The development of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) as mRNA therapeutics has revolutionized medicine, yet their current applications are often limited by the challenge of achieving tissue-specific delivery. A critical hurdle lies in targeting the lungs to treat a wide range of diseases, from genetic disorders to cancer, while avoiding off-target accumulation. At Creative Biolabs, we believe that high-throughput screening is the key to overcoming this obstacle and unlocking the full potential of mRNA-based therapies. Our expertise in lipid-based drug delivery systems enables us to provide the research ideas and solutions that accelerate your path to discovery.
The lung is a prime target for inhaled therapeutics due to its large, accessible surface area, offering new hope for diseases ranging from genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis to lung cancer. However, its unique physiology presents significant delivery challenges.
The lung's natural defenses—including a protective mucus layer and rapid mucociliary clearance—actively prevent nanoparticles from reaching their target. Adding to this complexity, standard intravenous LNP delivery often fails, as nanoparticles are quickly diverted to the liver and spleen by a protein corona that forms upon entering the bloodstream.
Effective lung-targeted therapy, therefore, demands a new class of LNPs specifically designed to evade these barriers. Success depends on creating formulations that are not only stable and biocompatible but are also optimized for deep lung penetration and efficient intracellular delivery.
Developing LNPs with specific organ tropism requires the systematic evaluation of vast libraries of lipid compounds. This is where high-throughput screening becomes indispensable. This technology allows researchers to simultaneously evaluate the in vivo delivery profile of hundreds of distinct LNP formulations.
This approach provides several critical advantages:
The research published in Nature Communications offers a clear roadmap for achieving lung tropism. The study's innovative methodology provides critical insights into the entire discovery process, from library design to therapeutic validation.
The study began with the combinatorial synthesis of a large library of 180 cationic, degradable lipid-like materials. This approach enabled the creation of a vast chemical space for exploration, allowing researchers to systematically test how subtle changes in lipid structure impact LNP performance. This initial step is crucial for generating a diverse and relevant pool of candidates for subsequent screening.
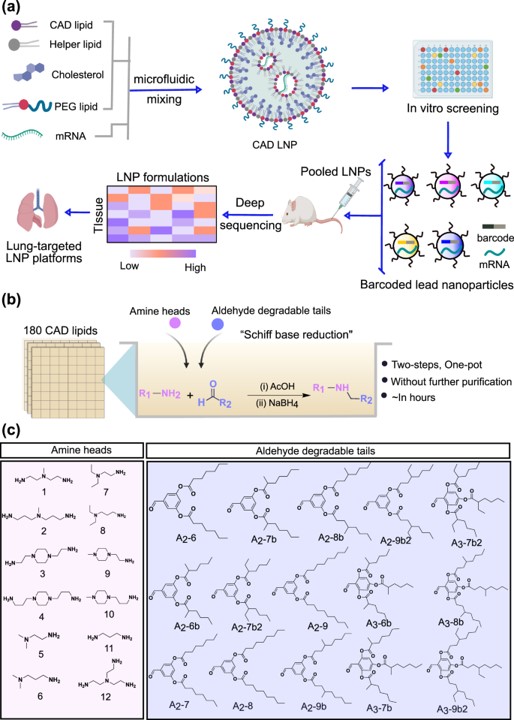 Fig. 1 High-throughput LNP screening. 1
Fig. 1 High-throughput LNP screening. 1
After an initial in vitro screen, the top 96 LNPs were each tagged with a unique DNA barcode. This allowed researchers to pool the formulations and administer them to a small cohort of mice, enabling the simultaneous quantification of LNP accumulation in the lungs and other organs. This barcoding technology dramatically accelerated the identification of LNPs with the desired lung tropism.
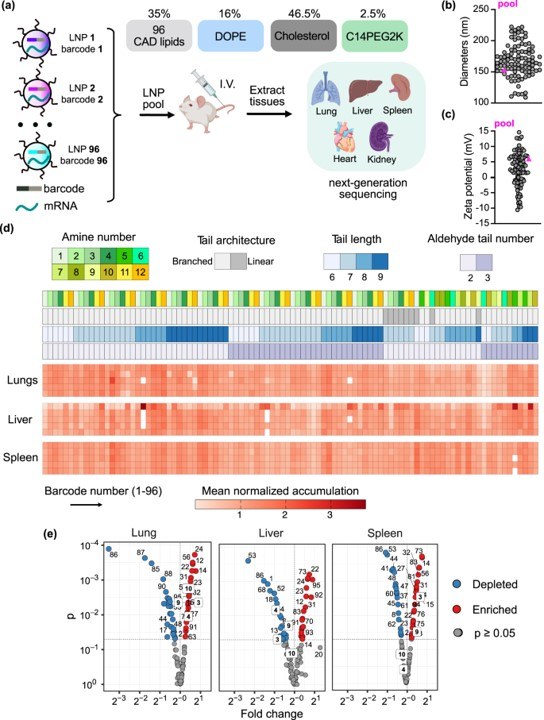 Fig. 2 Understanding CAD lipid structure and organ tropism relationships in vivo. 1
Fig. 2 Understanding CAD lipid structure and organ tropism relationships in vivo. 1
The research concluded by validating the therapeutic potential of the top-performing LNP. This formulation was used to deliver Cas9-based genetic editors, which exhibited a therapeutic effect in a lung tumor model in female mice. This critical step demonstrated that the newly identified LNP was not only capable of reaching the lungs but also of delivering a functional therapeutic payload.
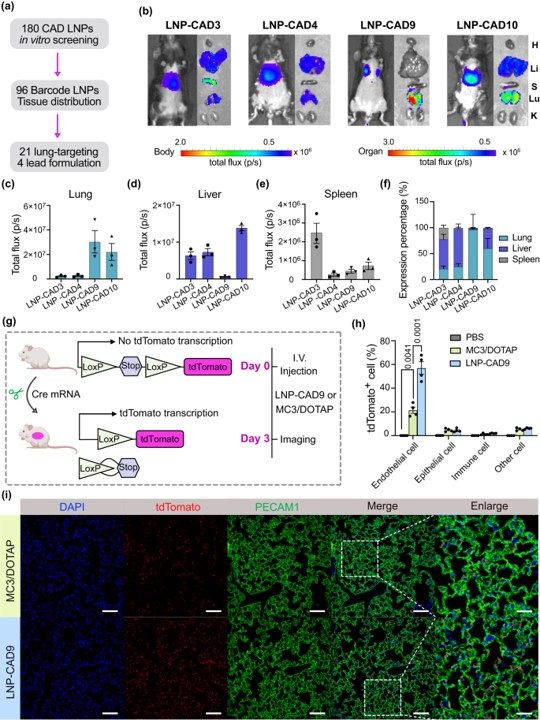 Fig. 3 Validation of top performing LNPs for mRNA delivery to the lungs. 1
Fig. 3 Validation of top performing LNPs for mRNA delivery to the lungs. 1
This groundbreaking research highlights the power of combining innovative screening techniques with a deep understanding of lipid chemistry to address complex delivery challenges. The ability to efficiently screen large libraries of LNPs in vivo is transforming the discovery process, paving the way for next-generation therapeutics. Contact our team to learn how we can apply these and other insights to accelerate your research.
Creative Biolabs offers a suite of specialized services to support your high-throughput screening and lipid-based drug delivery projects. Our expert team is equipped to address the complex challenges of LNP development for mRNA therapeutics for a wide range of applications.
| Services/Products | Description | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|
| Lipid Synthesis | Custom synthesis of novel cationic, degradable lipid libraries for your unique LNP formulation needs. | Inquiry |
| LNP Development | Expert formulation and optimization of liposomes and LNPs to achieve desired characteristics and delivery. | Inquiry |
| LNP Characterization | Comprehensive analysis of physicochemical properties, including size, PDI, zeta potential, and drug loading. | Inquiry |
| High-Throughput Screening | Rapid, parallel in vitro and in vivo screening of LNP libraries to identify top-performing candidates. | Inquiry |
| Process Optimization | Refinement of manufacturing protocols for scalability and reproducibility. | Inquiry |
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry