Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a very aggressive and fast-spreading type of breast cancer, often hard to diagnose early. This makes finding new and effective treatments crucial. At Creative Biolabs, our "Research Highlights" section is dedicated to exploring such cutting-edge developments. Today, we delve into a particularly promising area: the application of targeted lipocalin-2 (LCN2) siRNA liposomes for IBC treatment. This approach represents a significant leap forward in lipid-based drug delivery systems, offering a dual-pronged attack against this formidable disease.
IBC stands out as a particularly rare and aggressive form of breast cancer. It progresses rapidly, has a high tendency to metastasize, and unfortunately, carries a poor prognosis. What makes it especially challenging is that, unlike many other breast cancers, IBC often doesn't present with a distinct lump, making early detection much harder. Furthermore, its inherently aggressive nature frequently leads to resistance against standard treatments, including targeted therapies like trastuzumab, especially in HER2-positive cases. This urgent clinical need is pushing the boundaries of research, driving the search for innovative and more effective ways to combat this disease. This is where lipid-based drug delivery systems, especially liposomes, come into play. They've emerged as incredibly powerful tools in oncology. Think of them as smart carriers that can encapsulate a wide range of therapeutic agents, protecting these valuable drugs from breaking down before they reach their target. They also help significantly reduce the drug's impact on healthy tissues, thereby lessening systemic toxicity, while simultaneously boosting the concentration of the medication right at the tumor site. It's a promising avenue in the fight against challenging cancers like IBC.
The complexity of IBC necessitates a sophisticated therapeutic response. Our understanding of this disease has evolved, revealing key molecular pathways that contribute to its aggressive nature and resistance to treatment. This section will introduce the innovative dual-targeting strategy, which involves precisely modifying lipid-based drug delivery systems with trastuzumab for HER2-specific targeting, while simultaneously encapsulating LCN2 siRNA to address critical resistance pathways and achieve enhanced therapeutic efficacy against IBC.
Recent scientific literature has shed light on the crucial role of LCN2 in cancer progression, metastasis, and drug resistance. LCN2, a secreted glycoprotein, is overexpressed in various cancers, including breast cancer, where it contributes to cell proliferation, survival, invasion, and angiogenesis. Crucially, research has demonstrated that LCN2 overexpression is strongly associated with poor prognosis and, significantly in HER2-positive breast cancer. This makes LCN2 an attractive and potent target for therapeutic intervention, particularly in overcoming existing treatment limitations.
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) represents a powerful tool in gene therapy, capable of sequence-specific gene silencing. By harnessing the cell's natural RNA interference (RNAi) machinery, siRNA can effectively "switch off" the expression of disease-causing genes, such as LCN2. This precision offers a highly targeted therapeutic modality, avoiding the broad off-target effects often associated with conventional chemotherapy. However, the inherent instability of naked siRNA in biological fluids and its poor cellular uptake necessitate efficient and safe delivery systems.
Trastuzumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody, has revolutionized the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer, including IBC, by blocking HER2 signaling pathways. However, a significant clinical hurdle is the development of primary (intrinsic) or acquired (extrinsic) resistance to trastuzumab. HER2 receptor itself often remains highly expressed on the surface of these resistant cancer cells. It means that the targeting property of trastuzumab, its ability to specifically bind to HER2, can still be effectively leveraged. By conjugating therapeutic payloads, such as drug-loaded liposomes or other nanocarriers, with trastuzumab, we can achieve highly targeted delivery to HER2-positive IBC cells. This strategic use of trastuzumab as a precise targeting ligand, rather than solely a direct therapeutic agent, is crucial for developing advanced drug delivery systems that can overcome current treatment limitations by delivering alternative therapeutic agents directly to the resistant cells.
Liposomes, as advanced lipid-based nanoparticles, are ideally suited to overcome the inherent challenges associated with siRNA delivery. These spherical vesicles, composed of one or more lipid bilayers, offer numerous advantages:
Recent scientific literature, exemplified by the study "Dual-Targeting Strategy for the Treatment of Inflammatory Breast Cancer (IBC) by Ligand-Conjugated Liposomes Loaded with Trastuzumab and LCN2 siRNA" by Liu, published in Molecules, demonstrates the significant promise of targeted LCN2 siRNA liposomes for IBC treatment. This research showcases a sophisticated lipid-based delivery system designed to overcome the limitations of current therapies.
Researchers prepared dual-targeting liposomes using thin-film hydration. These liposomes, composed of DOPC, cholesterol, PEG2000-PE, and DSPE-PEG2000-Mal, were conjugated with trastuzumab via maleimide-thiol reaction. This ensured stable antibody attachment for active targeting, and the resulting nanoparticles were thoroughly characterized for optimal delivery properties.
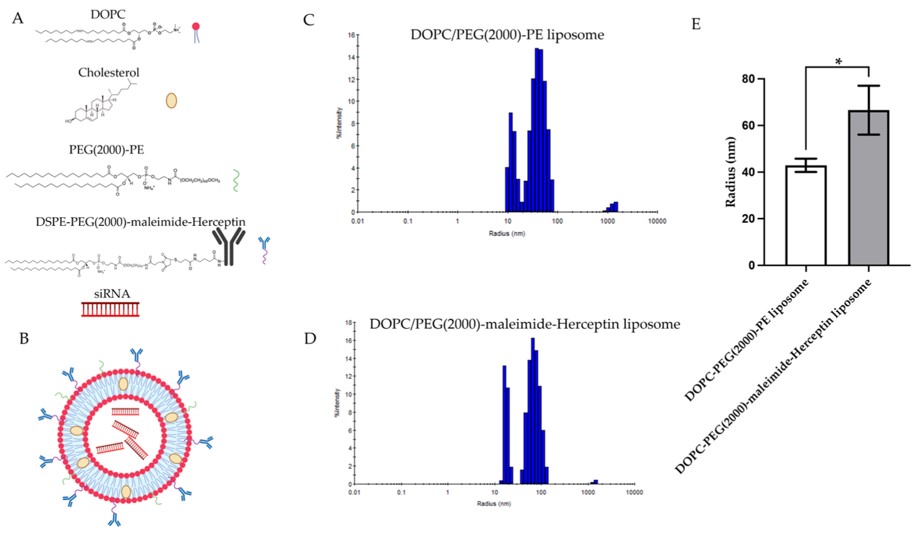 Fig. 1 Chemical composition, assembly, and DLS size distribution of liposomal formulations.1
Fig. 1 Chemical composition, assembly, and DLS size distribution of liposomal formulations.1
The trastuzumab conjugation significantly improved the uptake of the liposomal nanoparticles by HER2-overexpressing IBC cells, demonstrating effective active targeting. The study confirmed superior cellular uptake of trastuzumab-conjugated liposomes in HER2+ IBC cells. This efficient uptake is crucial for delivering siRNA to its intracellular target, validating the success of the active targeting strategy.
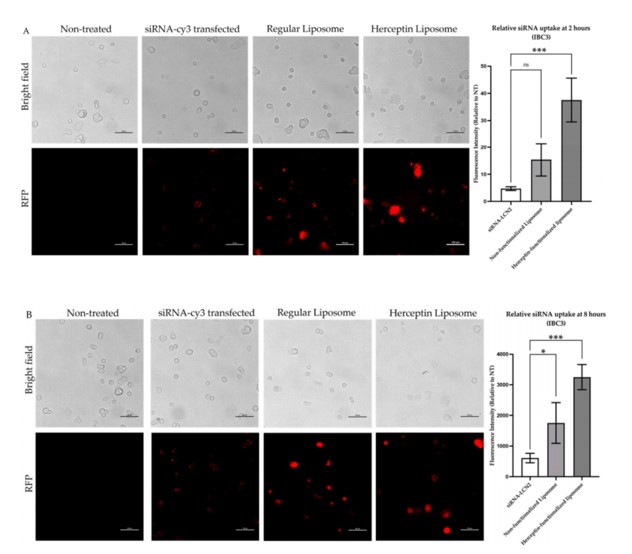 Fig. 2 Evaluation of siRNA-cy3 delivery for internalization efficiency.1
Fig. 2 Evaluation of siRNA-cy3 delivery for internalization efficiency.1
The LCN2 siRNA effectively suppressed LCN2 expression in IBC cells, confirming the successful delivery and functionality of the siRNA cargo.
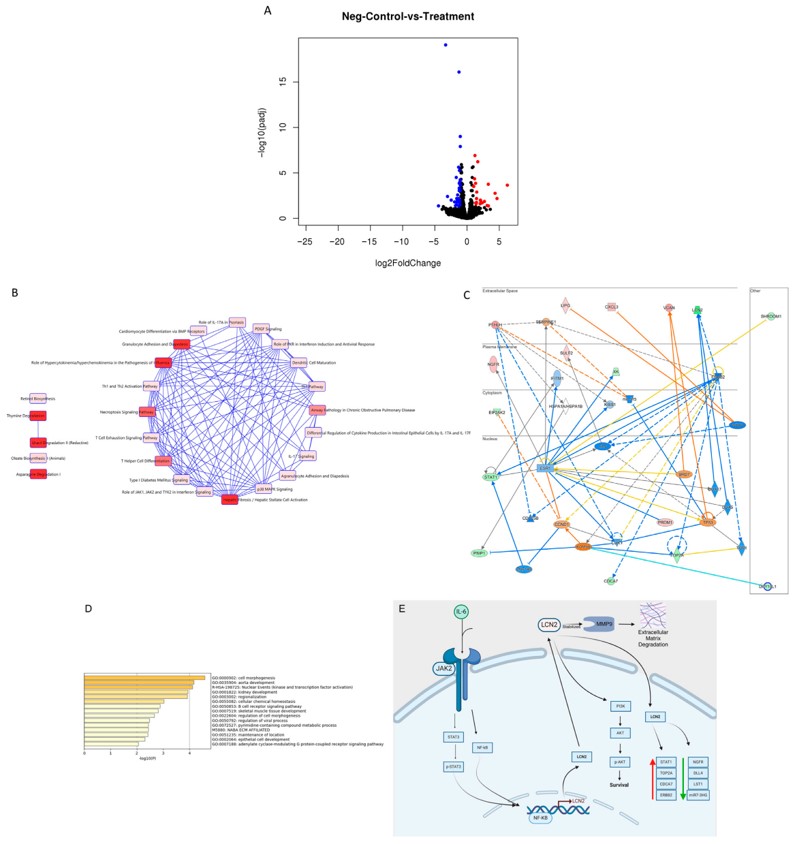 Fig. 3 Transcriptomic and pathway analysis of dysregulated genes following LCN2 knockdown in HER2+ MDA-IBC3 cells.1
Fig. 3 Transcriptomic and pathway analysis of dysregulated genes following LCN2 knockdown in HER2+ MDA-IBC3 cells.1
This research exemplifies how a well-designed, targeted lipid-based delivery system can synergistically combine different therapeutic modalities (antibody therapy and gene silencing) to achieve superior anti-cancer effects, particularly in challenging diseases like IBC.
Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of lipid-based drug delivery, offering unparalleled expertise in areas critical for advancing targeted therapies like LCN2 siRNA liposomes for IBC. Our comprehensive suite of services, from antibody and siRNA development to advanced liposome characterization and preclinical validation, positions us as your ideal partner in navigating the complexities of drug development. Contact us today to discuss how we can accelerate your next-generation drug delivery project.
At Creative Biolabs, we understand that translating groundbreaking scientific discoveries, such as targeted LCN2 siRNA liposomes for IBC treatment, from academic research to industrial application requires specialized expertise and comprehensive support. With over 20+ years of experience in lipid-based drug delivery systems, Creative Biolabs is uniquely positioned to bridge this gap for our clients.
| Service | Description | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|
| Antibody Development | From discovery to production, we offer services for developing high-affinity antibodies crucial for targeted therapies. | Inquiry |
| siRNA Synthesis | We provide custom siRNA synthesis services, ensuring high purity and quality for your gene silencing applications. | Inquiry |
| Antibody-Conjugated Liposome Development | Leveraging our deep understanding of lipid chemistry and nanoparticle engineering, we design, optimize, and thoroughly characterize antibody-conjugated liposomal formulations for efficient siRNA encapsulation, precise ligand conjugation, and optimal stability. | Inquiry |
| Advanced Characterization | We provide state-of-the-art analytical services for thorough characterization of your lipid nanoparticles, including particle size distribution, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, drug loading, release kinetics, and surface ligand density. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of your formulation's physicochemical properties. | Inquiry |
| Preclinical Validation Support | Our expertise extends to supporting preclinical validation, including in vitro studies (cellular uptake, gene silencing efficiency, cytotoxicity assays) and in vivo efficacy and safety assessments, crucial for demonstrating the therapeutic potential of your targeted delivery system. | Inquiry |
| Scale-Up & Manufacturing Guidance | We assist clients in navigating the complexities of scaling up production from laboratory to industrial scale, ensuring manufacturing consistency and compliance with regulatory standards. | Inquiry |
We are continuously expanding our services and products to meet the evolving needs of advanced drug delivery.
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry