Introduction
In cancer, glycosylation is far from a passive decoration; it acts as a molecular signature that influences tumor progression, metastasis, and immune evasion. Aberrant glycosylation has been recognized as a core hallmark of malignancy, driving phenotypic and functional heterogeneity across tumor types. At Creative Biolabs, we offer a comprehensive suite of glycosylation analysis services, tumor-associated glycan detection, glycosyltransferase gene expression profiling, and glycoengineering strategies. These platforms enable you to map glycosylation changes with high resolution, discovering novel diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets.
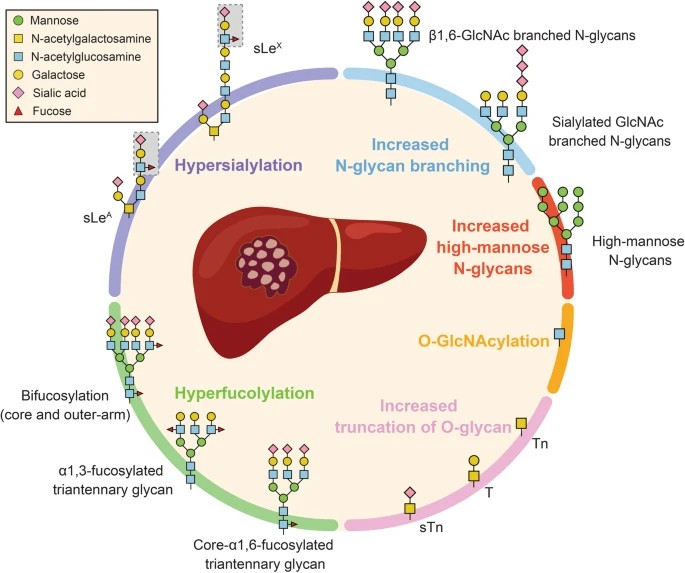 Fig.1 Protein glycosylation alteration in HCC.1,3
Fig.1 Protein glycosylation alteration in HCC.1,3
Aberrant Glycosylation as a Cancer Hallmark
In cancer cells, aberrant glycosylation patterns are often observed. Such aberrations are not incidental—they correlate with disease stage, prognosis, and metastatic potential. For example, in endometrial carcinoma, the stepwise shift in glycan composition and spatial distribution reflects malignant progression and may predict clinical outcomes. Cancer cells commonly remodel their glycosylation machinery. Key mechanisms include:
-
Core fucosylation mediated by FUT8 enhances melanoma invasiveness by altering cell adhesion and migration.
-
Sialylation, particularly catalyzed by ST6GAL1, equips breast cancer cells to breach pulmonary vasculature, facilitating pre-metastatic niche formation.
|
Glycan Alteration Type
|
Related Glycosyltransferase
|
Example Cancer Types
|
|
Increased N-glycan Branching
|
MGAT5 (GnT-V)
|
Pancreatic Cancer, Melanoma
|
|
Increased Core Fucosylation
|
FUT8
|
Melanoma, Prostate Cancer, Gastric Cancer
|
|
Hypersialylation
|
ST6GAL1, ST3GALs
|
Breast Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Colorectal Cancer
|
|
Truncated O-glycans
|
GALNTs (GALNT7)
|
Breast Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Colorectal Cancer, HCC
|
|
Altered O-GlcNAcylation
|
OGT, OGA
|
Prostate Cancer, Colorectal Cancer
|
Glycosylation Analysis for Cancer Diagnosis
Many well-established tumor markers, such as CEA, CA125, and AFP, are glycoproteins or glycan antigens, underscoring the diagnostic potential of glycans. Our tumor-associated glycan detection service utilizes advanced methodologies to precisely identify and characterize the types and distribution of glycans in tissue samples. This method leverages the highly specific binding of lectins to various glycan structures, enabling detailed mapping of glycosylation patterns directly within the tumor microenvironment. For example, the aberrant O-glycosylation of MUC1 in colon cancer, characterized by an increase in truncated glycan structures, has been recognized as a promising marker for early diagnosis. Our service can aid in its precise identification, offering high-resolution visualization and quantification of specific glycan structures critical for understanding disease state and progression.
To gain a more comprehensive understanding of the entire glycome, our cancer glycomics analysis service employs advanced techniques such as lectin arrays and high-resolution MS. Lectin arrays allow for high-throughput profiling of glycan binding patterns across a wide range of samples, revealing global changes in glycosylation. These arrays can differentiate between healthy and cancerous tissues based on their unique glycan binding profiles, offering a rapid screening method for potential biomarkers. Complementarily, mass spectrometry provides detailed structural information about individual glycans and glycopeptides, enabling the precise identification and quantification of novel cancer-specific glyco-biomarkers. This holistic approach facilitates the systematic elucidation of tumor-specific glycosylation signatures, critical for glyco-code based diagnostics. For instance, distinct glycosylation changes in early-stage lung cancer and specific glycan profiles in non-small cell lung cancer have been identified through glycomics analysis, showing promise for non-invasive detection and prognosis.
 Fig.2 Workflow for cancer glycomics-based biomarker discovery.
Fig.2 Workflow for cancer glycomics-based biomarker discovery.
Therapeutic Targeting of Glycosylation
Inhibiting Glycosyltransferase Activity
Selective inhibition or gene silencing of glycosylation enzymes offers a direct path to impair cancer cell fitness. For instance, FUT8 suppression reduces melanoma metastatic ability by decreasing fucosylation-dependent integrin signaling, GALNT7 downregulation interrupts the biosynthesis of tumor-promoting O-glycans in prostate cancer models. Our cancer-specific glycosyltransferase gene expression profiling service enables the precise identification of dysregulated glycosyltransferases in specific cancer types. Our service facilitates:
-
Identification of androgen-regulated enzymes in prostate cancer.
-
Correlation of enzyme overexpression with metastatic phenotypes or resistance profiles.
-
Integration with RNA-seq or microarray datasets to prioritize targetable nodes.
monoclonal antibodies can be profoundly influenced by their glycosylation patterns, particularly in their Fc region. Creative Biolabs provides custom protein glycoengineering and antibody glycoengineering services. Our service focuses on optimizing these glycan structures to enhance desired effector functions. This has led to the development of clinically approved "afucosylated" antibodies with superior anti-tumor activity, showcasing the power of glycoengineering to improve existing cancer immunotherapies and develop next-generation biotherapeutics.
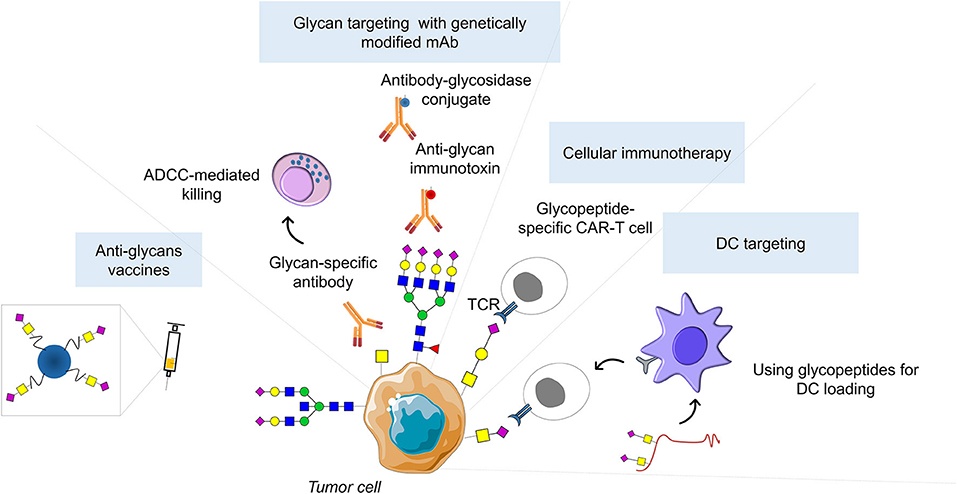 Fig.3 Glycan-based therapeutic strategies.2,3
Fig.3 Glycan-based therapeutic strategies.2,3
Service Portfolio: Glycosylation Solutions for Oncology Research
Aberrant glycosylation is more than a byproduct of malignancy—it is a driver of cancer progression, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance. As precision oncology evolves, the need to integrate glycosylation insights becomes increasingly urgent. Creative Biolabs offers a complete workflow to explore, quantify, and manipulate cancer-associated glycans. Our tools empower scientists to turn glycan complexity into actionable knowledge. Ready to take your cancer glycomics project further? Contact us for cutting-edge glycosylation analysis solutions tailored to your research needs!
References
-
Wang, Yifei, and Huarong Chen. "Protein glycosylation alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma: function and clinical implications." Oncogene 42.24 (2023): 1970-1979. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-023-02702-w
-
Peixoto, Andreia, et al. "Protein glycosylation and tumor microenvironment alterations driving cancer hallmarks." Frontiers in oncology 9 (2019): 380. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00380
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Protein glycosylation alteration in HCC.1,3
Fig.1 Protein glycosylation alteration in HCC.1,3
 Fig.2 Workflow for cancer glycomics-based biomarker discovery.
Fig.2 Workflow for cancer glycomics-based biomarker discovery.
 Fig.3 Glycan-based therapeutic strategies.2,3
Fig.3 Glycan-based therapeutic strategies.2,3

