Carbohydrate chains, often termed the "molecular code" of cell surfaces and secreted proteins, dynamically regulate immune recognition, inflammatory responses, and disease progression through glycosylation. In chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease, aberrant glycosylation alters the conformation of immune cell surface receptors, disrupting the balance of pro-inflammatory cytokine release. For instance, tumor cells evade immune surveillance via sialylated glycans, while the absence of fucosylation in the IgG Fc domain enhances anti-inflammatory activity. To unravel the molecular mechanisms of carbohydrate-mediated immune regulation, Creative Biolabs offers integrated solutions for custom glycan synthesis, carbohydrate analysis, glycan modification and labeling, and glycoengineering, supporting research from foundational studies to therapeutic development. By precisely deciphering glycan structures and functions, we empower clients to target inflammatory pathways and innovate therapies.
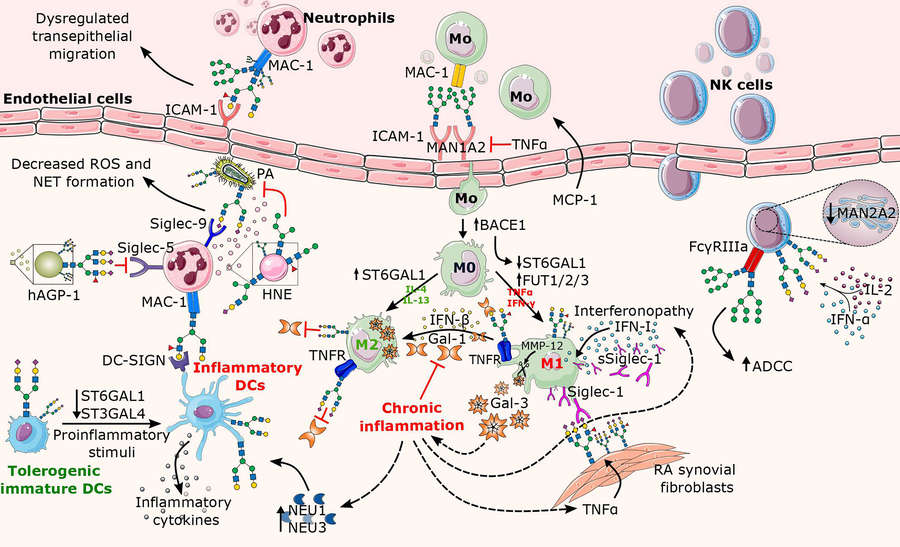 Fig.1 Altered N-glycosylation pathways in chronic inflammation.1
Fig.1 Altered N-glycosylation pathways in chronic inflammation.1
Decoding Inflammation-Associated Glycosylation Mechanisms
Inflammatory Glycosylation Markers and Their Regulation
Carbohydrate chains participate in inflammatory microenvironment regulation through dynamic modifications such as sialylation and sulfation. For example, sialylated glycans on selectin ligands mediate leukocyte migration to inflamed tissues, while O-glycans on intestinal mucins form gelling barriers to inhibit pathogen invasion. In allergic reactions, the alpha-gal carbohydrate side chain triggers mast cell degranulation, leading to severe anaphylaxis. Using advanced glycan analysis technologies (e.g., mass spectrometry, glycobiology microarray), we precisely resolve the fine structures of inflammation-associated glycans (e.g., sulfation sites, branching patterns), uncovering their links to disease progression.
Carbohydrate-Mediated Immune Cell Activation and Signaling
Acting as "molecular antennas," glycans directly modulate Toll-like receptor (TLR) and cytokine signaling pathways. Medium-chain carbohydrates, for instance, activate dendritic cells to enhance antigen presentation, while free radicals exacerbate inflammatory damage by oxidizing glycans and disrupting mitochondrial function. Through custom glycan synthesis, we replicate naturally occurring immunomodulatory glycosylation patterns (e.g., bisecting GlcNAc N-glycans), delivering high-purity standards for drug screening.
Carbohydrate Synthesis, Modification & Analysis: Bridging Research and Application
High-Precision Glycan Synthesis
Chemoenzymatic synthesis enables efficient production of homogeneous glycans. Introducing bisecting GlcNAc into antibody N-glycans, for example, enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), while custom-synthesized heparan sulfate (HS) mimics natural anti-inflammatory activity. Our chemical/enzymatic synthesis platform supports gram-scale production of complex glycoforms (e.g., high-mannose, hybrid types), meeting demands for drug development.
Tailored Glycan Modification & Labeling Strategies
Functional enhancements via sulfation, acetylation, and other modifications are well-documented. Sulfated polysaccharides suppress pro-inflammatory cytokine release by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway, while acetylated glycans resist enzymatic degradation. Our glycan modification and labeling technologies optimize physicochemical properties (e.g., solubility, targeting), accelerating the clinical translation of anti-inflammatory therapeutics.
Real-time tracking of glycan dynamics in inflammatory microenvironments is critical. Free radicals activate oxidative stress pathways via glycan-mediated mitochondrial damage, while emerging discoveries like glycoRNA highlight novel inflammatory signaling mechanisms. Leveraging live-cell glycan labeling, we spatially and temporally monitor glycan modifications in disease models, uncovering regulatory mechanisms.
Structural and Functional Glycan Profiling
Mass spectrometry-based N-glycan mapping reveals correlations between glycosylation sites and disease biomarkers. For instance, reduced IgG sialylation correlates with rheumatoid arthritis severity, while truncated mucin glycans compromise intestinal barrier integrity. We offer glycoprotein interaction studies using surface plasmon resonance (SPR) to analyze glycan-lectin binding kinetics, guiding rational drug design.
Glycoengineering-Driven Therapeutic Interventions in Inflammation
Antibody Glycoengineering Optimization
Glycosylation remodeling in mammalian/non-mammalian systems (e.g., CHO cells, yeast) enhances therapeutic efficacy. Defucosylation of IgG Fc boosts ADCC activity, while sialylation extends serum half-life. Our antibody glycoengineering platform enables custom modifications (e.g., fucose knockout, high-mannose glycoforms), advancing next-generation biologics.
Polysaccharide based Drug Development
Sulfated polysaccharides (e.g., heparin analogs) combat inflammation by inhibiting complement activation and cytokine storms. Custom low-molecular-weight HS targets IL-6 signaling, mitigating acute lung injury. We provide polysaccharides analysis services, including heparan sulfate analysis service, 3-O-sulfation analysis service, and fibre analysis service, to accelerate lead compound discovery.
Published Data
N-glycan biosynthesis plays a vital role in immune system regulation throughout inflammatory responses. The glycosyltransferases B4GALT1, FUTs, GCNT2 along with sialyltransferases ST6GAL1 and ST3GAL4 create structural changes to N-glycans present on endothelial cells, leukocytes and secreted proteins. The activity of key glycosyltransferases gets modulated by proinflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-1β which results in changes to glycan structures including sialylation, fucosylation and branching patterns. TNF-α boosts expression of FUT7/9 and ST3GAL4 which leads to increased production of sialyl-LewisX (sLeX) on selectin ligands and facilitates leukocyte-endothelial cell binding. Decreased ST6GAL1 activity results in reduced α2,6-sialylation which disrupts inhibitory Siglec interactions and increases inflammatory signaling. Immune cell activation and migration and cytokine release are directly governed by carbohydrate-dependent interactions which involve galectin attachment to LacNAc motifs and Siglec binding to sialylated glycans. The results show that glycan changes during inflammation create a dynamic bridge connecting cellular communication with disease progression while establishing glycosylation as a critical factor in immune system balance and chronic inflammatory disease pathways.
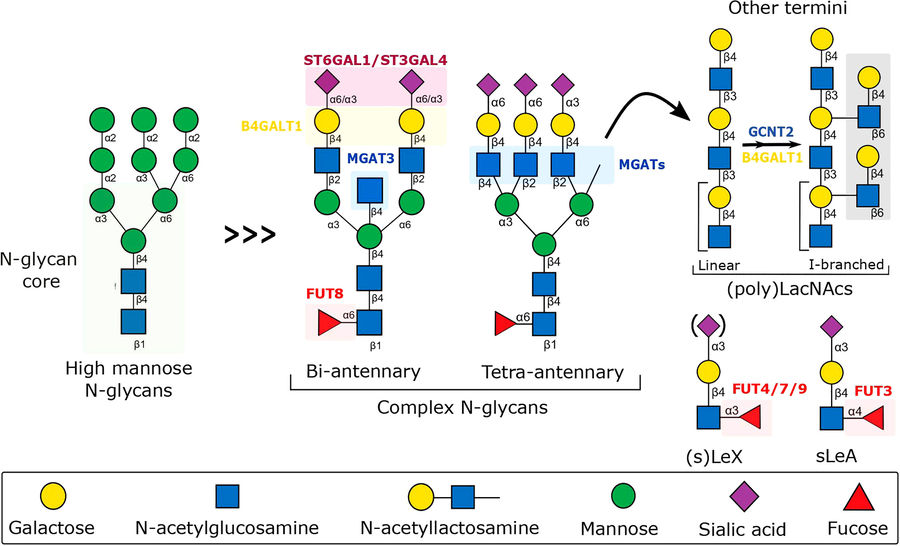 Fig.2 N-Glycan biosynthesis: Fine-tuning immune response to inflammation.1
Fig.2 N-Glycan biosynthesis: Fine-tuning immune response to inflammation.1
In chronic inflammation models, our glycan analysis can identify CD44 hyaluronic acid-binding domain glycosylation anomalies, revealing novel targets for osteoarthritis therapy. In allergen research, alpha-gal detection technologies aid in developing low-immunogenicity antibodies. Additionally, mucin glycan gelling modifications offer innovative solutions for oral drug delivery. Integrating glycomics with AI predictive models will propel carbohydrate research into the era of precision medicine. We are committed to cross-disciplinary innovation, advancing glycans in immunotherapy, regenerative medicine, and beyond. If you are interested in unlocking the molecular secrets of inflammation and immune regulation with our expertise, contact us for end-to-end tailored solutions from discovery to clinical translation.
Reference
-
Radovani, Barbara, and Ivan Gudelj. "N-glycosylation and inflammation; the not-so-sweet relation." Frontiers in immunology 13 (2022): 893365. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.893365
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Altered N-glycosylation pathways in chronic inflammation.1
Fig.1 Altered N-glycosylation pathways in chronic inflammation.1
 Fig.2 N-Glycan biosynthesis: Fine-tuning immune response to inflammation.1
Fig.2 N-Glycan biosynthesis: Fine-tuning immune response to inflammation.1

