Glycosylation—particularly N-linked and O-linked modifications—is central to the structure, function, and pharmacokinetics of many biologics. While both forms contribute to protein diversity and biological complexity, their differences in biosynthesis, linkage specificity, and structural variation demand distinct analytical strategies. At Creative Biolabs, we provide end-to-end glycosylation analysis solutions to resolve these complexities through advanced N-glycosylation analysis services and O-glycosylation analysis services, enabling precise glycoform characterization across diverse sample types.
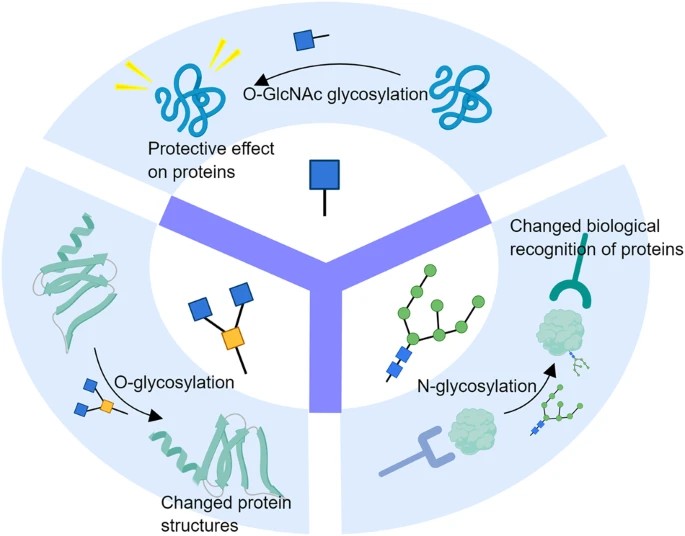 Fig.1 N-, O-, and O-GlcNAc Glycosylation in Protein Structure and Function.1
Fig.1 N-, O-, and O-GlcNAc Glycosylation in Protein Structure and Function.1
How to Analyze N- and O-Linked Glycosylation with Precision?
N-linked glycans are covalently attached to the asparagine residue within the Asn-X-Ser/Thr consensus motif, predominantly co-translationally in the endoplasmic reticulum. These structures are often branched and heavily modified in the Golgi apparatus, resulting in complex glycoforms that influence immunogenicity, serum half-life, and receptor interactions. In contrast, O-linked glycans are typically added to serine or threonine residues in a post-translational fashion, often without a clear consensus sequence, leading to a wider range of glycan structures, particularly in mucin-type proteins.
Such diversity poses analytical challenges—especially in glycosite mapping, microheterogeneity profiling, and glycan occupancy analysis. Creative Biolabs addresses these with a comprehensive platform that includes enzymatic deglycosylation, glycan labeling, HILIC and MALDI-TOF profiling, and high-resolution LC-MS/MS for both released glycans and intact glycopeptides. For O-glycans, where enzymatic cleavage is limited, we offer chemical β-elimination and optimized workflows for O-glycosylation mapping using tandem MS and lectin-enrichment strategies. These tailored methods ensure confident assignment of site occupancy and structural variations, even in low-abundance glycoforms.
With decades of project experience in glycoprotein biologics, antibody Fc engineering, recombinant mucin analysis, and vaccine glycosylation profiling, we support both basic research and regulated biologics development. Our services are flexible, customizable, and fully documented to meet regulatory expectations.
N-linked vs O-linked Glycosylation: Key Differences and Analytical Decision-Making
Researchers often ask: Which glycosylation type matters more in my biologic system? The answer depends on the protein context, expression system, and research goals.
N-linked glycosylation follows a conserved biosynthetic path and typically modifies secreted or membrane-bound proteins at defined Asn sites. It contributes to protein folding efficiency, thermal stability, and Fc receptor interaction in monoclonal antibodies. In contrast, O-linked glycosylation is more variable, often modulating mucin viscosity, pathogen binding, or immune shielding through tissue-specific glycoforms.
Because N-glycans are more predictable, analytical workflows such as PNGase F release followed by LC-MS are well-established. For proteins with complex N-glycosylation (e.g., mAbs, cytokines, hormones), Creative Biolabs delivers high-throughput, quantitative glycan profiling to support biosimilarity assessments and batch-release testing via our N-glycosylation analysis platform.
O-glycosylation, however, lacks universal enzymatic release tools and often requires protein- or tissue-specific optimization. This is especially relevant in mucin-domain proteins and membrane receptors such as MUC1 or CD43, where the O-glycan composition directly impacts biological activity and pathology. Our specialized O-glycosylation analysis platform provide not only glycan structural identification but also site-localization, glycosite occupancy evaluation, and core type differentiation, even in low-abundance scenarios.
Choosing the Right Approach: N vs O Glycosylation
|
Analytical Consideration
|
N-linked Focused
|
O-linked Focused
|
|
Predictable sites
|
✔ Yes
|
✘ No
|
|
Enzymatic deglycosylation
|
✔ PNGase F
|
✘ None universal
|
|
High abundance on proteins
|
✔ Often
|
✘ Often low
|
|
Glycan heterogeneity
|
✔ Complex types
|
✔ Core/extended variants
|
|
Research applications
|
Biologics, mAbs, Fc studies
|
Mucins, cancer, signaling
|
Biopharmaceutical Applications: From Antibodies to Cancer Mucins
Monoclonal Antibodies and Fc Glycosylation
Fc-linked N-glycans at Asn297 in IgG1 antibodies are essential for effector functions, particularly ADCC and CDC. Absence or truncation of fucose can enhance FcγRIIIa binding, a principle used in glycoengineered antibodies such as obinutuzumab. Creative Biolabs supports Fc glycan profiling, fucosylation ratio quantification, and glycoform batch consistency analysis, essential for biosimilar development and release testing.
Vaccine Antigen Glycosylation
Glycosylation on vaccine antigens can influence immunogenicity by shielding or exposing epitopes. For instance, in the HIV gp120 envelope glycoprotein, both N- and O-glycosylation patterns affect epitope accessibility and immune evasion. Accurate site mapping of these glycans is critical in rational immunogen design. Our MS-based mapping strategies have been employed for detailed analysis of envelope glycoprotein glycans in vaccine studies.
Cancer-Associated Mucin-type O-Glycosylation
Aberrant O-glycosylation in cancer alters mucin function and creates tumor-associated epitopes such as Tn, sTn, and core 1 antigens. Proteins like MUC1, overexpressed and hypoglycosylated in breast and pancreatic cancers, require detailed O-glycan mapping to guide biomarker development and immunotherapy. Creative Biolabs' mucin-targeted glycosylation services support researchers investigating these cancer-specific glycan signatures.
Why Partner with Creative Biolabs?
With several years of specialized experience in glycoprotein science, we provide deep technical insight and tailored analytical solutions that meet the evolving needs of academic researchers, biotech innovators, and biologics developers.
-
We provide full-spectrum N- and O-glycosylation analysis with integrated workflows from digestion to glycopeptide mapping.
-
Our protocols are tailored to protein type, expression system, and glycan complexity for reliable, site-specific results.
-
Our team brings decades of experience in analyzing antibodies, mucins, and membrane glycoproteins.
-
We work closely with clients, offering transparent communication and expert guidance at every step.
At Creative Biolabs, our glycoproteomics expertise, advanced instrumentation, and customizable workflows allow us to support complex N- and O-linked glycosylation studies for discovery-stage characterization. Whether you're working with monoclonal antibodies, recombinant enzymes, mucin-domain proteins, or viral glycoproteins, we offer technical excellence, project flexibility, and full data transparency.
FAQs
Q: How do I determine whether my protein is N-glycosylated, O-glycosylated, or both?
A: This depends on the protein sequence, structure, expression system, and post-translational modification patterns. At Creative Biolabs, we begin with an in silico prediction using established glycosylation motif databases, followed by preliminary experimental lectin-based screening. For ambiguous or dual-modified proteins, we apply integrated LC-MS/MS profiling to distinguish and localize N- and O-linked glycans simultaneously, offering a clear glycosylation map early in your project.
Q: My recombinant protein is expressed in CHO cells—how does that impact glycosylation analysis?
A: CHO cells primarily generate mammalian-type N-glycans with characteristic core fucosylation and sialylation, but may show limited O-glycosylation activity depending on the protein. We tailor our workflow accordingly: for N-glycans, we use standard enzymatic release with MS-based quantification; for O-glycans, we perform targeted chemical release and site mapping. Our CHO-optimized method accounts for host-specific glycoforms, ensuring precise detection and structural annotation across batches.
Q: Can you analyze glycosylation heterogeneity at specific glycosylation sites?
A: Yes. Our platform supports site-specific microheterogeneity analysis using high-resolution LC-MS/MS coupled with glycopeptide enrichment techniques. This allows us to quantify and compare different glycoforms (e.g., fucosylated, sialylated, high-mannose) present at each glycosylation site. For example, in Fc-region glycoprofiling, we can resolve fucosylation and galactosylation patterns at Asn297 with single-residue precision.
Q: Do you offer comparative glycosylation analysis for biosimilar development?
A: Yes. For biosimilar projects, we conduct comparative glycan profiling between the reference product and the candidate, covering site occupancy, glycoform distribution, and structural similarity. Differences in N- or O-glycosylation can impact efficacy or immunogenicity, so we use a combination of released glycan analysis and intact glycopeptide mapping to deliver a full similarity report. This data is instrumental in demonstrating biosimilarity.
References
-
Zhao, Jingwei, and Minglin Lang. "New insight into protein glycosylation in the development of Alzheimer's disease." Cell death discovery 9.1 (2023): 314. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-023-01617-5
-
Higel, Fabian, et al. "N-glycosylation heterogeneity and the influence on structure, function and pharmacokinetics of monoclonal antibodies and Fc fusion proteins." European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics 100 (2016): 94-100. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06121-4
-
Cao, Liwei, et al. "Differential processing of HIV envelope glycans on the virus and soluble recombinant trimer." Nature communications 9.1 (2018): 3693. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06121-4
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 N-, O-, and O-GlcNAc Glycosylation in Protein Structure and Function.1
Fig.1 N-, O-, and O-GlcNAc Glycosylation in Protein Structure and Function.1

