The true therapeutic potential of CRISPR gene editing hinges on solving a critical challenge: delivering it safely and effectively within the body. While viral vectors have long been the standard, their drawbacks—including immunogenicity and manufacturing constraints—demand a more advanced solution. As a pioneer in lipid-based delivery, Creative Biolabs is leading this charge. We provide comprehensive platforms and expert partnerships to accelerate your lipid nanoparticle (LNP) research and development, helping you transform complex scientific concepts into viable, life-changing therapies.
CRISPR-Cas9 is a groundbreaking gene-editing technology that acts as a pair of molecular scissors, allowing for precise modif ications to the genome. The system typically consists of two key components: the Cas9 endonuclease and a guide RNA (gRNA) that directs the Cas9 enzyme to a specific DNA sequence. By introducing these components into a cell, researchers can correct disease-causing mutations, knock out pathogenic genes, or insert therapeutic sequences.
However, the size and delicate nature of the CRISPR components—especially the Cas9 enzyme or its mRNA—make them difficult to deliver into cells on their own. This is where lipid nanoparticles excel. As a sophisticated drug carrier, an LNP is a sphere composed of lipids that can encapsulate a wide range of nucleic acids, protecting them from degradation and facilitating their entry into the cell's cytoplasm. The LNP's structure, typically composed of an ionizable lipid, a phospholipid, cholesterol, and a PEGylated lipid, is meticulously designed to balance stability and effective delivery.
The LNP-CRISPR combination offers several key advantages over viral vectors, including reduced immunogenicity, a transient delivery profile that lowers the risk of off-target effects, and a more streamlined, cost-effective manufacturing process.
The path to clinical application for LNP therapies involves overcoming several key challenges:
The groundbreaking research detailed in the scientific literature provides a clear roadmap for advancing the field. By methodically engineering and testing new components, the study provides compelling evidence for the potential of LNP-mediated gene editing.
Researchers successfully engineered a thermostable Cas9 protein from the bacterium Geobacillus stearothermophilus (GeoCas9) to create iGeoCas9 variants. These optimized variants were shown to enable more than 100× the genome editing of cells and organs compared to the native enzyme, demonstrating a significant leap in efficiency.
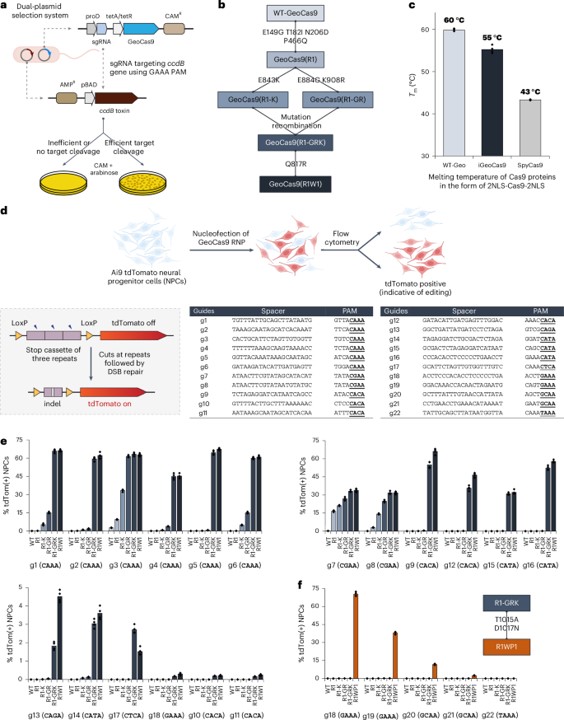 Fig. 1 Directed evolution improves GeoCas9's editing efficiency. 1
Fig. 1 Directed evolution improves GeoCas9's editing efficiency. 1
The iGeoCas9 ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes were shown to be effective across a variety of cell types. The complexes also successfully induced homology-directed repair, a form of precise gene correction, in cells that were co-delivered single-stranded DNA templates, confirming a broader range of applications.
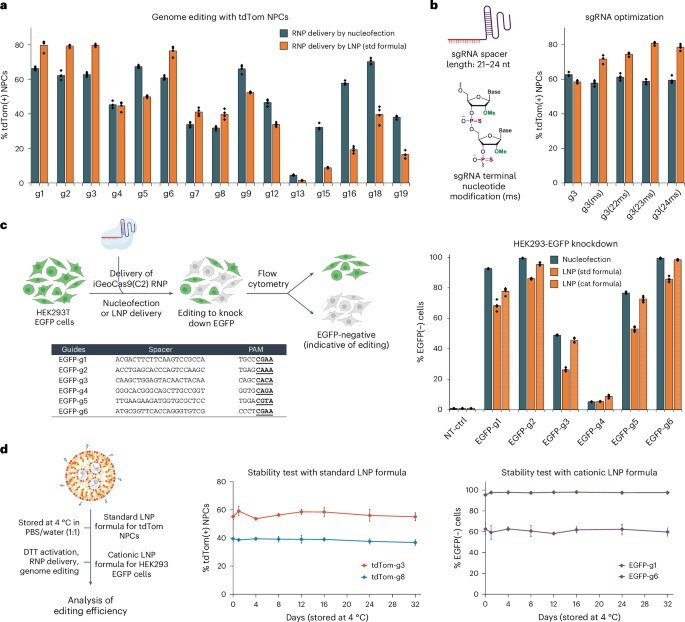 Fig. 2 iGeoCas9 RNP formulated in LNPs edits cells in vitro. 1
Fig. 2 iGeoCas9 RNP formulated in LNPs edits cells in vitro. 1
Using specially designed, tissue-selective LNP formulations, the study achieved significant in vivo results. Reporter mice receiving a single intravenous injection of iGeoCas9 RNPs demonstrated remarkable genome-editing levels of 16% to 37% in both the liver and the lungs, a major achievement in targeted delivery.
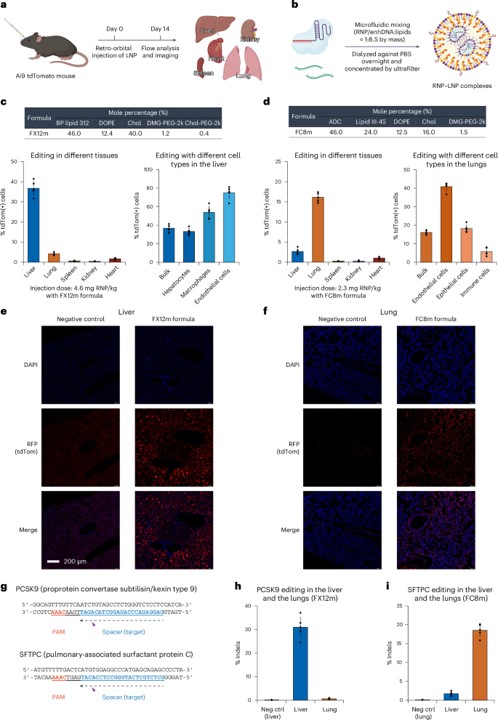 Fig. 3 iGeoCas9 RNP–LNP complexes edit organs efficiently in vivo. 1
Fig. 3 iGeoCas9 RNP–LNP complexes edit organs efficiently in vivo. 1
The research discussed above demonstrates that innovation at the molecular level, combined with advanced delivery systems, can unlock the full potential of gene-editing therapeutics. This is a complex process requiring a deep understanding of both the therapeutic payload and its LNP carrier. We encourage you to contact Creative Biolabs' team of experts to discuss how these research findings can be translated into a successful, large-scale commercial application for your specific therapeutic needs.
At Creative Biolabs, we provide a comprehensive suite of products and services to help you accelerate your research and development in lipid-based drug delivery. Our offerings are designed to address the challenges and opportunities presented by advanced delivery systems like LNDs.
| Services/Products | Description | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|
| Plasmid Construction | High-quality vector design and synthesis for producing therapeutic DNA, including Cas9-encoding plasmids and donor templates for gene correction. | Inquiry |
| Nucleic Acid Preparation | End-to-end services for the synthesis, purification, and quality control of therapeutic nucleic acids, such as mRNA and guide RNA, for LNP encapsulation. | Inquiry |
| Lipid Synthesis | Custom synthesis of novel and proprietary lipids, including ionizable lipids, to create next-generation LNP formulations with enhanced targeting and stability. | Inquiry |
| Gene Editing LNP Development | Comprehensive services for the rational design, formulation, and optimization of LNP systems tailored for specific gene-editing payloads. | Inquiry |
| Characterization | Advanced analytical services for the thorough characterization of LNP formulations, including dynamic light scattering (DLS) for size and zeta potential, and cryo-transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM) for morphology. | Inquiry |
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry