Monosaccharides, indigestible sugar units, serve as metabolic energy hubs and building blocks for polysaccharides, nucleic acids, and glycoproteins. Their synthesis, modification, and analysis underpin advancements in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and food science. With years of deep research on carbohydrate chains in glycobiology and development of glycan analysis technologies, Creative Biolabs provides one-stop solutions from custom monosaccharide synthesis, modification to monosaccharide analysis, and we are willing to partner with you to facilitate your glycan-related research.
Enzymatic Synthesis of Monosaccharides
Enzymatic synthesis capitalizes on biological catalysts to achieve high selectivity under mild conditions.
-
Glycosyltransferases transfer sugar moieties from activated donors (e.g., UDP-sugars) to acceptor molecules, enabling precise glycosidic bond formation critical for oligosaccharide and glycoconjugate assembly.
-
Glycosidases, traditionally associated with hydrolysis, can reverse-engineer transglycosylation under optimized pH/solvent conditions, creating tailored glycosidic linkages.
-
Epimerases facilitate chiral conversions (e.g., D-glucose to D-mannose), expanding precursor utility. This enzyme-driven flexibility reduces waste and avoids harsh chemical reagents.
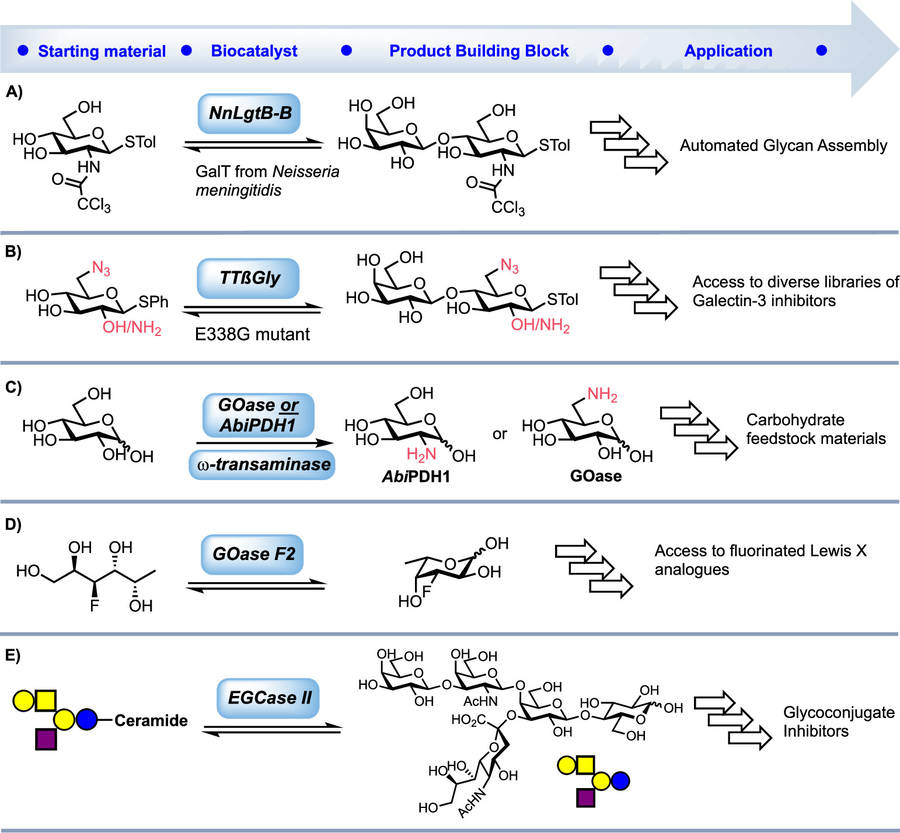 Fig.1 Enzyme-based strategies for producing building blocks in glycan synthesis.1,3
Fig.1 Enzyme-based strategies for producing building blocks in glycan synthesis.1,3
Chemical Synthesis of Monosaccharides
Chemical methods remain indispensable for complex sugar architectures:
-
Kiliani–Fischer synthesis extends aldose chains via cyanohydrin intermediates, yielding epimer mixtures (e.g., D-glucose/D-mannose from D-arabinose). The three-step protocol—cyanohydrin formation, hydrolysis, and reduction—has been refined for scalability. The three-step process involves:
-
Cyanohydrin formation: An aldose reacts with hydrogen cyanide (HCN) to form a cyanohydrin.
-
Hydrolysis: The cyanohydrin undergoes hydrolysis to yield an aldonic acid.
-
Reduction: The aldonic acid is reduced to form a new aldose.
-
Achmatowicz reaction converts furans to dihydropyrans, a versatile platform for natural product synthesis. Oxidation followed by rearrangement enables access to monosaccharides like ribose and derivatives for nucleoside drug development. The two general steps include:
-
Oxidation: A furan derivative is oxidized to form a dihydrofuran.
-
Rearrangement: The dihydrofuran rearranges into a dihydropyran structure.
Related Monosaccharides Synthesis Research
The Effect of Enhanced Growth Conditions on Monosaccharide Profiles in Algae
Research indicates that the monosaccharide composition of Ulva fenestrata changes when exposed to various abiotic factors including irradiance levels, temperature changes and different concentrations of nitrate and phosphate along with carbon dioxide partial pressure (pCO₂). Monosaccharide content rose when algae were cultivated in conditions with lowered nitrate levels and higher temperatures. The contents of iduronic acid and rhamnose rose by 70% and 26% respectively when conditions of higher irradiance and temperature were applied. The study demonstrates that by optimizing culture conditions we can control monosaccharide levels in algae to direct the production of algal polysaccharides with specific bioactivities.2,3
Modifications for Monosaccharides
Creative Biolabs provides a complete range of glycan modification and labeling services which include phosphorylated, halogenated, and sialylated derivatives to support the development of antiviral drugs, cancer treatments, and cardiac medications.
|
Modification Service
|
Description
|
|
Biotinylation
|
We attach biotin to glycans to make detection and purification easier. The strong biotin-avidin interaction ensures reliable binding, streamlining downstream applications.
|
|
PEGylation
|
By conjugating polyethylene glycol (PEG) chains to glycans, we improve their solubility, stability, and bioavailability—key factors in optimizing pharmacokinetics.
|
|
Sulfate Modification
|
Adding sulfate groups can significantly impact glycan function, influencing biological activity, molecular recognition, and cell signaling pathways.
|
|
Phosphorylation Modification
|
Phosphate groups play a crucial role in metabolism and cellular communication. We modify glycans through phosphorylation to help regulate these essential processes.
|
|
Acetylation Modification
|
Acetyl groups affect glycan structure and interactions, making them vital for the synthesis of complex carbohydrates and glycoconjugates. Our modification service ensures precise acetylation for enhanced functionality.
|
Purification & Analysis of Monosaccharides
-
Monosaccharides Purification: Normal-phase chromatography (polarity-based), affinity chromatography (lectin-based), and ion-exchange (charge-based) techniques isolate sugars with >95% purity.
-
Monosaccharides Analysis: HPAEC-PAD quantifies sugars via pulsed amperometry (e.g., glucose/rhamnose detection in algae), while MS and CE resolve structural isomers. Recent work on Ulva. fenestrate employed a four-step eluent gradient to distinguish acidic sugars like iduronic acid.
Industrial Translation
-
Pharmaceuticals: Glucose laurate (GLC12) and fructose laurate (FRU12) show antimicrobial activity (e.g., FRU12 inhibits S. aureus at 12.5%).
-
Food: Sugar alcohols (sorbitol) replace sucrose in low-calorie products.
-
Biotech: Fermentable monosaccharides from algae boost biofuel yields; chiral lactones derived from glucose enable biodegradable polymer synthesis.
Monosaccharides and Derivatives We Provide
With extensive experience in glycan synthesis, Creative Biolabs offers custom synthesis of monosaccharides and their derivatives through multi-step chemical or enzymatic processes. These bioactive monosaccharides, including site-specifically hydroxyl group-modified variants, stereoisomers, and regioisomers, are synthesized for pharmaceutical applications such as antiviral, antibacterial, anticancer, and cardiac therapies. Our strategic approach provides efficient and broad access to this valuable class of compounds. We are committed to provide various types of monosaccharides and their derivatives including:
-
Monosaccharides
-
Monosaccharides sulphates
-
Brominated monosaccharides
-
Sulphur containing monosaccharides
-
Nitrogen containing monosaccharides
-
Neuraminic acids (Neu5Ac or Neu5Gc)
-
Sialoside
-
Fucosides
-
Chiral lactones
-
Glucuronides
-
Phosphorylated sugars
-
High mannose type N-glycans
-
Xylose containing plant N-glycans
-
Complex type N-glycans
-
2-AB/AA labelled glycans
-
13C labelled glycan
Published Data
Researchers have studied the sugar composition of Ulva fenestrata, a type of green seaweed, by employing a two-step sulfuric acid hydrolysis technique. They utilized high-performance anion-exchange chromatography paired with pulsed amperometric detection (HPAEC-PAD) to quantify sugars like glucose, rhamnose, and iduronic acid. It is revealed that varying cultivation conditions led to significant differences in sugar content, especially in rhamnose and iduronic acid levels. The following graph outlines the eluent gradient program used in the HPAEC analysis, detailing the application of four different eluents and the post-column addition of a 300 mM NaOH solution.These insights highlight how external environmental factors can influence the sugar makeup of Ulva fenestrata. By adjusting these factors, it's possible to optimize the production of valuable sugars for various industrial uses.
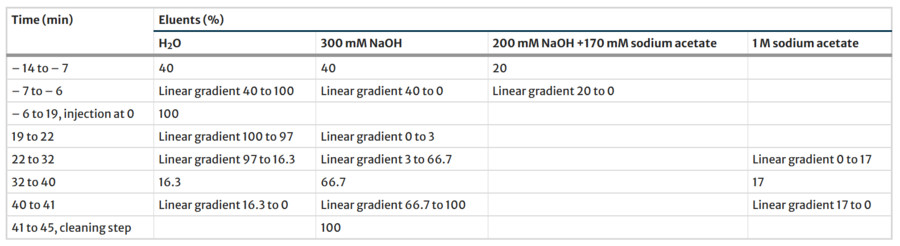 Fig.2 Impact of environmental conditions on monosaccharide content in Ulva fenestrate.2,3
Fig.2 Impact of environmental conditions on monosaccharide content in Ulva fenestrate.2,3
FAQs
Q: What reaction forms monosaccharides?
A: Monosaccharides are primarily formed through biochemical processes such as photosynthesis in plants and gluconeogenesis in animals. In laboratory synthesis, they can be generated via hydrolysis of polysaccharides or chemical synthesis methods. Additionally, monosaccharide derivatives, known as glycosides, are formed when a hemiacetal reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. This reaction replaces the hydroxyl (-OH) group on the anomeric carbon with an alkoxy (-OR) group from the alcohol, creating a stable glycosidic bond. This process is crucial in carbohydrate chemistry and glycan synthesis.
Q: Can synthetic monosaccharides be customized for specific research needs?
A: Yes! Synthetic monosaccharides can be modified to include functional groups, isotope labels, or specific linkages to match your research requirements. These customized sugars are widely used in glycan research, vaccine development, and therapeutic studies. Creative Biolabs provides expert guidance in designing and synthesizing tailor-made monosaccharides, ensuring high purity and structural accuracy for diverse applications.
Q: What are the challenges in monosaccharide synthesis, and how does Creative Biolabs overcome them?
A: Monosaccharide synthesis can be challenging due to the structural complexity, stereochemical control, and the need for high purity. Chemical synthesis may involve multiple protection and deprotection steps, while enzymatic approaches require highly specific enzymes. At Creative Biolabs, we leverage our expertise in glycoengineering, biocatalysis, and advanced purification techniques to efficiently produce high-quality monosaccharides while maintaining cost-effectiveness and reproducibility.
References
-
Dolan, Jonathan P., Sebastian C. Cosgrove, and Gavin J. Miller. "Biocatalytic approaches to building blocks for enzymatic and chemical glycan synthesis." JACS Au 3.1 (2022): 47-61. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacsau.2c00529
-
Olsson, Joakim, et al. "Cultivation conditions affect the monosaccharide composition in Ulva fenestrata." Journal of Applied Phycology 32.5 (2020): 3255-3263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02138-9
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Enzyme-based strategies for producing building blocks in glycan synthesis.1,3
Fig.1 Enzyme-based strategies for producing building blocks in glycan synthesis.1,3
 Fig.2 Impact of environmental conditions on monosaccharide content in Ulva fenestrate.2,3
Fig.2 Impact of environmental conditions on monosaccharide content in Ulva fenestrate.2,3

