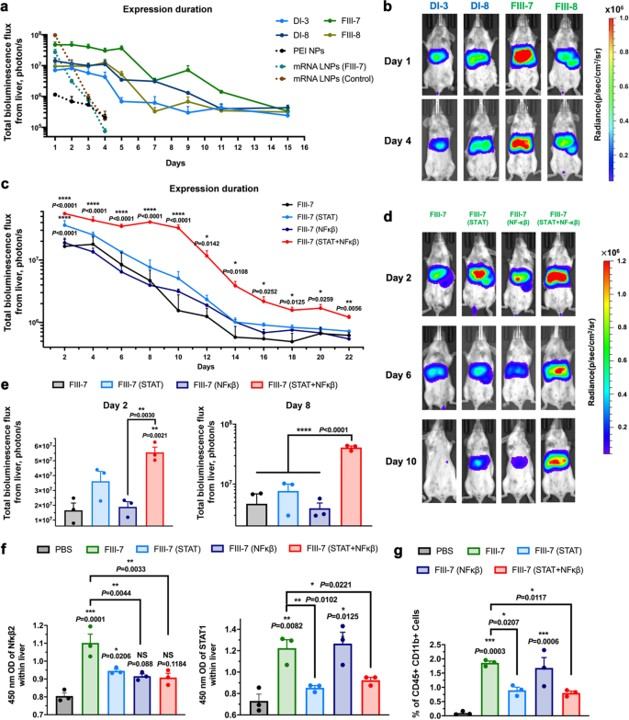 Fig. 4 LNPs that co-deliver anti-inflammatory siRNA and pDNA can prolong gene expression time. 1
Fig. 4 LNPs that co-deliver anti-inflammatory siRNA and pDNA can prolong gene expression time. 1
The systematic screening platform, in vitro and in vivo analysis, and co-delivery strategy described in the literature demonstrate a powerful approach for developing highly effective DNA-based LNPs. These research insights are a testament to the potential of lipid-based drug delivery systems to unlock durable therapeutic effects. Creative Biolabs can help you apply these principles to your own projects. Contact us to discuss how our expertise can support your research.
Creative Biolabs provides specialized services to accelerate your research in prolonged gene expression with DNA LNPs and lipid-based drug delivery systems. We understand the complexities of LNP-based gene therapy and offer a comprehensive suite of services to ensure your project's success, from initial design to final validation.
| Services/Products | Description | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|
| Ready-to-use Lipids | We offer a rich variety of high-quality lipids, including ionizable lipids such as DSPC, DOPE, DOTAP, and DLin-MC3-DMA, essential for robust LNP formulation. | Inquiry |
| Plasmid Construction | Our services include custom plasmid construction to optimize DNA sequences for high-yield expression and incorporation into LNPs. | Inquiry |
| High-throughput LNP Screening | Our proprietary platforms enable rapid and efficient screening of large LNP libraries to identify the most effective formulations for your specific therapeutic payload. | Inquiry |
| Co-delivery LNP Development | We design and optimize co-delivery formulations, such as DNA/siRNA LNPs, to enhance therapeutic efficacy and achieve desired long-term gene expression profiles. | Inquiry |
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry