Precise glycosylation of specific amino acid residues governs protein structure, stability, immune recognition, and therapeutic efficacy. Rather than a uniform process, glycosylation is highly site- and context-dependent, with distinct mechanisms modifying specific amino acids like asparagine, serine, threonine, tyrosine, tryptophan, lysine, and arginine. This article details the current understanding of residue-specific glycosylation, supported by mechanism diagrams, amino acid specificity, and relevance in biomedical research. At Creative Biolabs, we facilitate glycobiology research and biotherapeutic development through high-resolution, site-specific glycosylation profiling services, ensuring accurate structural elucidation and functional insight.
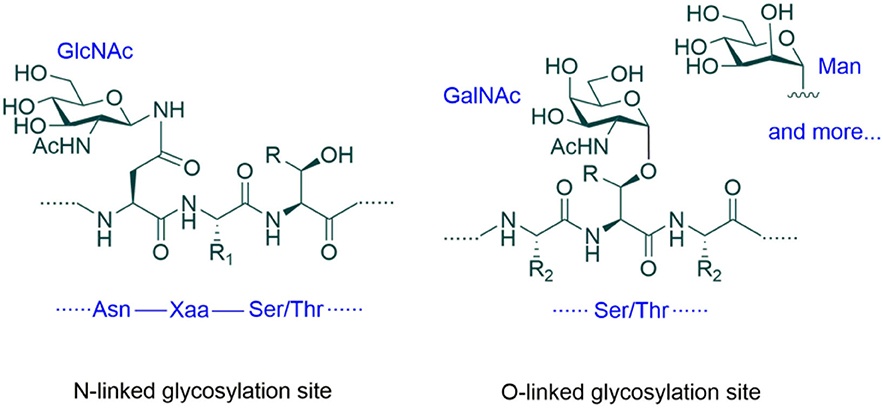 Fig.1 N- and O-linked glycosylation sites.1
Fig.1 N- and O-linked glycosylation sites.1
Overview: Amino Acids That Undergo Glycosylation
|
Amino Acid
|
Type of Glycosylation
|
Linkage
|
Common Contexts
|
|
Asparagine
|
N-glycosylation
|
N-glycosidic (amide N)
|
Secretory proteins, antibodies, receptors
|
|
Serine
|
O-glycosylation
|
O-glycosidic (hydroxyl O)
|
Mucins, cytoskeletal proteins, O-GlcNAc sites
|
|
Threonine
|
O-glycosylation
|
O-glycosidic
|
Mucin domains, IgA, adhesion proteins
|
|
Tyrosine
|
O-glycosylation (rare)
|
O-glycosidic
|
Regulatory proteins
|
|
Tryptophan
|
C-glycosylation
|
C–C bond (C2 of indole)
|
Thrombospondins, cell adhesion proteins
|
|
Lysine
|
O-GlcNAc-like (emerging)
|
ε-amino glycosidic
|
Epigenetic regulation, histone modification
|
Different Specific Amino Acid Glycosylation
Precise glycosylation of specific amino acids is central to protein folding, stability, signaling, and immunogenicity. Advances in glycoproteomics have made it possible to analyze glycosylation at the residue level, particularly for asparagine, serine, threonine, and emerging sites like lysine and tryptophan. This is now essential in both basic research and biopharmaceutical development. At Creative Biolabs, we provide a full suite of glycosylation analysis services, enabling high-resolution mapping, structural elucidation, and functional evaluation of glycosylation across all relevant amino acid types. Our platform combines LC-MS/MS, linkage-specific enzymatic cleavage, and glycan-specific enrichment strategies, tailored to the complexity of your project.
N-Glycosylation
N-glycosylation occurs at asparagine (Asn) residues within the canonical Asn-X-Ser/Thr motif (X ≠ Proline), where a lipid-linked oligosaccharide is transferred en bloc during protein synthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum. The attached glycan is trimmed and remodeled to produce high-mannose, hybrid, or complex N-glycans. This alteration affects protein folding, intracellular transport, and therapeutic antibody function. Specifically, Fc glycosylation at Asn297 affects ADCC and serum half-life. Our N-glycosylation analysis services offer detailed site occupancy determination, glycoform profiling, and structure-function correlation, using high-sensitivity MS and exoglycosidase sequencing, suitable for both discovery-stage and regulatory-submission-level studies.
O-Glycosylation
O-glycosylation modifies the hydroxyl groups of serine, threonine, and occasionally tyrosine without a fixed sequence motif. Mucin-type O-glycosylation starts with GalNAc addition, whereas O-GlcNAcylation, which occurs in nuclear and cytoplasmic sections, is more dynamic and reversible. These modifications affect epithelial integrity, transcription regulation, and immune responses. Aberrant O-glycans such as Tn/sTn are hallmarks of tumor transformation. Our O-glycosylation analysis services support detailed glycan structure mapping, isomer differentiation, and tumor-associated glycoform identification using techniques like ETD fragmentation, lectin arrays, and site-specific peptide enrichment.
C-Glycosylation
C-glycosylation, though rare, introduces a mannose residue directly onto the indole ring of tryptophan via a C–C bond. Catalyzed by C-mannosyltransferases in the ER, this modification is chemically stable and resistant to enzymatic cleavage, often influencing the folding and secretion of extracellular matrix proteins such as thrombospondins and adhesion molecules. Given its role in modulating cytokine receptor function and pathogen recognition, Creative Biolabs provides tailored LC-MS workflows with customized sample preparation to detect and quantify C-glycosylation even at low abundance.
Phosphoglycosylation
Phosphoglycosylation introduces sugar-phosphate groups to serine or threonine residues, forming phosphodiester linkages often seen in bacterial glycoproteins and lysosomal targeting signals. This negatively charged moiety alters solubility, trafficking, and immunogenicity. Although underexplored in eukaryotic systems, it holds value in microbial glycoproteomics and vaccine development. Our platform enables detection and characterization of phosphoglycosylation through high-resolution MS, offering new opportunities in bacterial glycoengineering and innate immune studies.
Glypiation
Glypiation is the covalent attachment of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors to the C-terminus of proteins, which aids in their localization to the cell membrane and lipid rafts. These membrane-tethered proteins, like as CD55 and CD59, are essential for immunological control and signal transmission. Disruption of GPI biosynthesis relates to diseases such as paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Creative Biolabs provides GPI-anchor detection and structural characterization, allowing for functional annotation of glypiated proteins and assessment of their involvement in membrane dynamics and therapeutic targeting.
Lysine Glycosylation
Recent research suggests that lysine residues, particularly those in histone proteins, may be glycosylated using O-GlcNAc or other sugar moieties. This uncommon alteration competes with acetylation and ubiquitination, implicating it in chromatin remodeling and gene expression regulation. Lysine glycosylation, despite being less well understood mechanistically, represents a new epigenetic regulatory pathway. At Creative Biolabs, we provide tailored enrichment techniques and top-down MS analysis to examine low-abundance, non-canonical glycosylation events, hence advancing research into transcriptional regulation and disease epigenetics.
Arginine Glycosylation
Arginine-linked glycosylation, though not confirmed in humans, has been observed in certain bacterial and parasitic systems, where it modifies host signaling pathways by targeting arginine residues on regulatory proteins. This strategy, used by Clostridium difficile and Toxoplasma gondii, highlights a unique mechanism of immune evasion. With increasing interest in pathogen-host glycosylation cross-talk, Creative Biolabs supports glycoimmunology research through sensitive PTM discovery platforms and de novo glycopeptide identification pipelines, helping researchers characterize novel glyco-modifications.
Why Choose Creative Biolabs for Amino Acid-Specific Glycosylation Analysis?
Creative Biolabs combines domain-specific expertise, advanced instrumentation, and flexible service modules to support every stage of your glycosylation research. Whether you are dissecting canonical Asn-linked pathways, studying rare C-linked events, or probing disease-relevant O-GlcNAc dynamics, our glycosylation analysis solutions offer:
-
Residue-specific mapping with site-level confidence
-
Structural elucidation of complex or novel glycans
-
Quantitative glycoform profiling with intact and glycopeptide-based workflows
-
Custom assay design for low-abundance or unconventional targets
Specific amino acid glycosylation governs diverse biological pathways and therapeutic outcomes. Asparagine (N-glycosylation) and serine/threonine (O-glycosylation) remain central, but growing evidence supports roles for C-, lysine-, and arginine-linked glycosylation in regulation and disease. At Creative Biolabs, we combine advanced mass spectrometry, glyco-specific labeling, and enzymatic validation to deliver residue-resolved glycosylation profiles for the development of modern glycoproteomics. Contact our glycoscience team to discuss your project goals or request a quote.
FAQs
Q: Which amino acids are involved in glycosylation?
A: Glycosylation occurs primarily on Asn (N-glycosylation), Ser and Thr (O-glycosylation), and occasionally Tyr (O-glycosylation). Less common modifications are found on Trp, Lys, and Arg. Creative Biolabs offers tailored glycosylation analysis services, utilizing advanced techniques to map these modifications and support your research needs comprehensively.
Q: On which amino acid does N-glycosylation occur?
A: N-glycosylation exclusively occurs on asparagine (Asn) residues, specifically within the consensus motif Asn-X-Ser/Thr (where X ≠ Proline). This modification is critical for protein folding, stability, and function, especially in therapeutic proteins like monoclonal antibodies. Our N-glycosylation analysis services provide in-depth mapping of glycan structures at Asn sites, helping researchers and biopharma companies achieve accurate glycosylation profiles for drug development.
Reference
-
Ma, Bo, et al. "Protein glycoengineering: an approach for improving protein properties." Frontiers in Chemistry 8 (2020): 622. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00622
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 N- and O-linked glycosylation sites.1
Fig.1 N- and O-linked glycosylation sites.1

