In the complex landscape of pharmaceutical development, achieving optimal drug bioavailability is paramount for therapeutic success. Many promising drug candidates face significant hurdles that limit their effectiveness in the body. At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in overcoming these challenges through cutting-edge lipid-based drug delivery systems. Our expertise in liposomal formulations allows us to significantly enhance drug bioavailability, ensuring maximum efficacy and therapeutic impact.
Drug bioavailability – the fraction of an administered drug that reaches systemic circulation in its original form – is a critical determinant of pharmacotherapeutic success. A drug's therapeutic impact is profoundly shaped by its bioavailability; higher levels typically translate to greater drug concentration at the target site, enhancing the intended effect.
However, many promising drug candidates face significant hurdles that limit their bioavailability. Common challenges include:
Overcoming these challenges is paramount for translating a potent molecule into a clinically viable therapeutic agent.
Within the exciting fields of nanotechnology and lipid-based drug delivery, liposomes really shine as incredibly versatile carriers. They offer a potent way to tackle the tricky issue of low bioavailability, essentially by acting like tiny protective bubbles that can safely encase both 'water-loving' (hydrophilic) and 'water-fearing' (hydrophobic) drugs. The ways they boost bioavailability are quite complex and varied, involving several key mechanisms, which include:
Recent scientific literature consistently highlights the transformative potential of liposomes in overcoming bioavailability limitations. A compelling example is the research on Jaspine B (JB), a natural product with promising anticancer activity but hindered by its poor water solubility and low oral bioavailability. A study published in Pharmaceuticals meticulously investigated the "Preparation, Characterization, and Pharmacokinetics of Jaspine B Liposomes". This research serves as a clear illustration of how liposomal encapsulation can dramatically improve a drug's pharmacokinetic profile and, consequently, its bioavailability.
Jaspine B was successfully encapsulated into liposomes with optimized characteristics, including appropriate particle size (around 100 nm), low polydispersity index (PDI), and high encapsulation efficiency. Accurate prediction of in vivo performance relies on these characterization parameters.
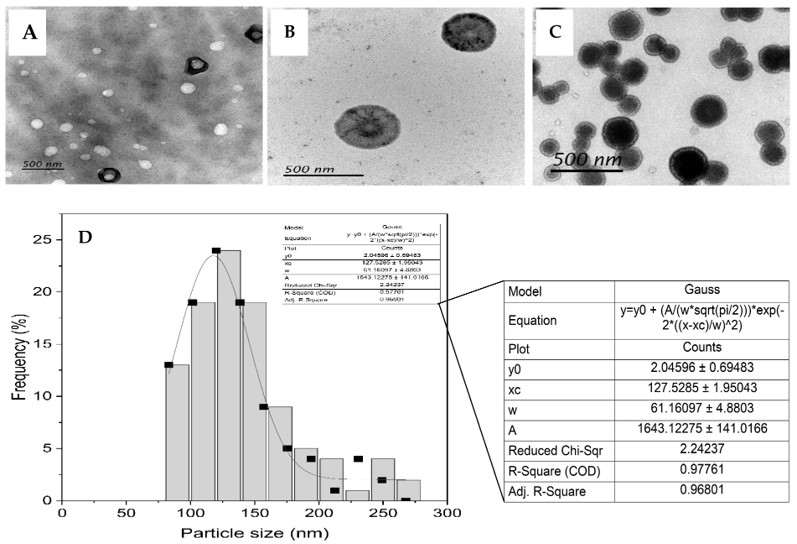 Fig. 1 Variable magnification TEM images of Jaspine B liposomes.1
Fig. 1 Variable magnification TEM images of Jaspine B liposomes.1
Utilizing a validated LC-MS/MS method ensured the precise and reliable quantification of Jaspine B in rat plasma. This analytical rigor was paramount, providing the accurate concentration data necessary to construct robust pharmacokinetic profiles. Such dependable measurements are indispensable for conclusively demonstrating the improved systemic exposure and enhanced bioavailability achieved by liposomes.
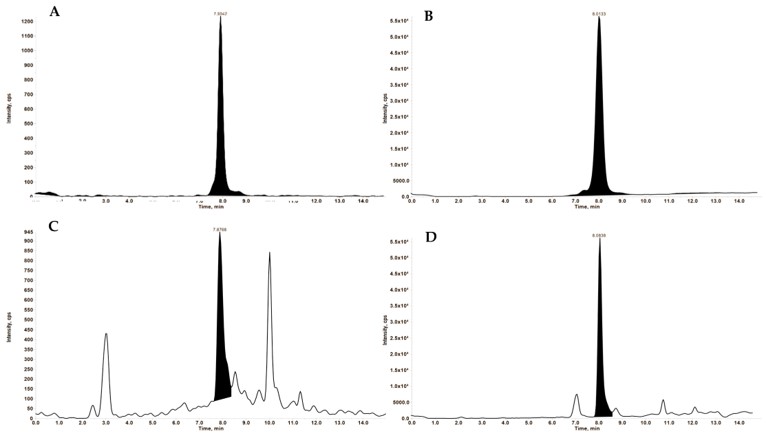 Fig. 2 Representative extracted ion chromatograms (XIC).1
Fig. 2 Representative extracted ion chromatograms (XIC).1
Pharmacokinetic data definitively confirms enhanced bioavailability. The significant increase in AUC0-t for liposome signifies significantly greater systemic drug exposure. The prolongation of half-life (t1/2) and mean residence time (MRT) demonstrates extended retention time and circulation time, directly leading to sustained blood drug concentration and enhanced efficacy.
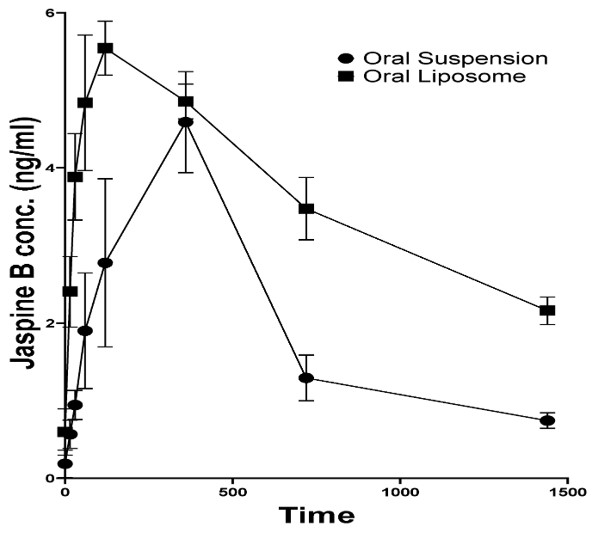 Fig. 3 Plasma concentration-time profile of Jaspine B in rats.1
Fig. 3 Plasma concentration-time profile of Jaspine B in rats.1
| Formulation | Tmax (h) | Cmax (ng/mL) | t1/2 (h) | AUC0-t (ng.h/mL) | MRT (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JB-Suspension | 6.0 ± 0.02 | 4.6 ± 1.1 | 7.9 ± 2.3 | 48.0 ± 12.8 | 12.9 ± 3.7 |
| JB-Liposome | 2.0 ± 0.02 | 5.5 ± 0.6 | 26. 7 ± 7.3 | 88.2 ± 3.9 | 39. ± 9.7 |
| p value | <0.0001 | 0.2840 | 0.0370 | 0.0303 | 0.0202 |
| p < 0.05 considered statistically significant. | |||||
This research exemplifies how liposomes can prolong the retention time and circulation time of the drug in the body, overcome the challenges of oral medication (by enabling effective delivery for a poorly soluble compound), and ultimately enhance the efficacy of therapeutic agents by improving their systemic exposure.
Creative Biolabs, with its expertise in lipid-based drug delivery systems, offers advanced solutions to significantly enhance drug bioavailability. By leveraging innovative liposomal formulations, we can overcome common challenges like poor solubility and degradation, particularly for oral drugs, thereby maximizing their therapeutic efficacy and prolonging their presence in the body. To learn more about how Creative Biolabs can help you improve drug bioavailability and accelerate your development, please do not hesitate to contact us.
At Creative Biolabs, we offer a seamless, one-stop service continuum designed to address your most pressing bioavailability challenges. From initial compound synthesis and precise encapsulation into advanced lipid-based drug delivery systems like liposomes, all the way through comprehensive preclinical evaluation, we are equipped to guide your project to success. Our integrated approach ensures that your drug candidates achieve optimal bioavailability, maximizing their therapeutic potential and streamlining your development pathway.
| Services | Description | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|
| Compound Synthesis | Tailored synthesis of your active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) to meet specific purity and quantity requirements for drug delivery applications. | Inquiry |
| Liposome Formulation Development | Expert design and optimization of liposomes for diverse drug candidates, including those with poor solubility (e.g., like Jaspine B), to overcome the challenges of oral medication and improve systemic delivery. | Inquiry |
| Advanced Characterization | Full suite of analytical techniques for precise characterization of liposomes, including particle size analysis, zeta potential measurement, encapsulation efficiency determination, and in vitro release studies, crucial for predicting in vivo performance | Inquiry |
| Pharmacokinetic (PK) Studies Support | Expert guidance in designing and interpreting pharmacokinetic studies, including assessment of blood drug concentration and half-life, to understand the in vivo performance of your liposomal formulations. This helps to prolong the retention time and circulation time of the drug in the body and ultimately enhance the efficacy. | Inquiry |
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry