Glycosylation is a key biological process. It's not just about structure—it also sends active signals in the immune system. In immunology, glycans influence many things. They guide how receptors send signals, how antibodies work, immune tolerance, and inflammatory responses. These sugar structures are dynamic. They change as cells differentiate, when diseases occur, or during treatment. At Creative Biolabs, we offer glycosylation analysis services. Our team uses advanced analytical tools and has deep knowledge of glycol-immunology, supporting basic research, therapeutic design, and biomarker discovery. Our custom services help researchers study and adjust immune glycosylation accurately.
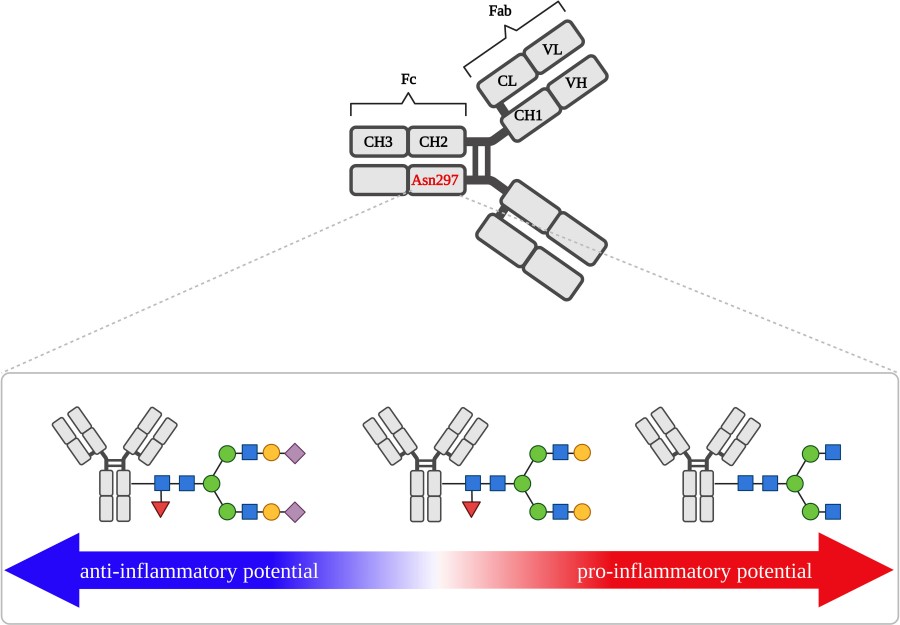 Fig.1 How Fc N-glycan structure at Asn297 shapes IgG's pro- or anti-inflammatory function.1
Fig.1 How Fc N-glycan structure at Asn297 shapes IgG's pro- or anti-inflammatory function.1
Immunoglobulin Glycosylation
Immunoglobulins—including IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE—carry N-linked (and sometimes O-linked) glycans that profoundly affect their biological behavior. Glycans modulate interactions with Fc receptors, complement components, and antigenic targets, while influencing molecule conformation, solubility, and in vivo stability.
|
Isotype
|
Major Glycosylation Sites
|
Glycan Type
|
Functional Impacts
|
|
IgG
|
Asn297 (Fc), ±Fab
|
N-glycan
|
Effector function (ADCC, CDC), half-life
|
|
IgA1
|
O-glycan-rich hinge, Asn Fc sites
|
N- and O-glycan
|
Mucosal defense, IgA nephropathy risk
|
|
IgM
|
Multiple Asn in Fc
|
N-glycan
|
Complement activation, pentamer stability
|
|
IgE
|
6–7 N-glycans in Fc
|
N-glycan
|
Allergenicity, mast cell activation
|
IgG Glycosylation: A Central Regulator of Immune Activity
The Fc region of IgG contains a conserved N-glycosylation site at Asn297. This single site defines a multitude of immunological consequences:
-
Fucosylation reduces FcγRIIIa affinity and dampens ADCC; afucosylated IgG enhances cytotoxic potential.
-
Sialylation confers anti-inflammatory effects, underpinning mechanisms of IVIg therapy.
-
Galactosylation decreases with aging and inflammation; higher levels associate with immunosuppressive activity.
-
Bisecting GlcNAc enhances receptor engagement and cytotoxic response.
IgG glycosylation also occurs in the Fab domain in up to 25% of antibodies, impacting antigen affinity and pharmacokinetics. Notably, Fab glycans tend to be more galactosylated and sialylated than their Fc counterparts, highlighting differential regulatory potential within the same molecule.
Isotype-Specific Glycosylation Characteristics
-
IgA: Particularly IgA1 carries clustered O-glycans in the hinge region. Aberrant O-glycosylation is linked to IgA nephropathy and altered mucosal protection.
-
IgM: With five Fc N-glycosylation sites, glycan remodeling affects multimer formation and classical complement activation.
-
IgE: Dense N-glycosylation is essential for FcεRI binding and anaphylaxis initiation. Removal of a single glycan can prevent mast cell degranulation.
When You Need to Analyze Glycosylation in Immunology
Glycosylation analysis is not routine—it's strategic. Below are key contexts where detailed glycan profiling is essential:
Therapeutic Antibody Development
Antibodies used in cancer or infectious disease immunotherapy must be glyco-optimized. Afucosylated variants are now standard for enhancing ADCC. Glycoengineering allows fine-tuning of efficacy, safety, and half-life. Creative Biolabs offers robust platforms for generating and comparing glycoforms during clone screening and cell line development.
Autoimmune Disease Research
Changes in IgG glycosylation patterns—reduced galactosylation, desialylation, altered fucosylation—correlate with disease activity and treatment response in RA, SLE, and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Monitoring these shifts provides both mechanistic insight and potential diagnostic value.
Allergy and IgE Functional Modulation
In allergic disease research, IgE glycosylation status affects receptor binding and effector cell activation. By manipulating glycosylation, it's possible to design hypoallergenic variants for safer desensitization therapies.
Vaccine Antigen Design
Many viral glycoproteins are shielded by host-derived glycans. Profiling and engineering glycosylation on antigens can improve immune recognition and enhance vaccine efficacy.
Biomarker Discovery
Glycan-based biomarkers—such as agalactosylated IgG species—are being validated for use in early detection, prognosis, and therapeutic monitoring.
Technologies for Glycosylation Analysis
Creative Biolabs provides a suite of complementary platforms to characterize immune glycosylation at multiple levels. Each technology is integrated with robust data analysis pipelines, supporting glycan structure assignment, relative abundance, and glycoform comparison across biological conditions. Our offerings include but not limited to:
-
LC-MS/MS: Gold standard for in-depth glycan and glycopeptide structural elucidation. Enables site-specific occupancy, microheterogeneity analysis, and quantitation.
-
UPLC with Fluorescence or MS Detection: High-resolution separation of labeled glycans for quantitative comparisons across samples.
-
CE-LIF: Ultra-sensitive detection and profiling of charged glycans, including sialylation variants.
-
Glycan Microarrays & Lectin Profiling: Rapid screening of glycan motifs and binding interactions with immune receptors or antibodies.
Tailored Solutions at Creative Biolabs
We offer end-to-end solutions for immunoglobulin glycome analysis:
Fine-tune therapeutic antibodies with our customized engineering pipelines:
-
Afucosylated IgG1/IgG3 production
-
Sialylation enhancement for anti-inflammatory use
-
Glycoform editing in cells
Creative Biolabs offers end-to-end support for the discovery and characterization of antibodies against glycosylated antigens:
-
Antibodies against tumor-associated glycoepitopes
-
Anti-glycan antibodies that targeting conserved viral or bacterial glycans for infectious diseases
-
Glycoform-specific antibody screening to identify antibodies that differentiate glycosylated and non-glycosylated protein.
-
Customized antigen design used for high-affinity antibody induction.
Glycosylation orchestrates immune outcomes with molecular finesse. As research progresses toward more selective immune modulation and antibody-based interventions, glycan profiling becomes indispensable. Whether you're mapping subtle shifts in IgG glycosylation in autoimmune diseases, developing a next-gen glycoengineered mAb, or exploring B-cell glycan biology, Creative Biolabs delivers the analytical rigor and technical flexibility your work demands. Contact us to partner with us in studying glycosylation-driven immunology.
Reference
-
Trzos, Sara, Paweł Link-Lenczowski, and Ewa Pocheć. "The role of N-glycosylation in B-cell biology and IgG activity. The aspects of autoimmunity and anti-inflammatory therapy." Frontiers in Immunology 14 (2023): 1188838. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1188838
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 How Fc N-glycan structure at Asn297 shapes IgG's pro- or anti-inflammatory function.1
Fig.1 How Fc N-glycan structure at Asn297 shapes IgG's pro- or anti-inflammatory function.1

