In glycobiology and disease research, "glycosylation" and "glycation" refer to fundamentally different molecular events, yet they are often confused due to overlapping terminology. At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in resolving this complexity with tailored analytical solutions that distinguish enzymatic glycosylation from non-enzymatic glycation. By offering high-resolution profiling platforms, we support researchers working on glycoproteins, biologics, and glycation-linked pathologies with unmatched technical precision.
How Glycosylation and Glycation Differ?
Glycosylation is a controlled, enzyme-mediated modification that decorates proteins and lipids with carbohydrate chains. This process occurs mainly in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, where glycosyltransferases build complex glycan structures with defined biological roles. In contrast, glycation is a spontaneous, non-enzymatic reaction between reducing sugars and amino groups, often leading to irreversible damage and the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs).
|
Feature
|
Glycosylation
|
Glycation
|
|
Enzymatic?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Site-specific?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Biological Role
|
Regulatory, structural
|
Pathological, damage-associated
|
|
Clinical Marker
|
Cancer glycans, CDGs
|
HbA1c, AGEs
|
|
Detection Method
|
LC-MS/MS, HPLC, lectin profiling
|
AGE-specific ELISA, MS
|
|
Research Use
|
Antibody/vaccine development, glycoengineering
|
Diabetes, neurodegeneration, aging
|
Creative Biolabs offers glycosylation analysis services tailored to differentiate these modifications and reveal their functional implications in health and disease.
Glycosylation: Enzymatic Control with Functional Impact
Glycosylation plays a critical role in protein conformation, stability, receptor interactions, and immunogenicity. It affects biologics' pharmacokinetics, especially monoclonal antibodies and vaccines. Aberrant regulation is linked to congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDGs), tumor progression, and immune dysfunction.
Key Types of Glycosylation
-
N-linked glycosylation: Glycan attachment to the asparagine (Asn) residue within the Asn-X-Ser/Thr motif.
-
O-linked glycosylation: Sugar chains added to the hydroxyl groups of serine or threonine residues.
-
O-GlcNAcylation: Cytosolic/nuclear modification, reversible and dynamic like phosphorylation.
How Creative Biolabs Supports Glycosylation Research?
Our N-glycosylation analysis service focuses on asparagine-linked glycans (Asn-X-Ser/Thr motifs), offering:
-
Site-specific glycopeptide mapping
-
High-throughput glycan profiling by LC-MS/MS
-
Structural analysis to support biopharmaceutical QC and functional validation
For serine/threonine-linked glycans, our O-glycosylation analysis service delivers:
-
O-glycan release and derivatization
-
Detailed sialylation and core structure analysis
-
Support for mucin-type glycoprotein research
Additionally, for functional studies, we offer glycosylation inhibition services using agents such as tunicamycin, swainsonine, and kifunensine. These tools help define the role of glycosylation in protein activity, folding, and immune evasion—critical for target validation and mechanism exploration.
Glycation: A Non-Enzymatic Threat
In contrast to glycosylation, glycation is unregulated, driven by glucose accumulation and oxidative stress. It begins with the non-enzymatic reaction between sugar carbonyl groups and free amino groups on proteins, forming Schiff bases and Amadori intermediates, which can progress to AGEs. Pathological effects of glycation include:
-
Structural impairment of extracellular matrix proteins
-
Chronic inflammation via AGE-RAGE signaling
-
Tissue damage in diabetes, neurodegeneration, atherosclerosis, and renal failure
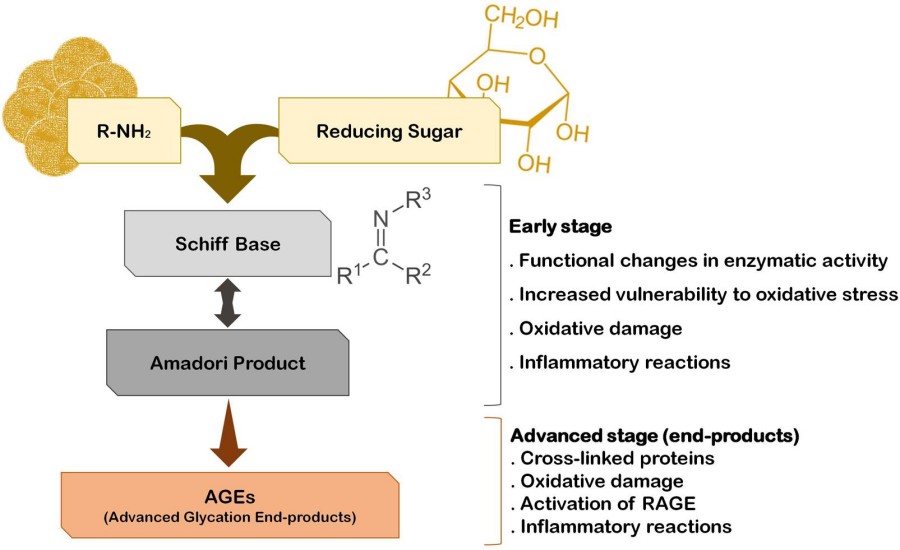 Fig.1 Non-enzymatic protein glycation and AGE pathways.1
Fig.1 Non-enzymatic protein glycation and AGE pathways.1
While Creative Biolabs does not directly provide glycation detection kits, our glycan profiling expertise helps differentiate glycosylated or glycated proteins, especially in biomarker discovery and therapeutic protein characterization.
Advanced Glycosylation Analysis Technologies at Creative Biolabs
To support high-precision glycomics, we employ a suite of cutting-edge platforms for glycosylation analysis:
-
LC-MS/MS for site-specific glycan profiling
-
MALDI-TOF and CE-LIF for structural elucidation
-
Lectin microarrays for glycan pattern comparison
-
SDS-PAGE with glycoprotein-specific staining
-
Glycosylation inhibition assays to investigate biological relevance
Our solutions are tailored for:
-
Biologic drug development
-
Vaccine and antibody engineering
-
Host cell line characterization
-
Biomarker validation in oncology, inflammation, and neurodegeneration
Whether you are screening glycosylation mutants or validating glycoform-dependent function, our end-to-end services ensure reproducibility, throughput, and analytical depth.
Why Researchers Choose Creative Biolabs?
At Creative Biolabs, we combine decades of glycobiology expertise with state-of-the-art instrumentation to deliver:
-
Accurate N- and O-glycan profiling
-
Functional readouts through inhibitor screening
-
Customizable workflows for recombinant proteins, antibodies, and cell lysates
-
Data quality that supports regulatory submission and publication
We ensure every project benefits from our in-depth scientific consultation, customizable assay design, and fast turnaround times. Researchers trust us to deliver actionable results that move discovery forward.
Glycosylation and glycation may sound similar, but their implications are vastly different. Glycosylation is essential and regulated; glycation is uncontrolled and often harmful. Accurate distinction is vital for therapeutic design, disease modeling, and biomarker development. With a full portfolio of high-resolution analytical services, Creative Biolabs is your reliable partner for dissecting glycan complexity. Ready to decode the glycan landscape? Contact us for a customized consultation today.
FAQs
Are glycated and glycosylated the same?
No, glycated and glycosylated are not the same. Glycosylation is an enzyme-mediated and site-specific process that adds glycans to proteins, essential for folding, stability, and function—especially in biologics. Glycation, by contrast, is a non-enzymatic reaction where reducing sugars bind randomly to proteins, often leading to damage and formation of AGEs, associated with diabetes and aging. At Creative Biolabs, we offer advanced glycosylation analysis services, including N-/O-glycan profiling and glycosylation inhibition assays, helping researchers accurately differentiate these modifications and assess their biological relevance in therapeutic development and disease studies.
Can Creative Biolabs help differentiate glycosylated vs glycated proteins in complex biological samples?
Yes. Our analytical platforms are specifically designed to differentiate between enzymatically glycosylated proteins and non-enzymatically glycated proteins. While glycation detection typically relies on AGE-specific assays, our glycosylation profiling workflow uses advanced techniques such as LC-MS/MS, HILIC enrichment, lectin binding assays, and enzymatic deglycosylation strategies to detect site-specific glycan modifications. We do not directly quantify AGEs, but our service helps eliminate false positives by confirming true glycosylation events, which is especially critical when analyzing recombinant proteins, plasma samples, or disease-related glycoprotein biomarkers.
Does Creative Biolabs offer solutions to study how glycosylation affects protein function?
Absolutely. Understanding how specific glycans influence protein function is essential in both basic research and drug development. Our glycosylation inhibition services enable clients to:
-
Inhibit glycosylation pathways using small molecules
-
Study the biological consequences of hypo- or altered glycosylation
-
Validate the functional role of glycan moieties in signaling, binding, or stability
Reference
-
Videira, Paula AQ, and Margarida Castro-Caldas. "Linking glycation and glycosylation with inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease." Frontiers in neuroscience 12 (2018): 381. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00381
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Non-enzymatic protein glycation and AGE pathways.1
Fig.1 Non-enzymatic protein glycation and AGE pathways.1

