Creating highly effective vaccines requires more than just a potent antigen; it demands a sophisticated approach to immune modulation. The use of adjuvants to enhance vaccine-induced immune responses presents a significant challenge, as traditional methods often fall short of eliciting a comprehensive, high-quality response. Lipid-based drug delivery systems offer a promising solution, enabling precise control over how the immune system interacts with a vaccine. At Creative Biolabs, we provide the specialized knowledge and services to help our clients pioneer innovative research in this crucial area, turning scientific breakthroughs into practical applications.
The efficacy of a vaccine hinges on its adjuvant, which is engineered to direct the nature and potency of the immune response. Adjuvants function by creating a targeted microenvironment that promotes efficient antigen processing and presentation by immune cells. This mechanism enables the deliberate programming of either a humoral or cellular response, making the adjuvant selection a critical parameter in defining a vaccine's overall protective profile.
Vaccine efficacy is no longer defined by neutralizing antibody quantity alone. While a critical first line of defense, a truly robust immune response depends on the functional quality of those antibodies and their ability to synergize with the entire immune system. This evolving understanding is driving innovation beyond conventional adjuvants, such as aluminum hydroxide. Proven for their safety in eliciting basic antibody responses, these traditional options often fall short when the goal is a more sophisticated, multifaceted immunity required for next-generation vaccines.
Liposomes are microscopic vesicles composed of one or more lipid bilayers. Their unique structure makes them an ideal platform for vaccine delivery and immune modulation. They can encapsulate antigens, protect them from degradation, and present them in a highly organized manner to immune cells. This controlled presentation mimics the way pathogens naturally interact with the immune system, leading to a more potent and specific response.
The superior performance observed with liposome-based adjuvants (ILA) is not accidental. The physical and chemical properties of liposomes—including their size, surface charge, and lipid composition—can be precisely tuned to influence how they are taken up by antigen-presenting cells, thereby dictating the type of immune response that is generated. The ability to co-encapsulate both an antigen and an immune-stimulating molecule within the same nanoparticle further enhances this effect, providing a powerful synergy that a simple, soluble adjuvant cannot match.
A recent study directly compared the immune responses generated by a novel ILA to the traditional aluminum hydroxide (alum) adjuvant. By administering a SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein formulated with each adjuvant to mice, the researchers were able to conduct a systems serology analysis to gain a comprehensive understanding of the humoral immune profiles. This efficacy analysis of the two different adjuvants and their resulting vaccine performance revealed several key findings:
The study found no significant differences in the overall levels of antigen-specific total IgG or neutralizing antibody titers between the ILA and alum groups. This highlights that traditional metrics, while important, may not tell the whole story about an adjuvant's effectiveness.
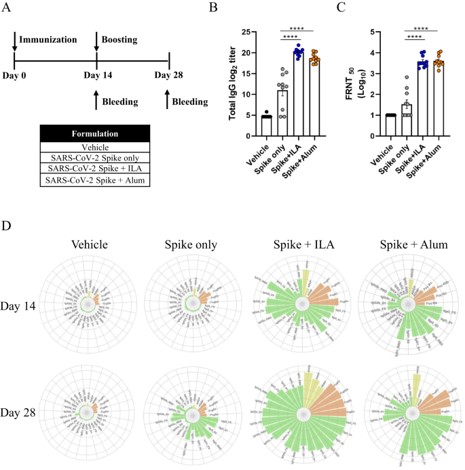 Fig. 1 Humoral immune responses induced by the adjuvants.1
Fig. 1 Humoral immune responses induced by the adjuvants.1
A deeper analysis revealed a key difference in the quality of the antibodies produced. The ILA-adjuvanted group exhibited a broader spectrum of humoral immune responses, with significantly higher levels of the potent IgG2a, IgG2b, and IgG3 antibody subclasses compared to the alum group. This shift in the subclass profile is indicative of a more robust and effective immune activation.
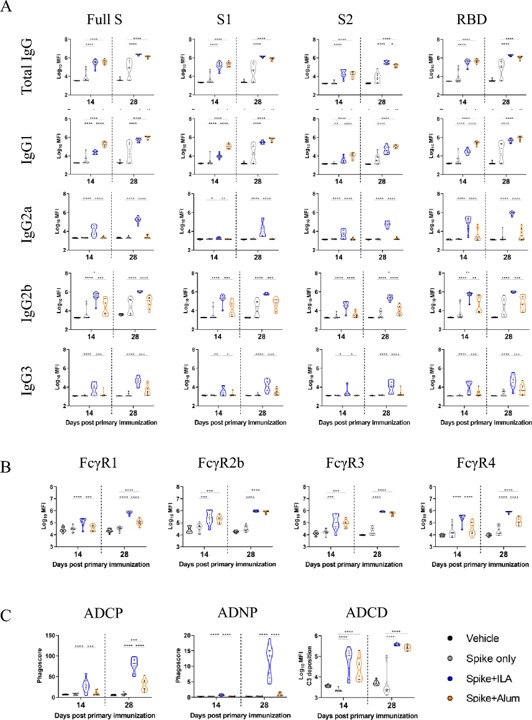 Fig. 2 Univariate analysis of functional antibody responses induced by the adjuvants.1
Fig. 2 Univariate analysis of functional antibody responses induced by the adjuvants.1
The ILA-induced antibodies also showed a significantly higher ability to bind to Fcγ receptors (FcγR1and FcγR4) on immune cells. This superior binding capacity is critical, as it is the prerequisite for initiating Fc-mediated effector functions, which are essential for clearing pathogens and infected cells.
The study went beyond simple binding and measured functional outcomes. It was demonstrated that Fc-mediated effector functions, such as antibody-mediated monocyte and neutrophil phagocytosis, were significantly more active in the ILA-adjuvanted group. This finding provides direct evidence that the liposome-based adjuvant generates a qualitatively superior, more effective immune response that is better equipped to fight infection.
In summary, this research confirms that modern lipid-based adjuvants like ILA offer a distinct advantage over traditional methods by inducing a superior, functionally robust immune response. This finding is a testament to the power of advanced delivery systems in vaccine development. Creative Biolabs has the expertise and resources to help you apply these principles to your own projects. Contact us today to discuss how our services can help you design, characterize, and validate the next generation of vaccines.
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive suite of specialized services to support the development of next-generation vaccine adjuvants and the efficacy analysis of vaccines, adjuvants, and liposome adjuvants. Leveraging our deep expertise in lipid-based drug delivery systems, we guide our clients through every stage of their project, from initial design to final validation. Our services are tailored to address the unique complexities of liposome-based adjuvants, ensuring a path to success.
| Services/Products | Description | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|
| Vaccine Formulation & Development | Comprehensive design and development of vaccine formulations using liposome-based systems. | Inquiry |
| Immune Response Profiling | Advanced analysis of humoral and cellular immune responses to evaluate vaccine efficacy. | Inquiry |
| In Vitro Efficacy Testing | Assays to measure immune cell activation, cytokine production, and antibody-mediated functions. | Inquiry |
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry