Why is Gastric Cancer (GC) Research related to Glycosylation Analysis necessary?
Glycosylation, the pervasive modification of proteins and lipids, plays a pivotal role in cellular function and disease pathogenesis. Aberrant glycosylation is a hallmark of cancer, presenting unique and highly specific molecular signatures invaluable for disease diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic development. Gastric cancer (GC), a leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally, particularly benefits from these advanced glycomic insights due to the limitations of current detection methods. Leveraging sophisticated analytical techniques and computational power, glycosylation analysis offers an unprecedented opportunity for earlier, more accurate, and less invasive diagnostics. Creative Biolabs' GC glycosylation analysis service offers precise, data-driven solutions to enhance your research and development in cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. We provide specific glycan signatures and comprehensive analytical insights, enabling you to develop superior diagnostic tools and understand critical disease pathways. Our services help overcome the limitations of traditional biomarkers by leveraging the highly specific and functionally relevant changes in glycosylation patterns associated with GC. This allows for earlier, more accurate detection and the potential for personalized treatment strategies.
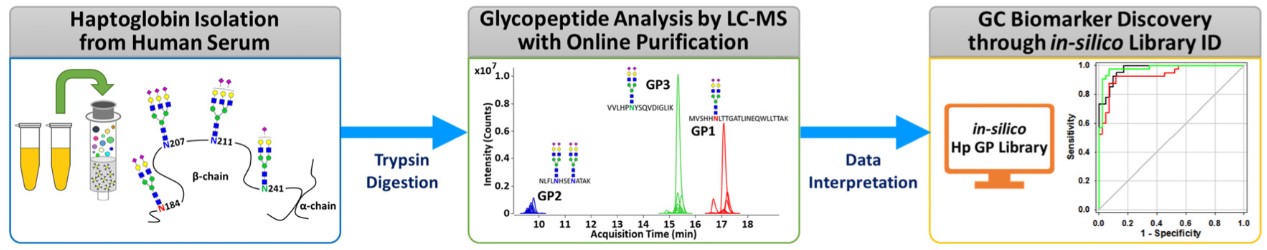 Fig.1 The middle and upper glycoproteomics approach for GC diagnosis.1,3
Fig.1 The middle and upper glycoproteomics approach for GC diagnosis.1,3
How Creative Biolabs Provides GC Glycosylation Services?
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive suite of glycosylation analysis services tailored for GC research, encompassing diverse sample types and analytical depths:
Serum/Plasma Glycan Profiling
-
LC-MS and MALDI-TOF MS: For global N-glycan profiling, identifying high-mannose, complex type, biantennary, and multi-branched glycan structures. This allows for the discovery of novel glycan signatures and the quantification of their relative abundances.
-
DNA sequencer-assisted fluorophore-assisted carbohydrate electrophoresis (DSA-FACE): For high-resolution separation and quantification of fluorophore-labeled glycans, providing detailed electrophoretic profiles.
Targeted Glycoprotein Analysis
-
Middle-up-down glycoproteome platform: This advanced platform enables online purification and direct separation and detection of abnormal glycosylation on specific target proteins. This approach offers enhanced accuracy, speed, and clinical compatibility compared to broad glycan profiling.
Tissue Glycan Analysis
-
MALDI-MS: Proteins are extracted from the GC and adjacent non-tumor FFPE tissues. N-glycans are released, labeled, and analyzed by MALDI-MS. The resulting N-glycomic data is then processed using advanced machine learning algorithms to build highly accurate predictive models.
Functional Glycosylation Studies
-
Method: Integration of glycomic data with cell biology experiments (e.g., proliferation assays, pathway analysis) to confirm the functional role of altered glycosylation (e.g., impact of core-fucosylation on cell growth).
Why is glycosylation analysis crucial in GC research?
-
Early detection & improved specificity: Traditional GC biomarkers (e.g., CEA, CA19-9) often lack the sensitivity and specificity for early-stage detection. Aberrant glycans provide highly specific "molecular signatures" of malignant transformation, enabling earlier and more accurate diagnosis, which is critical for effective treatment. Diagnostic models based on N-glycans have demonstrated superior diagnostic efficacy compared to these conventional markers.
-
Non-invasive biomarkers: Glycan biomarkers can be detected in easily accessible body fluids like serum, offering non-invasive alternatives for screening and monitoring.
-
Understanding pathogenesis & functional roles: Glycans are not merely markers, but actively participate in cancer biology. Analyzing specific glycan changes provides insights into the underlying mechanisms of cancer progression, cell proliferation, and immune evasion, opening avenues for novel therapeutic targets.
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of glycomics research, offering unmatched expertise and a commitment to precision that sets your project apart. Our integrated approach, combining advanced analytical platforms with cutting-edge bioinformatics and machine learning, delivers highly accurate and actionable insights for GC research. We go beyond mere data generation to provide deep biological interpretations that accelerate your discoveries.
Creative Biolabs' GC glycosylation analysis service provides cutting-edge solutions for the discovery, validation, and mechanistic understanding of glycan biomarkers. Ready to advance your GC research with the power of glycomics? Our expert team is eager to discuss your specific project needs and explore how our specialized services can provide the solutions you require. Please contact us, and we look forward to partnering with you on your next breakthrough.
Published Data
This research paper focuses on uncovering new N-glycan-based indicators for identifying GC. The study encompassed 347 participants, categorizing them into groups of GC patients, individuals with atrophic gastritis, and healthy controls, which were then utilized for training and validation of diagnostic models. The methodology involved profiling serum N-glycans, a process that revealed nine distinct N-glycan structures and a reduction in core fucose residues within GC cases. Based on these findings, two diagnostic models, named GCglycoA and GCglycoB, were formulated. These models demonstrated superior precision and sensitivity when compared to existing tumor markers, suggesting their potential as valuable tools for GC detection. The observed decrease in core-fucosylation is hypothesized to stem from a reduced expression of fucosyltransferase enzymes.
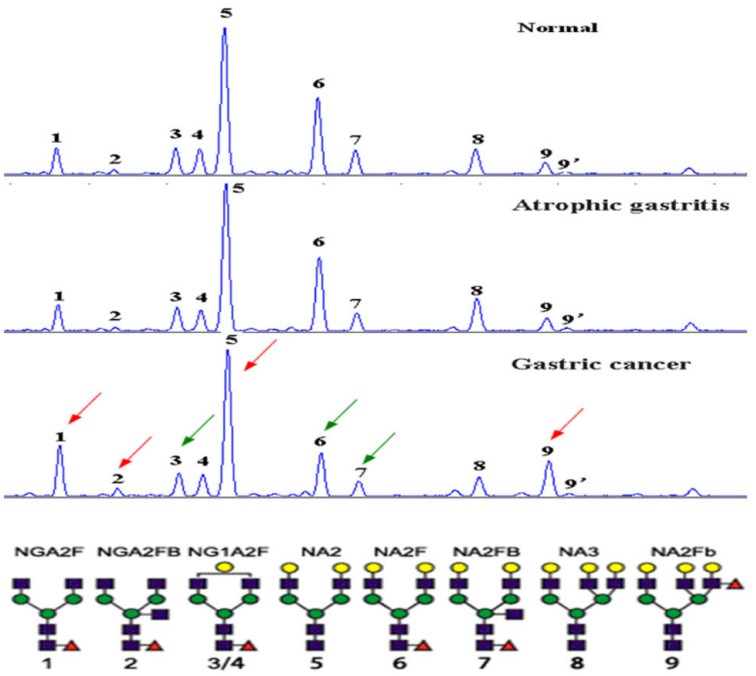 Fig.2 Desialylated N-glycan profiles in serum samples.2,3
Fig.2 Desialylated N-glycan profiles in serum samples.2,3
FAQs
Q1: What types of samples can Creative Biolabs analyze for GC glycosylation research?
A1: We are equipped to analyze a wide range of biological samples, including serum, plasma, tissue biopsies (fresh-frozen and FFPE), and gastric fluid. Our flexible platforms ensure optimal glycan extraction and analysis regardless of sample origin.
Q2: How do Creative Biolabs' glycosylation analysis services compare to traditional GC biomarkers like CEA or CA19-9?
A2: Our glycan-based biomarkers offer significantly higher diagnostic specificity and sensitivity for GC, especially for early detection. Unlike traditional markers, which often have limitations in distinguishing early-stage cancer from benign conditions, our advanced glycomic models have demonstrated superior AUC values, providing more reliable insights.
Q3: What is the typical turnaround time for a GC glycosylation analysis project, and what factors influence it?
A3: The typical timeframe ranges from 8 to 10 weeks. This depends on factors such as the number and type of samples, the complexity of the desired glycan profiling (e.g., global vs. targeted), and the extent of data analysis. We work closely with our clients to establish realistic timelines and deliver timely results.
Customer Review
Unparalleled Accuracy
"Using Creative Biolabs's glycosylation analysis service in our GC early detection project has significantly improved the specificity of our serum biomarker panel. Their core fucose analysis was particularly insightful, providing diagnostic performance far exceeding traditional markers." - Mr. T. And***n.
Targeted Glycoprotein Analysis
"The development of our new haptoglobin-based diagnostic assay for GC was critically facilitated by Creative Biolabs's middle-up-down glycoproteome platform. Their precise, targeted analysis of haptoglobin glycosylation provided the clarity we needed for clinical translation, avoiding the noise of global glycan profiling." - Prof. B. Tho***s.
References
-
Jeong, Seunghyup, et al. "Detection of aberrant glycosylation of serum haptoglobin for gastric cancer diagnosis using a middle-up-down glycoproteome platform." Journal of Personalized Medicine 11.6 (2021): 575. DOI: 10.3390/jpm11060575.
-
Liu, Long, et al. "The identification and characterization of novel N-glycan-based biomarkers in gastric cancer." PloS one 8.10 (2013): e77821. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077821.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Services
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 The middle and upper glycoproteomics approach for GC diagnosis.1,3
Fig.1 The middle and upper glycoproteomics approach for GC diagnosis.1,3
 Fig.2 Desialylated N-glycan profiles in serum samples.2,3
Fig.2 Desialylated N-glycan profiles in serum samples.2,3

