Why Glycosylation Analysis in Lung Disease is Essential?
Glycosylation Analysis in lung disease research is essential because glycans are highly dynamic and sensitive indicators of physiological and pathological states. They are involved in critical processes like cell-cell communication, immune regulation, and inflammatory responses. Alterations in glycosylation patterns can serve as highly specific and sensitive biomarkers for early disease detection, progression monitoring, and predicting therapeutic response. It often reflects changes not captured by traditional protein or genetic analyses. This makes them invaluable for deciphering complex disease mechanisms and developing precision medicine approaches for conditions such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), lung cancer, and interstitial lung diseases. Our lung disease research-related glycosylation analysis service helps you accelerate biomarker discovery, elucidate disease mechanisms, and streamline therapeutic development for lung diseases through advanced mass spectrometry-based glycoprofiling and innovative bioinformatic analysis. We provide precise quantitative glycan profiles, rigorously identified glycoprotein biomarker candidates, and actionable data for therapeutic target identification. Our service is designed to accelerate your understanding of lung disease pathology and inform your strategic development decisions.
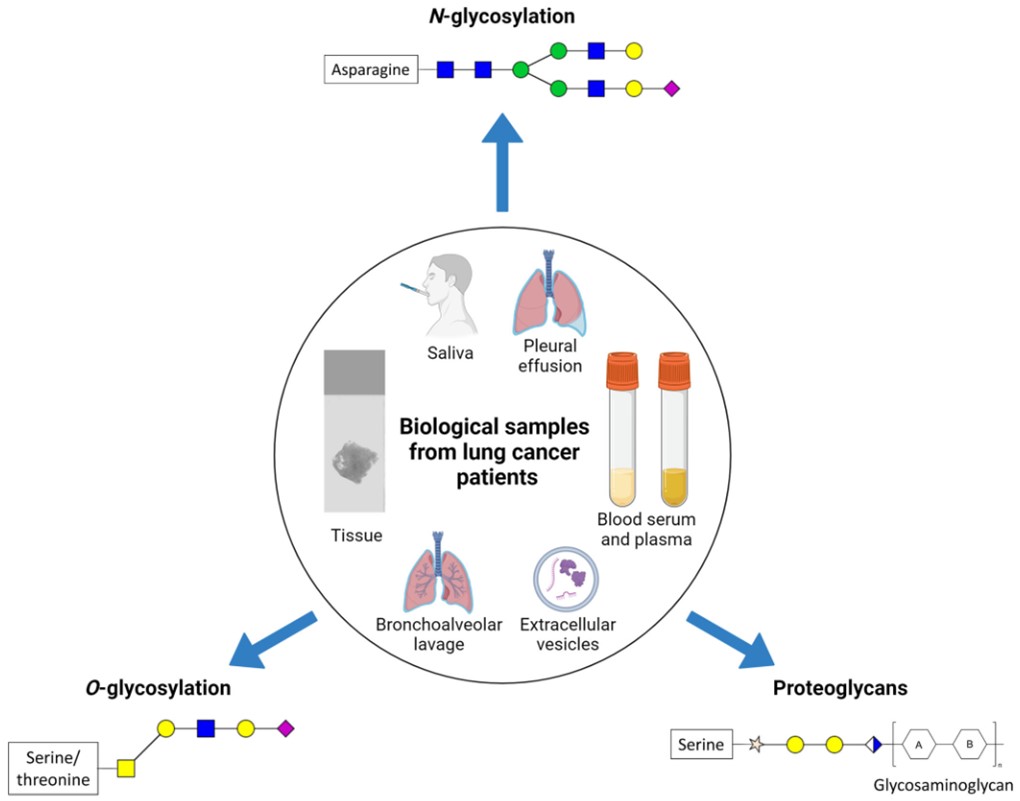 Fig.1 Biological sample types and potential glycosylation types of lung cancer.1,3
Fig.1 Biological sample types and potential glycosylation types of lung cancer.1,3
Our Comprehensive Glycosylation Analysis Services
Creative Biolabs offers a suite of specialized glycosylation analysis services tailored for lung disease research, leveraging advanced mass spectrometry platforms.
-
N-Glycan Analysis
-
Application: Comprehensive analysis of N-linked glycans released from total plasma proteins, IgG, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid, tissue biopsies, and saliva.
-
Relevance: Crucial for identifying diagnostic markers for COPD (e.g., hybrid N-glycans unique to COPD in BAL fluid) and lung cancer (e.g., high-mannose, fucosylated, sialofucosylated N-glycans in tissue/serum). It’s essential for understanding inflammatory signatures and smoking-induced pathophysiological changes.
-
O-Glycan Analysis
-
Application: Detailed characterization of O-linked glycans, particularly mucin-type O-glycans, from tissue and other relevant biological samples.
-
Relevance: While analytically challenging, O-glycosylation is critical in cancer progression. We focus on identifying aberrant truncated O-GalNAc glycans (Tn and sTn antigens) and analyzing the differential regulation of mucin O-glycosylation in lung cancer subtypes, which can serve as subtype-specific biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
-
Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) Analysis
-
Application: Analysis of Metabolomics (e.g., chondroitin sulfate (CS), heparan sulfate (HS)) from tissue and other sources.
-
Relevance: GAGs play vital roles in the extracellular matrix and cell signaling. Changes in GAG amounts and sulfation patterns (e.g., increased total CS and altered sulfation in lung cancer tumors) provide insights into tissue remodeling, inflammation, and tumor microenvironment dynamics.
-
Intact Glycoprotein Analysis
-
Application: Characterization of whole glycosylated proteins without prior glycan release or peptide digestion.
-
Relevance: Offers a holistic view of proteoforms, revealing microheterogeneity that might be missed by other approaches, crucial for understanding functional diversity and biomarker development.
Our detailed analysis process leverages the power of mass spectrometry to provide unparalleled depth in glycosylation analysis. From meticulous sample preparation to the application of advanced UPLC-MS platforms, every step is optimized for sensitivity and accuracy. Bioinformatic processing involves rigorous data normalization, multi-variate statistical modeling, and pathway enrichment analyses to derive biological meaning from complex glycan data. Our approach moves beyond mere detection to provide comprehensive quantitative data, allowing for the confident identification of subtle yet significant glycosylation changes in lung diseases.
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs stands as a leader in glycoscience, providing unparalleled expertise and a distinct advantage for your lung disease research. Our commitment to scientific rigor, coupled with state-of-the-art technology, ensures the highest quality and most insightful results. We offer a comprehensive approach that integrates deep biological understanding with advanced analytical capabilities, allowing us to unravel the complex roles of glycosylation in health and disease. Our multidisciplinary team excels in complex data integration and delivers robust, actionable insights, making us the partner of choice for accelerating your discoveries.
Related Services: Comprehensive Solutions for Your Research
To further support your lung disease research and beyond, Creative Biolabs offers a suite of complementary services designed to provide a holistic view of biological systems.
-
Proteomics Services: Comprehensive protein identification, quantification, and post-translational modification analysis, complementing glycoprofiling with a full protein perspective.
-
Metabolomics Services: High-throughput analysis of metabolites to understand metabolic pathways and their interplay with glycosylation in disease.
-
Bioinformatics & Data Integration: Expert consultation and custom solutions for integrating diverse omics datasets to unlock deeper biological insights.
-
Targeted Antibody Development: Leveraging glycosylation insights for the development of highly specific antibodies for diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner in advancing lung disease research through the power of glycoscience. We are ready to discuss your specific project needs and demonstrate how our expertise can accelerate your breakthroughs. Please contact our team for more information.
Published Data
This literature explores the molecular underpinnings of cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells, specifically highlighting the role of N-glycosylation. The research employs a comprehensive analytical strategy to identify membrane proteins that change abundance and glycosylation status as NSCLC cells develop resistance to cisplatin, a common chemotherapy drug. The findings suggest a significant global increase in glycosylation within cisplatin-resistant cell lines. Figure 2 illustrates the comparative analysis between sensitive and resistant NSCLC cells, involving the meticulous isolation of membrane proteins. These proteins then undergo enzymatic breakdown, followed by a crucial step of enriching specific N-glycopeptides, which are essentially sugar-modified peptides. The enriched samples are subsequently subjected to high-resolution liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). This advanced technique allows for the precise quantification of both total protein levels and their N-glycosylation patterns, providing a detailed snapshot of the proteomic and glycoproteomic landscape during the development of drug resistance.
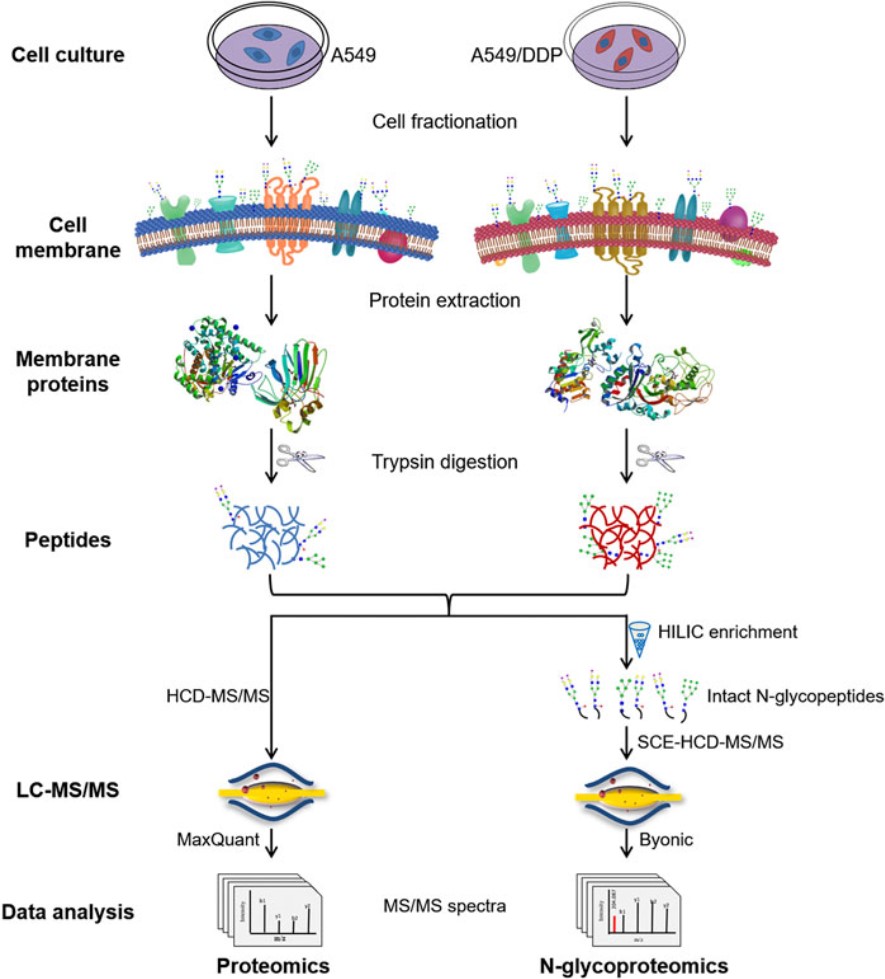 Fig.2 Proteomics analytical workflow.2,3
Fig.2 Proteomics analytical workflow.2,3
FAQs
Q1: Can your service help understand the impact of smoking on lung health at a molecular level?
A1: Absolutely. Our glycoprofiling service excels at identifying smoking-induced alterations in N-glycosylation in both plasma and bronchoalveolar fluid. These changes, including shifts in complex and oligomannose N-glycans, provide critical insights into the long-term molecular effects of smoking and can help identify individuals at higher risk for COPD or lung cancer. Discuss your specific needs with our experts.
Q2: Is mass spectrometry the only technology you use for glycosylation analysis?
A2: While mass spectrometry is our primary and most powerful tool for comprehensive and site-specific glycosylation analysis due to its sensitivity and versatility, we integrate it with advanced separation techniques like HILIC-UPLC and leverage sophisticated bioinformatic platforms for data interpretation. This ensures robust and in-depth characterization of the glycome.
Q3: How can Creative Biolabs' glycosylation analysis contribute to therapeutic development for lung diseases?
A3: By elucidating aberrant glycosylation pathways, we can pinpoint novel therapeutic targets, including specific glycans or the enzymes that regulate their synthesis. For example, understanding metabolism-driven glycosylation in macrophages or differential mucin O-glycosylation in lung cancer subtypes can lead to the development of targeted small molecules or biologics. Let's explore how our insights can accelerate your drug discovery pipeline.
Customer Review
Unprecedented Specificity!
"Using Creative Biolabs's lung disease research-related glycosylation analysis service in our lung cancer screening research has significantly improved the specificity of our serum-based biomarkers. Their detailed alpha-1-antitrypsin (A1AT) glycosylation analysis allowed us to differentiate adenocarcinoma from benign conditions with remarkable clarity, far surpassing previous methods." - Dr. J. Hal***l.
Insightful COPD Glycoprofiling
"Creative Biolabs's service provided invaluable insights into the long-term effects of smoking on bronchoalveolar N-glycosylation. Their comprehensive data helped us understand the shift towards oligomannose N-glycans in smokers with COPD, allowing us to identify high-risk patient subgroups, which was critical for our therapeutic strategy development." - Mr. K. You***g.
References
-
Balbisi, Mirjam, Simon Sugár, and Lilla Turiák. "Protein glycosylation in lung cancer from a mass spectrometry perspective." Mass Spectrometry Reviews (2024). DOI: 10.1002/mas.21882.
-
Zeng, Wenjuan, et al. "Elevated N-glycosylation contributes to the cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells revealed by membrane proteomic and glycoproteomic analysis." Frontiers in Pharmacology 12 (2021): 805499. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.805499.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Services
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Biological sample types and potential glycosylation types of lung cancer.1,3
Fig.1 Biological sample types and potential glycosylation types of lung cancer.1,3
 Fig.2 Proteomics analytical workflow.2,3
Fig.2 Proteomics analytical workflow.2,3

