What Are Pentose and Hexose Monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides are the fundamental building blocks of carbohydrates, categorized by their carbon atom count. Pentose (C₅H₁₀O₅) and Hexose (C₆H₁₂O₆) sugars play pivotal roles in biological processes, particularly in cell metabolism, nucleic acid synthesis, and disease mechanisms. Creative Biolabs, equipped with state-of-the-art glycan analysis technologies , our monosaccharides analysis services provide precise characterization of pentose and hexose sugars, supporting research in cell metabolism, disease research, and glycoprofiling for biomedical applications.
Pentose Monosaccharides
Pentose sugars predominantly exist in furanose (five-membered) and linear forms, playing key roles in nucleic acid structure, cellular metabolism, and enzymatic functions. Pentoses play a central role in genetic information storage and transmission:
-
In RNA: Ribose links with adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and uracil (U).
-
In DNA: Deoxyribose bonds with A, G, C, and thymine (T), forming a stable double-helix structure.
|
Pentose Type
|
Structure
|
Function
|
Primary Biological Role
|
|
Xylose
|
Aldopentose
|
Structural component of plant cell walls
|
Forms xylan, a key component in hemicellulose
|
|
Xylulose
|
Ketopentose
|
Involved in pentose phosphate pathway (PPP)
|
Xylulose-5-phosphate regulates metabolic balance
|
|
Apiose
|
Aldopentose
|
Found in plant glycosides
|
Occurs in celery and parsley compounds
|
|
Ribose
|
Aldopentose
|
Key structural unit in nucleotides (RNA, ATP, NADH)
|
Forms the backbone of RNA and energy carriers
|
|
Deoxyribose
|
Aldopentose
|
Component of DNA nucleotides
|
Enhances DNA stability for genetic storage
|
Explore Our Pentose Analysis Services:
Hexose Monosaccharides
Hexoses exhibit structural diversity due to their spatial hydroxyl (-OH) arrangements, leading to multiple isomeric forms.
|
Hexose Type
|
Structure
|
Function
|
Metabolic Pathway
|
|
Glucose
|
Aldohexose
|
Primary cellular energy source
|
Enters glycolysis → ATP production
|
|
Fructose
|
Ketohexose
|
Alternative energy source
|
Converts to fructose-1-phosphate before glycolysis
|
|
Galactose
|
Aldohexose
|
Forms lactose (milk sugar)
|
Requires conversion to glucose for metabolism
|
The Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP)
The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) is an essential metabolic route that supports anabolic metabolism, antioxidant defense, and nucleotide synthesis. PPP consists of two distinct phases:
-
Oxidative Phase (Irreversible)
-
Converts glucose-6-phosphate → ribulose-5-phosphate
-
Generates NADPH (crucial for lipid biosynthesis and antioxidation)
-
Releases CO₂ as a byproduct.
-
Non-Oxidative Phase (Reversible)
-
Interconverts pentoses and triose sugars
-
Facilitates metabolic flexibility through transketolase and transaldolase reactions.
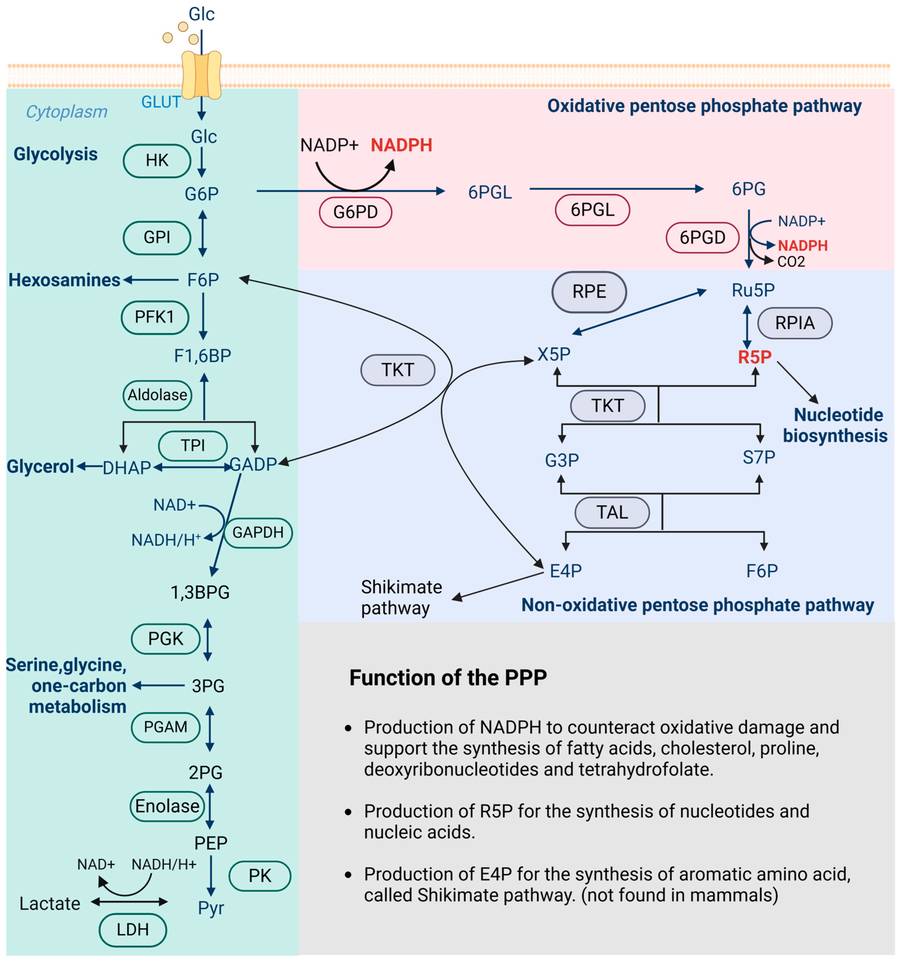 Fig.1 The process of glycolysis, oxPPP, and non-oxPPP.1,3
Fig.1 The process of glycolysis, oxPPP, and non-oxPPP.1,3
Role of Xylulose and Its Derivate in PPP
Analyzing xylulose' content and its conversion efficiency, we can gain deep insights into the metabolic state of cells and their energy metabolism mechanisms. Xylulose is converted into Xylulose-5-phosphate through a phosphorylation reaction. Xylulose-5-phosphate serves as a crucial intermediate in the pentose phosphate pathway and functions as a central component within its non-oxidative phase. It regulates cellular antioxidant defence as well as nucleic acid synthesis and sugar metabolism via the metabolic network of the PPP. Bacteria and plants both utilize xylulose-5-phosphate in their metabolic processes. Bacteria transform xylulose 5-phosphate into various metabolites through multiple reactions to supply energy and materials required for their growth and reproduction. In plants, Xylulose-5-phosphate enables plant life by supporting both photosynthesis and respiration processes which supply essential energy and materials. Xylulose-5-phosphate plays an essential role in controlling nucleotide biosynthesis and oxidative stress response while maintaining metabolic balance in both bacteria and plants through multiple metabolic transformations in the PPP.
|
Reactant
|
Enzyme
|
Product
|
|
Xylulose-5-Phosphate + Ribose-5-Phosphate
|
Transketolase
|
Sedoheptulose-7-Phosphate + Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate
|
|
Xylulose-5-Phosphate + Erythrose-4-Phosphate
|
Transaldolase
|
Fructose-6-Phosphate + Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate
|
PPP in Bacteria vs. Plants
In Plants
-
Provides NADPH for lipid biosynthesis and antioxidant defense.
-
Integrates with the Calvin cycle in photosynthesis.
In Bacteria
-
Contributes to antibiotic resistance through metabolic reprogramming.
-
Supports oxidative stress tolerance in diverse environments.
Linking PPP to Glycolysis and Disease Mechanisms
PPP cross-talks with glycolysis and impacts various diseases:
|
Disease
|
PPP Dysregulation
|
Clinical Impact
|
|
Cancer
|
Upregulates NADPH and ribose synthesis
|
Supports rapid cell proliferation
|
|
Von Gierke's Disease
|
Deficiency in glucose-6-phosphatase
|
Leads to glycogen accumulation, hypoglycemia
|
|
Neurodegenerative Disorders
|
PPP-derived NADPH protects against oxidative stress
|
Impacts Alzheimer's, Parkinson's disease
|
By analyzing PPP intermediates, the activity and metabolic state of PPP can be understood, providing a basis for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
-
Assessment of PPP activity can be achieved by measuring the levels of PPP intermediates such as NADPH and ribose within the intracellular environment.
-
In certain diseases, such as cancer and diabetes, there may be alterations to PPP activity. By detecting the levels of PPP intermediates, we can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms of disease development, providing a solid foundation for effective diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Creative Biolabs offers advanced metabolic profiling for disease diagnostics:
Active Hexose Correlated Compounds (AHCC) in Cancer Therapy
AHCC is a polysaccharide-based immune modulator extracted from Basidiomycetes mushrooms, studied for its anticancer and immunomodulatory properties. It shows promising effects in breast, liver, and pancreatic cancer models but requires large-scale clinical trials.
|
Application
|
Mechanism
|
Outcome
|
|
Cancer Therapy
|
Enhances NK cell activation
|
Improves immune surveillance
|
|
Chemotherapy Support
|
Reduces toxicity from anticancer drugs
|
Minimizes side effects
|
|
Liver Health
|
Regulates oxidative stress and inflammation
|
Improves hepatoprotection
|
Pentose and hexose sugars are metabolic cornerstones, impacting cellular energy, nucleic acid synthesis, and disease progression. Their involvement in PPP, glycolysis, and glycoprofiling holds substantial therapeutic and industrial value. Creative Biolabs pioneers glycoprofiling research, delivering cutting-edge solutions for metabolic studies and therapeutic innovations. Contact us now for further information!
Published Data
Achieving efficient production of diverse chemicals from biomass monosaccharides depends on selecting proper catalysts and optimizing reaction conditions. Catalytic conversion processes transform glucose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (5-HMF), which serves as a precursor for valuable products like 2,5-dimethylfuran (2,5-DMF). Xylose transforms into furfural after dehydration which further turns into lactic acid and methyl lactate. Researchers have shown that algal biomass can be transformed into bioethanol and lactic acid through catalyzed chemical reactions, along with other chemical products. The economic feasibility of biomass catalytic transformations requires further advancements in catalyst stability and selectivity along with improved regenerability. The figure presents the catalytic conversion routes which transform xylose into numerous valuable chemicals using dehydration, reduction, cyclization, oxidation along with other reactions. The network transforms xylose into several compounds including furfural, furfuryl alcohol, lactic acid, methyl lactate, levulinic acid, γ-valerolactone, valeric acid and valaric acid. This shows direct pathways from xylose to ethanol, lactic acid and methyl lactate which prevent furfural build-up to maximize target chemical production.
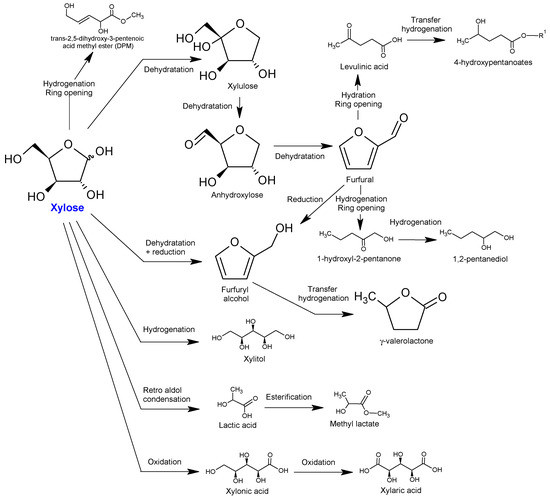 Fig.2 Catalytic conversion pathways from xylose to high-value chemicals.2,3
Fig.2 Catalytic conversion pathways from xylose to high-value chemicals.2,3
FAQs
Q: Where can I access professional pentose and hexose analysis services?
A: You can access professional pentose and hexose analysis services at Creative Biolabs, a leading biotechnology company specializing in glycoprofiling and glycan analysis.
Q: What reagent is used to distinguish between pentoses and hexoses?
A: Bial's test is a biochemical assay designed to differentiate pentoses from hexoses by utilizing orcinol and iron(III) chloride as reagents. The test relies on the formation of furfural derivatives when pentoses undergo dehydration under acidic conditions. In the presence of orcinol and ferric chloride, pentoses produce a distinctive blue-green color, whereas hexoses either do not react or yield a different coloration.
References
-
Qiao, Jincheng, et al. "The Pentose Phosphate Pathway: From Mechanisms to Implications for Gastrointestinal Cancers." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26.2 (2025): 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020610
-
Esteban, Jesús, Pedro Yustos, and Miguel Ladero. "Catalytic processes from biomass-derived hexoses and pentoses: A recent literature overview." Catalysts 8.12 (2018): 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120637
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 The process of glycolysis, oxPPP, and non-oxPPP.1,3
Fig.1 The process of glycolysis, oxPPP, and non-oxPPP.1,3
 Fig.2 Catalytic conversion pathways from xylose to high-value chemicals.2,3
Fig.2 Catalytic conversion pathways from xylose to high-value chemicals.2,3

