This page highlights how enzyme-responsive liposomes offer a groundbreaking therapeutic strategy to precisely target tumors, such as breast cancer, which often exhibit high expression of specific enzymes like MMP-2. The principle involves engineering liposomes to remain stable in circulation but release their therapeutic payload only when triggered by these tumor-specific enzymatic activities, thereby maximizing therapeutic efficacy and minimizing systemic side effects. As an expert in biology with over two decades of experience, Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive suite of services related to this cutting-edge field. We empower our clients to leverage these intelligent nanocarriers, offering support from responsive peptide synthesis and custom liposome formulation to advanced characterization and robust pre-clinical validation.
Traditional drug delivery often relies on systemic administration, leading to non-specific distribution, off-target side effects, and suboptimal therapeutic indices. Lipid-based drug delivery systems, particularly liposomes, have long offered a superior alternative by encapsulating therapeutic agents, improving solubility, enhancing bioavailability, and reducing toxicity. However, the next generation of drug delivery demands even greater precision. This has led to the emergence of "smart" or "responsive" nanocarriers that can selectively release their payload at a desired physiological site, triggered by specific internal or external stimuli. Among these intelligent systems, enzyme-responsive liposomes stand out as a highly promising strategy. They leverage the overexpression of certain enzymes in diseased tissues (such as tumors, inflammatory sites, or infection foci) to trigger controlled drug release, thereby maximizing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing systemic exposure.
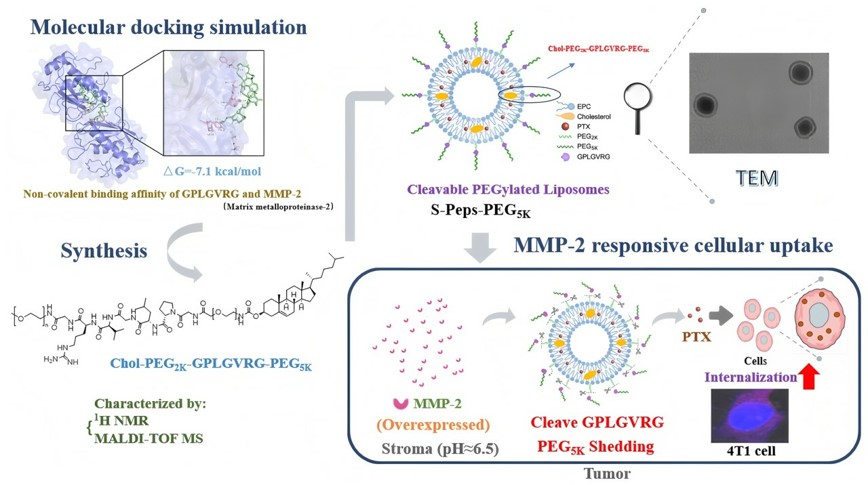 Fig. 1 Matrix metalloproteinase-2-responsive peptide-modified cleavable PEGylated liposomes for paclitaxel delivery.1
Fig. 1 Matrix metalloproteinase-2-responsive peptide-modified cleavable PEGylated liposomes for paclitaxel delivery.1
Paclitaxel, a potent antineoplastic agent, is a cornerstone in the treatment of various cancers, including breast cancer. Despite its remarkable efficacy, paclitaxel (PTX) presents significant formulation challenges due to its poor aqueous solubility and is associated with dose-limiting toxicities, primarily neurotoxicity and hypersensitivity reactions, when administered conventionally. Liposomal encapsulation has proven effective in mitigating some of these issues, but achieving precise, tumor-specific drug release remains a critical unmet need.
The core principle behind enzyme-responsive liposomes is their ability to undergo a structural or chemical change in response to specific enzymatic activity. This change then facilitates the release of the encapsulated drug. In the context of cancer therapy, this approach capitalizes on the altered enzymatic microenvironment of tumors. For instance, many solid tumors, including breast cancer, exhibit elevated levels of certain proteases, such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs).
Recent research, exemplified by a study on enzyme-responsive peptide modified liposomes for targeted PTX delivery in breast cancer, highlights the ingenuity of this approach. These innovative liposomes are engineered with enzyme-cleavable linkers, often peptides, strategically incorporated into their structure. When these liposomes encounter the specific enzyme (e.g., MMP-2 in the tumor microenvironment), the peptide linker is cleaved, leading to a conformational change or degradation of the liposome, and subsequent drug release.
The research initiated with molecular docking studies to investigate the affinity between MMP-2 and the GPLGVRG peptide sequence. This computational approach provided initial insights into their binding interactions, predicting a strong affinity that supported the rationale for designing an MMP-2-responsive linker. Following these computational predictions, the GPLGVRG peptide and the complete cholesterol-PEG2K-GPLGVRG-PEG5K linker were successfully synthesized, paving the way for the development of the responsive liposomes.
The study meticulously detailed the preparation of the S-Peps-PEG5K liposomes loaded with paclitaxel, alongside the control liposome formulations (Lip, Lip-PEG2K, and S-Peps). Comprehensive characterization was performed to assess critical physicochemical properties, including particle size, zeta potential, and encapsulation efficiency. These characterization steps ensured the successful formation of stable liposomal nanoparticles with consistent properties, crucial for reliable in vitro and in vivo evaluations.
| Liposomes | Size (nm) | Zeta (mV) | PDI | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lip | 136.8 ± 0.3 | 8.1 ± 0.5 | 0.057 ± 0.002 | 91.4 ± 4.0 |
| Lip-PEG2K | 186.5 ± 1.4 | −23.6 ± 0.4 | 0.078 ± 0.003 | 92.7 ± 3.5 |
| S-Peps | 158.9 ± 4.2 | −25.8 ± 0.9 | 0.095 ± 0.003 | 94.6 ± 2.1 |
| S-Peps-PEG5K | 179.9 ± 0.7 | −26.3 ± 0.3 | 0.060 ± 0.002 | 90.3 ± 4.5 |
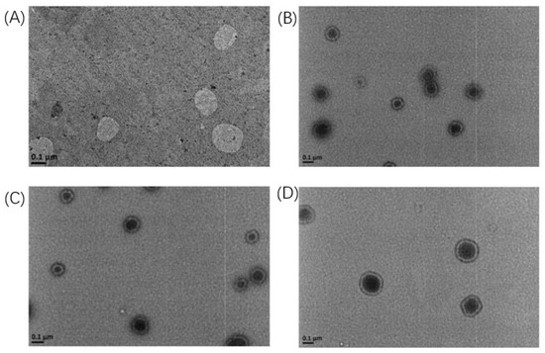 Fig. 5 The morphology of liposomes under TEM.1
Fig. 5 The morphology of liposomes under TEM.1
These cellular assays critically demonstrated the functional success of the enzyme-responsive liposome design for targeted therapy. Enhanced uptake in 4T1 breast cancer cells, triggered by MMP-2-mediated PEG5K shedding, validated precise targeted delivery. This led to significant proliferation inhibition and enhanced cytotoxicity, demonstrating the intelligent liposomes' ability to effectively combat breast cancer through enzyme-triggered drug release.
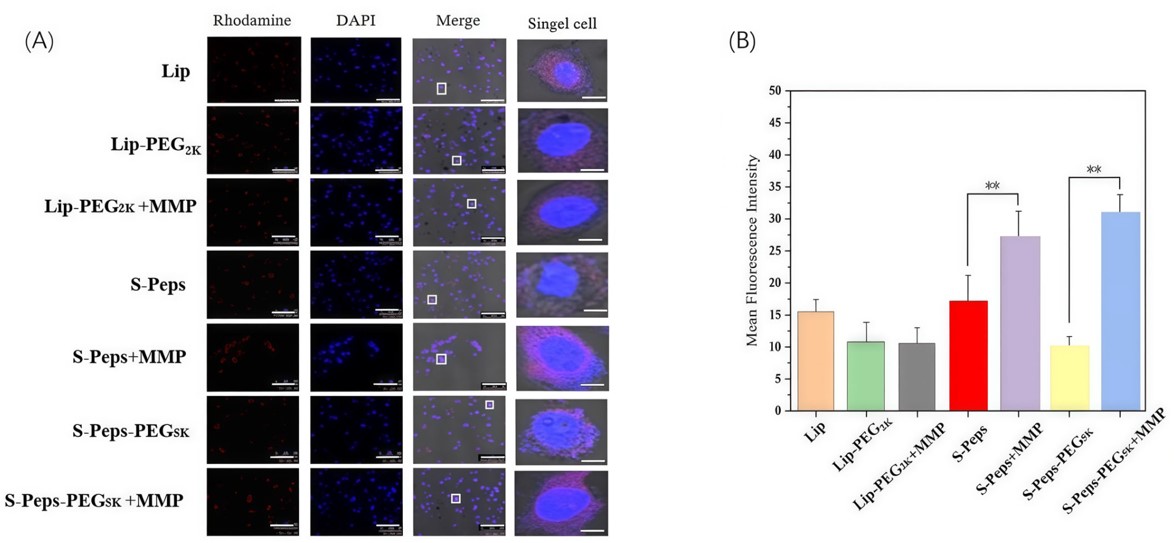 Fig. 6 Intracellular distribution of Rhod-modified liposomes in 4T1 cells.1
Fig. 6 Intracellular distribution of Rhod-modified liposomes in 4T1 cells.1
The in vitro drug release profile elucidated the precise triggers for paclitaxel release, a cornerstone of controlled drug delivery. The study identified the acidic tumor microenvironment (approximately pH 6.5) as a crucial factor facilitating MMP-2 activity and subsequent peptide cleavage, initiating drug release. A clear dose-dependent relationship between MMP-2 concentration and release validated molecular docking predictions. This confirms the intelligent design ensures controlled, targeted drug release within the tumor microenvironment, maximizing therapeutic impact.
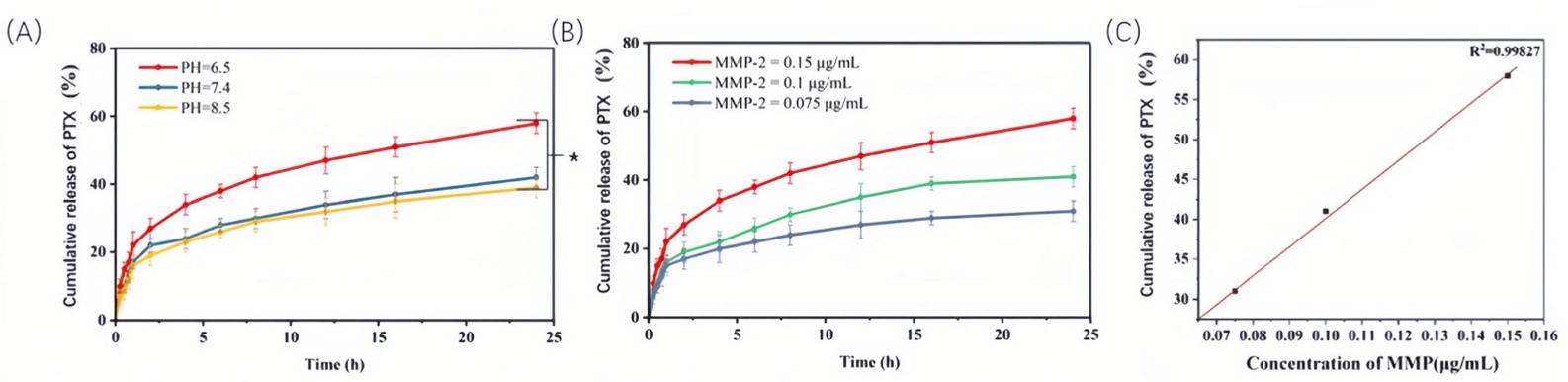 Fig. 7 In vitro PTX release experiment.1
Fig. 7 In vitro PTX release experiment.1
Creative Biolabs stands as a leader in lipid-based drug delivery, offering unparalleled expertise and services to advance your therapeutic strategies. Our deep understanding of enzyme-responsive liposomes, coupled with our capabilities in responsive peptide synthesis, advanced characterization, and comprehensive pre-clinical validation using various animal models (including breast cancer), positions us as your ideal partner. We provide ready-to-use Pegylated lipids and high-quality APIs like PTX to streamline your research. Contact us today to learn how we can help you overcome research bottlenecks and accelerate the development of innovative, targeted enzyme-responsive solutions.
The development of sophisticated drug delivery systems like enzyme-responsive liposomes demands deep scientific expertise and robust technical capabilities. At Creative Biolabs, we possess over two decades of experience in lipid-based drug delivery, positioning us uniquely to translate groundbreaking academic research into tangible pharmaceutical solutions.
| Service | ||
|---|---|---|
| Responsive Peptide Synthesis | We provide custom synthesis and conjugation of enzyme-responsive peptides, essential components for engineering smart liposomal systems that precisely respond to specific enzymatic triggers in the biological microenvironment. | Inquiry |
| Custom Development and Formulation | Our experts specialize in designing and optimizing lipid formulations, including enzyme-responsive liposomes and Pegylated liposomes, tailored to specific drug payloads and therapeutic targets. | Inquiry |
| Advanced Characterization | We employ state-of-the-art analytical techniques to thoroughly characterize your lipid-based drug delivery systems. This includes precise measurements of particle size, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, stability, and crucially, in vitro enzyme-triggered drug release kinetics. | Inquiry |
| Pre-clinical Validation | We support comprehensive pre-clinical validation studies, including in vitro cellular uptake and cytotoxicity assays, and in vivo pharmacokinetic, biodistribution, and efficacy studies. We offer access to various animal models to assist in drug efficacy evaluation, including breast cancer models. | Inquiry |
| Products | ||
| Pegylated Lipids | We offer a variety of ready-to-use Pegylated lipids, essential for creating long-circulating and enzyme-responsive liposomes. Our selection includes multiple selectable PEG molecular weights (e.g., PEG 2000, PEG 5000). and various functionalized lipids such as DESP-PEG-NHS, DESP-PEG-mal, and more, allowing for flexible and precise formulation development. | Inquiry |
| Functionalized Lipids | We offer various functionalized lipids such as DESP-PEG-NHS, DESP-PEG-mal, and more, allowing for flexible and precise formulation development. | Inquiry |
| API and Research Compounds | We provide high-quality research-grade compounds, including Paclitaxel and many other drugs, to facilitate your drug delivery research and development efforts. | Inquiry |
| Paclitaxel Liposomes | Ready-to-use liposomal formulations of paclitaxel, designed for enhanced solubility, improved pharmacokinetics, and reduced toxicity compared to conventional administration. | Inquiry |
| Paclitaxel-Curcumin Liposomes | Innovative co-encapsulated liposomal formulations combining paclitaxel and curcumin, offering potential synergistic therapeutic effects for various cancer treatments. | Inquiry |
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry