Introduction
Ribose and deoxyribose are key sugar molecules in nucleotides, influencing genetic material and biological processes. Their structures and alterations influence gene expression, disease processes, and treatment advancements. Understanding these sugars is critical to biomedical research and diagnostics. Equipped with various technologies and experienced expert staff, Creative Biolabs is proud to offer advanced solutions for ribose and deoxyribose research. Our custom monosaccharide synthesis service provides tailored synthesis of ribose and deoxyribose derivatives to support structural and functional studies. With our monosaccharides analysis services, we offer precise composition and quantification analysis to help researchers understand sugar-related biological processes. Additionally, our glycoengineering services enable custom modifications and engineering of sugar components, assisting in the development of novel therapeutics and diagnostics.
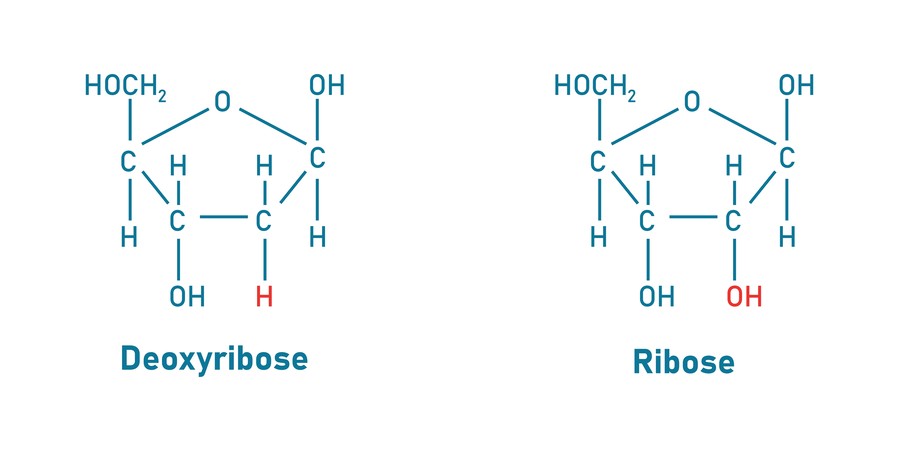 Fig.1 Ribose and deoxyribose.
Fig.1 Ribose and deoxyribose.
What Is Ribose?
Ribose, a naturally occurring five-carbon (pentose) sugar, with the chemical formula C₅H₁₀O₅. Ribose is a component of ribonucleotides, which include RNA (ribonucleic acid), ATP (adenosine triphosphate), and other coenzymes including NADH and FAD. The presence of a hydroxyl (-OH) group at the 2'-carbon position renders ribose chemically reactive, enabling RNA's dynamic character in biological processes such as enzymatic activity (ribozymes), protein synthesis (mRNA translation), and regulatory mechanisms.
What Is Deoxyribose?
Deoxyribose is a variant of ribose in which the 2'-hydroxyl group is replaced by a hydrogen atom. The molecular formula of C₅H₁₀O₄ makes DNA more durable than RNA, allowing for long-term genetic information storage. The lack of a hydroxyl group makes DNA less susceptible to hydrolysis, strengthening its role as a long-lasting hereditary storage.
Ribose vs. Deoxyribose
|
Property
|
Ribose
|
Deoxyribose
|
|
Chemical Formula
|
C₅H₁₀O₅
|
C₅H₁₀O₄
|
|
Functional Group
|
Aldehyde (open chain), hydroxyl (-OH) at C2
|
Aldehyde (open chain), hydrogen (-H) at C2
|
|
Ring Forms
|
β-Furanose (5-membered), β-Pyranose (6-membered)
|
β-Furanose (DNA backbone), β-Pyranose (rare)
|
|
Reducing Capacity
|
Yes (reducing sugar)
|
No (lacks C2 hydroxyl)
|
|
Molar Mass
|
150.13 g/mol
|
134.13 g/mol
|
|
2'-Carbon Group
|
Hydroxyl (-OH)
|
Hydrogen (-H)
|
|
Stability
|
Less stable due to hydroxyl reactivity
|
More stable for genetic storage
|
|
Biological Role
|
RNA backbone, ATP, NADH
|
DNA backbone
|
|
Function
|
Facilitates enzymatic reactions, RNA folding, and mRNA translation
|
Provides structural integrity to genetic material
|
|
Genetic Implications
|
Prone to hydrolysis, allowing rapid RNA turnover
|
High stability ensures long-term genetic storage
|
Ribose & Deoxyribose Analysis
Ribose Analysis
The study of ribose is essential in cellular metabolism and bioenergetics. Analytical techniques used to study ribose levels include:
-
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): Quantifies ribose in biological samples.
-
Mass Spectrometry (MS): Identifies ribose-derived metabolites.
-
NMR Spectroscopy: Elucidates ribose structure and conformation.
Deoxyribose Analysis
Deoxyribose plays a significant role in DNA integrity and repair. Analytical techniques used to study its modifications include:
-
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): Used to detect oxidative damage in DNA.
-
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): Measures deoxyribose oxidation products (e.g., 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG)) in biological fluids.
-
Fluorescence Microscopy: Visualizes DNA strand breaks and modifications in genomic studies.
Creative Biolabs' Glycan Analysis Technologies
|
Techniques
|
Advantages in Ribose and Deoxyribose Analysis
|
|
MS
|
- Highly sensitive and specific for ribose and deoxyribose detection.
- Can differentiate structural isomers and sugar modifications.
- Suitable for identifying sugar composition in nucleotides, nucleosides, and nucleic acids.
|
|
LC-ESI-MS
|
- Enables accurate mass determination of ribose- and deoxyribose-containing biomolecules.
- Effective in profiling nucleotides and sugar modifications.
- Useful for studying glycosylation patterns in nucleic acids.
|
|
MALDI-TOF MS
|
- High-throughput and rapid sugar profiling.
- Suitable for analyzing sugar derivatives, including ribose and deoxyribose in nucleic acids.
- Low sample consumption and automation-friendly.
|
|
GC-MS
|
- Ideal for monosaccharide composition analysis, including ribose and deoxyribose.
- High sensitivity (detection in pM range).
- Effective for detecting sugar degradation products.
|
|
HPLC
|
- Separates ribose and deoxyribose efficiently in complex biological samples.
- High resolution and reproducibility.
- Suitable for sugar modifications and nucleotide analysis.
|
|
HPAEC-PAD
|
- Direct analysis of monosaccharides without derivatization.
- Sensitive for detecting ribose and deoxyribose in nucleotide and nucleoside mixtures.
- Suitable for isomer differentiation.
|
|
NMR
|
- Non-destructive analysis, maintaining sample integrity.
- Capable of structural elucidation of ribose and deoxyribose.
- Provides detailed conformational and dynamic information.
|
|
FTIR
|
- Rapid identification of functional groups in ribose and deoxyribose.
- Non-invasive and label-free analysis.
- Can detect sugar modifications in nucleotides.
|
|
TLC
|
- Simple and cost-effective for qualitative analysis of ribose and deoxyribose.
- Suitable for separation of sugar derivatives in complex mixtures.
- Effective for rapid screening of carbohydrate components.
|
Ribose and Deoxyribose in Genetic Coding and Disease
Ribose in RNA
Unlike DNA, RNA adopts complex three-dimensional structures due to the flexibility conferred by ribose. These conformations enable functional molecules such as:
-
Ribozymes: RNA molecules with catalytic activity, essential in self-splicing reactions and viral replication (e.g., Hepatitis Delta Virus (HDV) ribozyme).
-
mRNA Vaccines: Modified ribose nucleotides improve mRNA stability and translational efficiency, as seen in COVID-19 vaccines.
-
tRNA Modifications: Ribose undergoes methylation at the 2'-O position, influencing codon recognition and translational fidelity.
DNA Deoxyribose Damage
Deoxyribose's absence of the 2'-hydroxyl group prevents RNA-like hydrolysis, enhancing DNA's structural stability. This chemical property is crucial for genetic fidelity, preventing frequent mutations caused by spontaneous hydrolysis. However, oxidative damage to deoxyribose can introduce mutagenic lesions, such as 8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine, which have been implicated in carcinogenesis and neurodegenerative diseases. Deoxyribose oxidation plays a crucial role in genomic instability and cancer progression. Oxidative markers, such as 8-OHdG, are widely used in cancer research:
|
Oxidative Marker
|
Role in Disease
|
Detection Method
|
|
8-OHdG
|
Biomarker for oxidative stress
|
GC-MS, ELISA
|
|
AP (Apurinic/Apyrimidinic) Sites
|
Indicators of DNA strand breaks
|
Fluorescence Microscopy
|
|
DNA Adducts
|
Chemical modifications in oncogenesis
|
HPLC-MS
|
Advanced Applications
D-Ribose Examination: Metabolic Support and Disease Models
D-Ribose supplementation has been explored in mitochondrial and metabolic disorders due to its role in ATP synthesis. Clinical applications include:
|
Condition
|
Role of D-Ribose
|
Clinical Evidence
|
|
MELAS Syndrome
|
Supports mitochondrial ATP production
|
Pilot trials demonstrate energy enhancement
|
|
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
|
Improves cellular metabolism
|
Positive outcomes in small-scale studies
|
|
Post-Ischemic Recovery
|
Facilitates cardiac ATP regeneration
|
Shown to enhance recovery post-myocardial infarction
|
Deoxyribose Properties: Biomarkers for Genetic Disorders
Deoxyribose metabolites serve as critical biomarkers for oxidative stress and DNA damage. Notable examples include:
-
Urinary 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG)
-
Elevated levels in urine indicate increased oxidative DNA damage, correlating with cancer, neurodegeneration, and autoimmune disorders.
-
DNA Strand Breaks in Radiation Therapy
-
The release of deoxyribose degradation products is measured to evaluate radiation-induced genotoxicity in cancer treatment.
With the increasing understanding of sugar modifications in nucleic acids, ribose and deoxyribose analysis has become essential in diagnostics. These sugar components play key roles in genetic regulation and disease mechanisms. Equipped with an advanced technologies for glyco-code based diagnostics, Creative Biolabs is committed to providing comprehensive solutions for glyco-code based diagnostics services. Our services include but are not limited to the following:
Engineering Ribose/Deoxyribose Derivatives
The modification of ribose and deoxyribose has led to biotechnological advancements in gene therapy and diagnostics. Locked nucleic acids (LNAs), for instance, have been developed to improve gene editing by enhancing:
-
Target specificity.
-
Resistance to enzymatic degradation.
-
Improved binding affinity to nucleic acids.
Our platform offers a wide range of glycan modification and labeling services, including : fluorescence labeling, biotinylation service, PEGylation, isotope labeling, sulfate modification, phosphorylation modification, acetylation modification, and berberine labeling studies.
Ribose and deoxyribose play distinct yet complementary roles in nucleic acid function, genetic stability, and cellular metabolism. While ribose facilitates RNA's versatility in cellular signaling and catalysis, deoxyribose provides structural integrity for stable DNA storage. Their modifications and derivatives hold promise in biomedical applications, including gene therapy, metabolic support, and disease biomarker discovery. Future research into engineered nucleic acid analogs, such as LNAs and chemically modified ribose, will further advance precision medicine and biotechnological innovations. Over the past several years, Creative Biolabs has received high praise from researchers worldwide. We are confident that our professional services will contribute to the success of your projects. If you are interested in our ribose- and deoxyribose-related solutions, please feel free to contact us for more details and a customized quote. Let us know your research challenges, and we will be glad to assist you.
FAQs
Q: What is the function of ribose and deoxyribose?
A: Ribose and deoxyribose are important sugars found in nucleic acids. Ribose is contained in RNA, whereas deoxyribose is present in DNA. They combine with phosphate groups and nitrogenous bases to form nucleotides. These nucleotides serve as the foundation for genetic information storage and transmission. Furthermore, their structures affect the stability and overall shape of RNA and DNA molecules.
Q: What is the structural difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
A: Ribose and deoxyribose have virtually identical structures, with one major variation. Ribose contains a hydroxyl group at carbon 2. In contrast, deoxyribose contains a hydrogen atom at the same carbon but no oxygen atom. This makes the deoxyribose molecule more stable than the ribose molecule. The molar mass of ribose is 150.13 g/mol, while that of deoxyribose is 134.14 g/mol. The difference in molar mass is due to the absence of one oxygen atom in the deoxyribose molecule.
Reference
-
Nuevo, Michel, George Cooper, and Scott A. Sandford. "Deoxyribose and deoxysugar derivatives from photoprocessed astrophysical ice analogues and comparison to meteorites." Nature communications 9.1 (2018): 5276. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07693-x
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Ribose and deoxyribose.
Fig.1 Ribose and deoxyribose.

