We begin with a detailed discussion to understand your specific research goals, sample types, and desired outcomes. This ensures a customized analytical strategy.
-
Services
- Custom Synthesis
- Therapeutic Glycoprotein Development
- Glycan & Glycoprotein Structure & Profiling
- Glycoprotein Detection
- Glycoprotein Structure Analysis
- Glycoprotein Quantification
- High-Throughput Glycan Screening
- Glycosylation Analysis for Virus Glyoprotein
- Antibody Glycoprofiling
- Serum Glycoprofiling
- Plasma Glycoprofiling
- Tumor Tissue Glycoprofiling
- Tumor Cell Line Glycoprofiling
- Urine Glycoprofiling
- Quantitative Sialic Acid Analysis
- Quantitative Monosaccharaide Analysis
- Sugar Nucleotide Analysis
- Glycosaminoglycan Analysis
- Glycosylation Analysis in Diseases
- Glycoengineering
- Carbohydrate Analysis
- Glycan Modification & Labeling
- Glycoconjugation
- Glycoprotein Conjugation
- GFP Binding Protein Glycoconjugation
- Antibody Glycoconjugation
- Growth Factor Glycoconjugation
- GlcNAc-type Glycoprotein Conjugation
- LacNAc-type Glycoprotein Conjugation
- LacNAc-Sia-type Glycoprotein Conjugation
- Aldehyde Reaction based Glycoprotein Conjugation
- Azide Reaction based Glycoprotein Conjugation
- Glycoprotein Conjugation
- Bioactive Carbohydrates Screening
- Tumor Glyco-diag
- Anti-Carbohydrate Antigen Antibody Development
- Anti-Tumor-associated Glycan Antibody Development
- Anti-Tumor-associated Glycoprotein Antibody Development
- Anti-Tumor-associated Glycolipid Antibody Development
- Anti-Sialic Acid Antibody Development
- Anti-Poly-Sialic Acid Antibody Development
- Anti-Lewis Antigen Antibody Development
- Anti-Blood Group Antibody Development
- Anti-Viral Glycan Antibody Development
- Anti-Bacterial Glycan Antibody Development
- Anti-Fungal Glycan Antibody Development
- Anti-Plant & Algal Glycan Antibody Development
- Anti-Proteoglycan Antibody Development
- Anti-Glycan related Enzyme Antibody Development
- Anti-Glycosaminoglycan Antibody Development
- Glyco-based Vaccine Development
- Glycoproteomics-based Liquid-biopsy LDT Development
- Glyan-related Enzyme Activity Analysis
- Biomass Enzyme Degradation Efficiency Analysis
- Enzymatic Decomposition Reaction-based Residue Content Analysis
- Enzymatic Decomposition Reaction-based Fermentation Inhibitors Analysis
- Enzyme-Mediated Saccharification Efficiency Analysis
- Cellulase Activity Assessment
- Cellulolytic Enzyme Activity Assessment
- Amylolytic Enzyme Activity Assessment
- Sucrase Activity Assessment
- Biomass Components Quantitative Profiling
- Lignocellulose Quantitative Profiling
- In-process Chemical Composition Analysis
- Plant Chemistry Profiling
- Seaweed Multi-component Quantitative Profiling
- Seaweed Simple Sugar Quantitative Profiling
- Amino Acid Composition Profiling
- Aflatoxin Profiling
- Seaweed Elemental Quantitative Analysis
- Seaweed Multi-element Simultaneous Profiling
- Fatty Acid Composition Analysis
- Pigment Quantitative Analysis
- Seaweed Plant Hormones Determination
- Seaweed Vitamers Quantitative Analysis
- Total Phenolics Analysis
- Phenolic Composition Analysis
- Seaweed Tannin Qualitative & Quantitative Profiling
- Alginate Molecular Size Analysis
- Seaweed Total Phlorotannins Content Analysis
- Seaweed Bromoform Content Analysis
- Algae Multi-Component Quantitative Profiling
- Biogas Fermentation Process-based Quantitative Profiling
- BMP Assessment
- Biological & Chemical Analysis
- Chemical Oxygen Demand Detection
- Biological Oxygen Demand Detection
- VFA Profiling
- Digestate Solid Impurities Determination
- Ammoniacal Nitrogen Profiling
- Nitrates Profiling
- Viable Weed Seed Analysis
- Organic Matter Profiling
- SHA Determination
- SAdA Determination
- SMA Determination
- Microbiological Activity Assessment
- FOS/TAC Ratio Analysis
- Sludge Granule Size Analysis
- Sludge Activity Analysis
- Toxicity Assessment in Microbial Digestion Processes
- Persistent Digestion Process Profiling
- Bio-Oil Components Profiling
- Biochar Manufacturing & Characterization
- Biomass Combustion Property Profiling
- Biomass Physical Property Characterization
- Polyamine Quantitative Profiling
- Polyphenol Quantitative Profiling
- Terpene Quantitative Profiling
- Energy Metabolite Analysis
- Nutrition & Metabolism Research based Compound Analysis
- Organic Acid Quantitative Analysis
- Bile Acid Quantitative Analysis
- Arachidonic Acid Quantitative Analysis
- Carotenoid Quantitative Analysis
- Catechin Quantitative Analysis
- Anthocyanin Quantitative Analysis
- Biogenic Amine Quantitative Analysis
- Alkaloid Quantitative Analysis
- Flavonoid Quantitative Analysis
- Neurotransmitter Quantitative Analysis
- TMAO Quantitative Analysis
- Soil Analysis
- Glycoproteomics Quantitative Analysis
- One-Stop Glycan Crystal & Glycoprotein Crystal Analysis
-
Products
- Glycopeptides
- Glycoproteins
- Monosaccharides
- Oligosaccharides
- Polysaccharides
- Carbohydrate-based Surfactants
- Blood Group Antigens
- Glycoprotein Assay Kits
- Glycoprotein Reagents
- Glycoengineered Cells
- Glycoengineering Viral Particles
- Nucleotide Sugars
- Glycolipids
- Glycan Libraries
- N-Glycan Libraries
- O-Glycan Libraries
- HMO-Glycan Libraries
- Mannose Glycan Libraries
- Lacto Glycan Libraries
- Tandem Repeat Epitope Glycan Libraries
- Blood Group Antigen Libraries
- Glycosaminoglycan Libraries
- Methylated Glycan Libraries
- Sulfated Glycan Libraries
- Tag based Glycan Libraries
- Monoclonal Antibody Glycan Libraries
- Technologies
- Resources
- Company

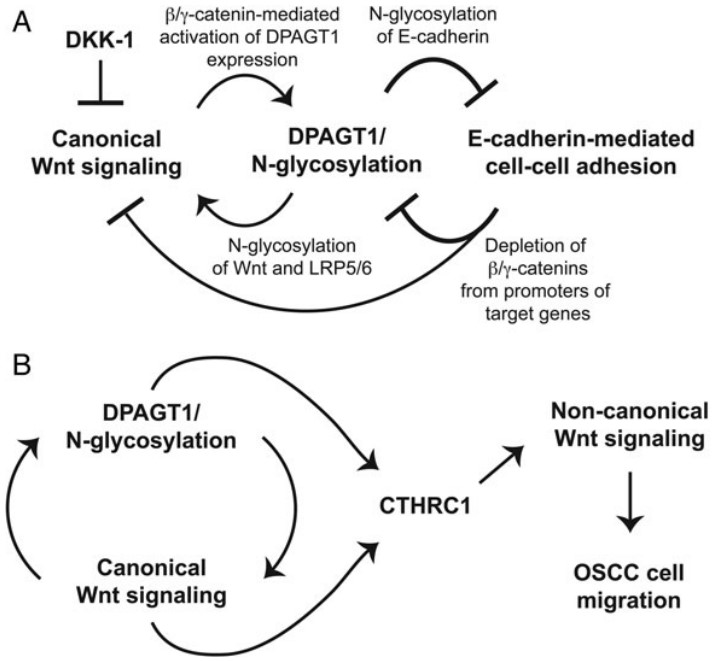 Fig.1 DPAGT1/Wnt/E-cadherin network of the control group and oral cancer group.1
Fig.1 DPAGT1/Wnt/E-cadherin network of the control group and oral cancer group.1
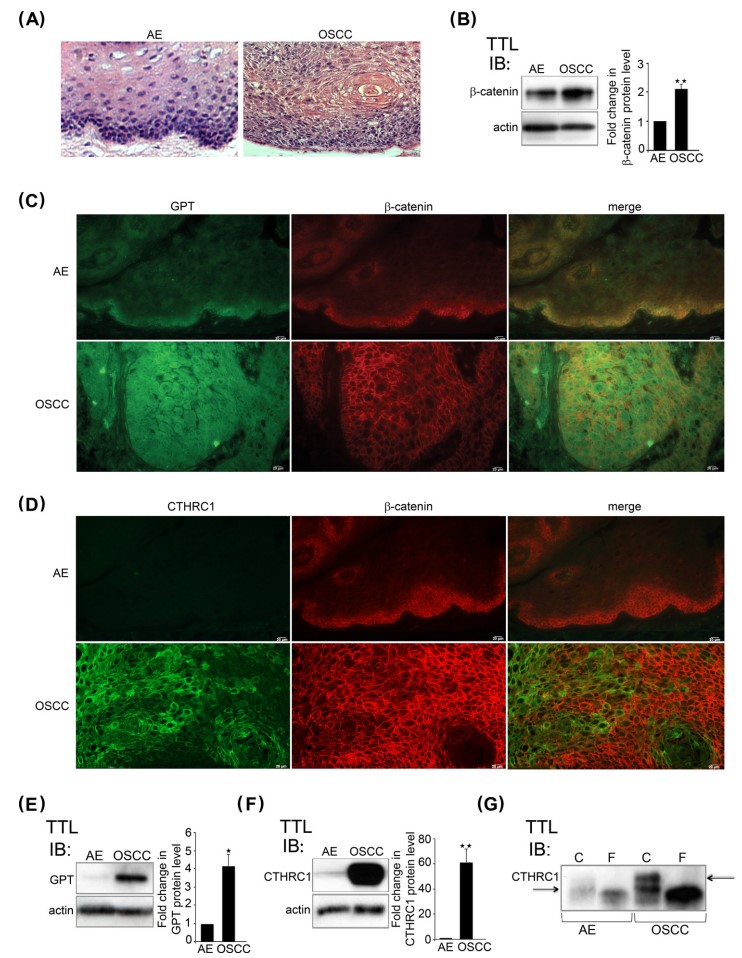 Fig.2 Expression results of β-catenin, GPT, and CTHRC1 in OSCC.2
Fig.2 Expression results of β-catenin, GPT, and CTHRC1 in OSCC.2

