Glycosylation is a critical biochemical process that significantly impacts cellular behavior and protein structure while shaping therapeutic design. In fact, over 50% of mammalian proteins are glycosylated, and these modifications are essential for protein folding, receptor function, immune recognition, and disease progression. At Creative Biolabs, we explore the definition, biosynthesis, functional roles, types, and analytical strategies of glycosylation, along with our specialized services in glycosylation analysis with cutting-edge technologies.
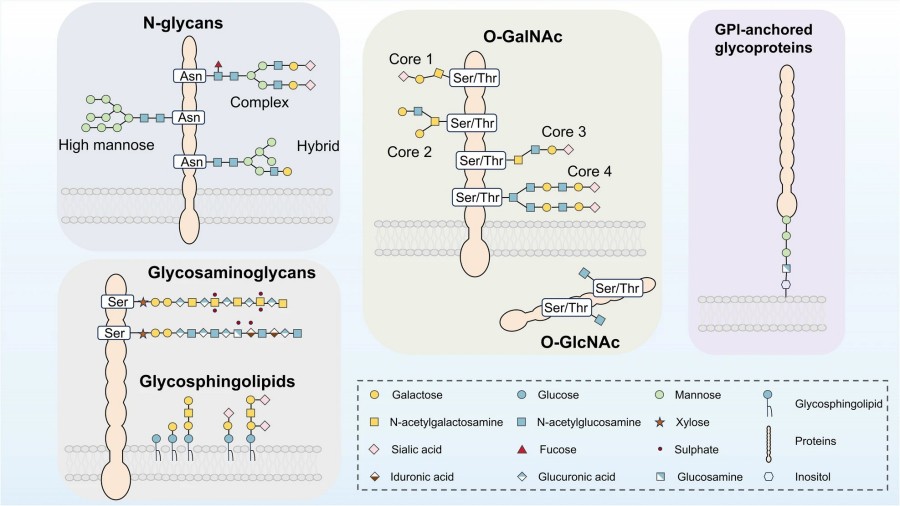 Fig.1 Major types of glycosylation on proteins.1
Fig.1 Major types of glycosylation on proteins.1
Defining Glycosylation
Unlike the non-enzymatic glycation, glycosylation is the enzymatic process of covalently attaching a carbohydrate (glycan) to a protein or a lipid, creating glycoproteins or glycolipids. It begins co-translationally or post-translationally in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and continues in the Golgi apparatus, where the attached glycans are further trimmed and remodeled. While many post-translational modifications are reversible and regulatory (like phosphorylation), glycosylation often imparts structural and functional stability. These glycosylated forms of proteins and lipids decorate the extracellular surface of the plasma membrane and secretory pathways, forming a glycan-rich interface with the environment.
Types of Protein Glycosylation
1. N-linked Glycosylation
This is the most prevalent form in secretory and membrane proteins. The glycan is attached to the amide nitrogen of asparagine in the consensus motif Asn-X-Ser/Thr (where X is not proline). The process begins with the transfer of a 14-sugar precursor (Glc₃Man₉GlcNAc₂) from dolichol pyrophosphate to the nascent polypeptide in the ER, followed by trimming and elaboration in the Golgi.
2. O-linked Glycosylation
This form involves stepwise addition of monosaccharides, starting with N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) to the hydroxyl group of serine or threonine residues. There is no strict consensus sequence, and the modification occurs entirely within the Golgi.
3. C-Mannosylation: Modification of tryptophan residues in thrombospondin motifs
4. GPI Anchoring: Covalent attachment of proteins to membrane lipids via a glycan-phosphatidylinositol anchor
5. O-GlcNAcylation: Occurs in the cytoplasm and nucleus, dynamically regulated and involved in signal transduction, especially under nutrient-sensitive conditions
Which Amino Acids Can Be Glycosylated?
While Asn, Ser, and Thr are most commonly glycosylated, additional residues can be modified:
|
Residue
|
Glycosylation Type
|
Example
|
|
Asparagine
|
N-linked
|
Glycoprotein hormones
|
|
Serine
|
O-linked
|
Mucins
|
|
Threonine
|
O-linked
|
IgA antibodies
|
|
Tryptophan
|
C-linked
|
Perforin
|
|
Tyrosine
|
O-GlcNAc or sulfated glycans
|
Some neuronal proteins
|
|
Hydroxylysine
|
O-glycosylation
|
Collagens
|
Where Does Glycosylation Occur?
Glycosylation predominantly occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi apparatus. The biosynthetic pathway depends on the type of glycosylation:
-
N-linked glycosylation
Initiated in the ER where a preassembled oligosaccharide is transferred to Asn residues; further processed in the Golgi to generate high-mannose, hybrid, or complex glycans.
-
O-GalNAc glycosylation
Occurs mainly in the Golgi, where GalNAc is added to Ser/Thr residues by ppGalNAcTs, followed by core glycan elaboration.
-
O-GlcNAc glycosylation
Takes place in the cytoplasm and nucleus; a single GlcNAc is dynamically added to Ser/Thr residues by OGT, modulating intracellular signaling and transcription.
-
O-fucosylation / O-glucosylation
Occurs in the ER lumen, modifying specific Ser/Thr sites on EGF-like domains, particularly within Notch receptors.
-
C-mannosylation
Takes place in the ER, where mannose is directly linked to tryptophan residues, affecting protein secretion and stability.
-
GPI anchoring
Assembled in the ER, where a glycan-phosphatidylinositol moiety is attached to the C-terminus of target proteins for membrane anchoring.
-
Phosphoglycosylation
Happens in the ER or Golgi, where sugars are attached via phosphate diester linkages, often to Ser residues.
-
GAG (glycosaminoglycan) attachment
Initiated in the ER with xylose addition to Ser, followed by chain elongation in the Golgi to form proteoglycans.
Glycosylation Analysis: Why and How
Glycosylation analysis is also critical for:
Altered glycosylation patterns are hallmarks of numerous diseases:
|
Disease
|
Glycosylation Defect
|
Clinical Consequence
|
|
Colorectal Cancer
|
↑Sialyl-Lewisa, ↑core-fucosylated N-glycans
|
Liver metastasis, poor prognosis
|
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis
|
Agalactosylated IgG Fc
|
Complement activation, inflammation
|
|
Alzheimer's Disease
|
↑O-GlcNAcylation of tau/APP
|
Amyloid-β accumulation
|
|
COVID-19 Severity
|
Defective spike protein glycosylation
|
Immune evasion
|
Analytical Objective & Methods: How to Analyze Glycosylation
|
What is Your Objective?
|
Details Description
|
Technologies for Glycosylation Analysis
|
|
Glycosite Identification
|
Detect specific amino acid residues (e.g., Asn, Ser, Thr) that are glycosylated
|
LC-MS/MS, site-mapping algorithms, ETD fragmentation
|
|
Glycan Profiling
|
Determine glycan composition, branching, and terminal modifications
|
HILIC-HPLC, MALDI-TOF-MS, CE-LIF, released glycan labeling
|
|
Quantitation
|
Measure relative or absolute abundance of glycoforms
|
Label-free MS, isotopic labeling, fluorescence-based HPLC, CE
|
|
Structural Elucidation
|
Resolve isomers, linkages, and saccharide sequences
|
Exoglycosidase digestion + MS, NMR
|
|
Functional Correlation
|
Connect glycan features to biological or pharmacological outcomes
|
Lectin microarrays, SPR/BLI glycan-protein binding, cell-based reporter assays
|
Full Glycosylation Analysis Services at Creative Biolabs
At Creative Biolabs, we offer a comprehensive suite of glycosylation-related services, enabling deep functional insights and regulatory-compliant characterization:
Application
Glycosylation in Disease Research
Aberrant glycosylation drives cancer, congenital disorders, and neurodegeneration; a key focus in disease mechanism studies.
Glycosylation in Immunology
Glycans regulate antibody function and immune signaling; changes link to autoimmunity and inflammation.
Glycosylation in Virus Research
Viruses exploit host glycans for entry and immune evasion; glycosylation is central to viral pathogenesis.
Glycosylation Pathway Analysis
Analyzing biosynthetic glycosylation pathways reveals disease mechanisms and optimizes therapeutic glycoprotein design.
Glycosylation in Receptor Biology
Receptor glycosylation affects folding, trafficking, and signaling; essential for cell communication and drug targeting.
Glycosylation is a fundamental determinant of biomolecular identity and function. From glycosylated amino acids to complex N- and O-linked glycan trees, understanding the nuances of this modification is indispensable for modern biomedicine. Creative Biolabs is committed to delivering customizable glycosylation analysis and engineering solutions, enabling researchers and developers to innovate. Contact our experts to start your project.
Reference
-
He, Mengyuan, Xiangxiang Zhou, and Xin Wang. "Glycosylation: mechanisms, biological functions and clinical implications." Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 9.1 (2024): 194. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01886-1
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Major types of glycosylation on proteins.1
Fig.1 Major types of glycosylation on proteins.1

