Carbohydrate Chains in Neural Development
During the initial phases of neural development, carbohydrate chains control vital processes including neural differentiation, migration, and synaptogenesis. The post-translational modification known as glycosylation involves attaching sugar molecules to proteins and lipids to facilitate essential cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions required for neural network organization.
Glycosylation in Brain Cell Differentiation
Precise glycosylation in neurons as a post-translational modification process initiates the organization of carbohydrate chains which regulate neurogenesis during neural development. Neural stem cells (NSCs) divide asymmetrically during embryonic cortical development through glycoconjugate-mediated signaling pathways. Specific glycoforms including LewisX antigens found on neural stem cell surface markers establish the link between glycosylation and neural stem cells by maintaining stemness through Wnt/β-catenin pathway modulation. Creative Biolabs can help you with that:
-
Glycosylation in brain cells determines NSC fate via Notch signaling modulation.
-
Polysialic acid (PSA) on NCAM regulates radial glial cell migration.
-
O-GlcNAcylation of transcription factors (Sox2, Pax6) controls neuroepithelial differentiation.
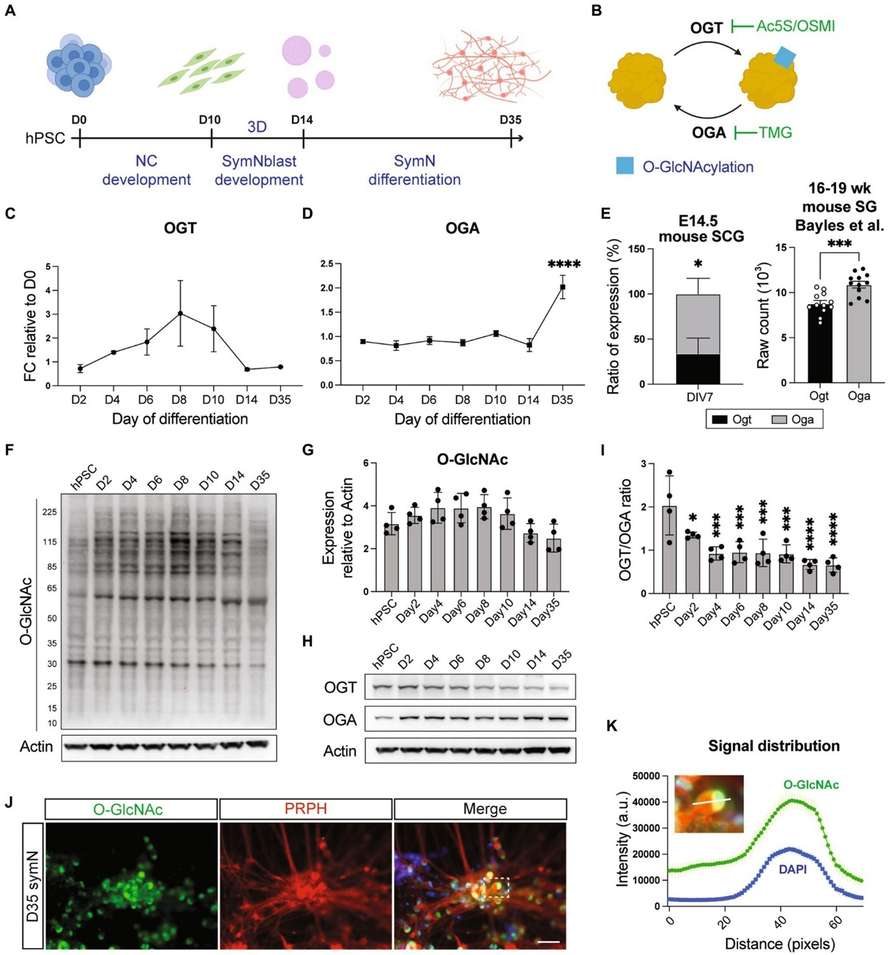 Fig.1 O-GlcNAcylation in sympathetic neurons.1
Fig.1 O-GlcNAcylation in sympathetic neurons.1
Impact on Neural Maturation
As neurons mature, carbohydrate chains in cell membrane components undergo dynamic remodeling. The transition from PSA-NCAM to mature NCAM isoforms coordinates:
-
Axonal pathfinding through glycosaminoglycan (GAG)-semaphorin interactions.
-
Dendritic arborization via N-glycan-dependent TrkB receptor clustering.
-
Myelination regulated by galactocerebroside-sulfatide ratios in oligodendrocytes.
Our neuronal maturation glycan array demonstrates how β1,6-branched N-glycans:
-
Stabilize glutamate receptor subunits (GluA2/3) at postsynaptic densities.
-
Modulate voltage-gated sodium channel clustering through sialic acid residues.
-
Facilitate GABAergic synapse maturation via glypican-3 heparan sulfate interactions.
At Creative Biolabs, we offer a wide range of glycobiology microarrays, including specialized glycan microarrays, to advance your research in glycoproteins, glycosaminoglycans, and more.
Carbohydrates in Brain Signaling Pathways
The carbohydrate chains in cell signaling function as molecular antennas, with specific glycoepitopes acting as:
-
Co-receptors for growth factors (FGF2-HS proteoglycan complex).
-
Spatial organizers of receptor tyrosine kinases (EGFR galectin lattice).
-
Modulators of chemokine gradient formation (CXCL12-syndecan interactions).
Key mechanisms include:
-
Carbohydrate side chains in the nervous system creating signaling microdomains.
-
Sialylation-dependent masking/unmasking of recognition motifs.
-
Chondroitin sulfate patterning in perineuronal nets regulating signal transduction.
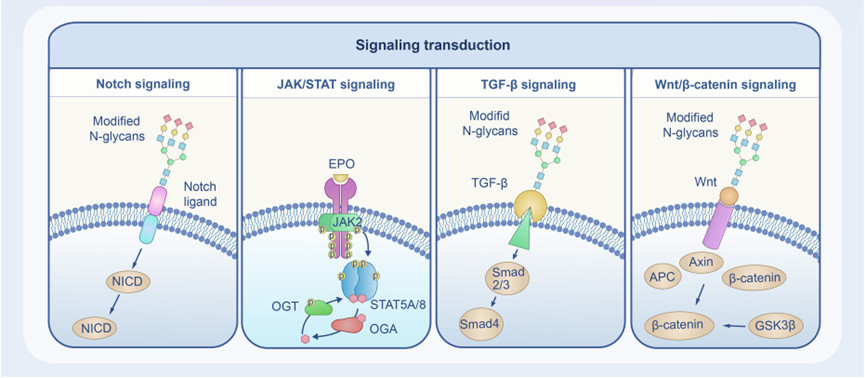 Fig.2 Glycosylation involved in cell signaling processes.2,3
Fig.2 Glycosylation involved in cell signaling processes.2,3
Carbohydrates in Synaptic Function
Synaptic function benefits from carbohydrate chains which provide structural support and actively modulate synaptic signaling. Synaptic plasticity processes that support learning and memory depend on the involvement of carbohydrates in synaptic function. Glycosylated proteins and lipids control this process by affecting neurotransmitter release as well as receptor signaling and synapse stability.
Impact on Synaptic Plasticity and Signaling
The carbohydrate chains that operate within synaptic functions play essential roles in synaptic plasticity by regulating long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) mechanisms which boost or diminish synaptic strength respectively. Neurotransmitter receptor glycosylation including AMPA and NMDA types affects their movement within cells and how they gather at synapses as well as their functional control. AMPA receptors' glycosylation adjusts their phosphorylation ability which leads to improved receptor functioning and synaptic transmission. Carbohydrate chains in synaptic function directly modulate:
-
AMPA receptor trafficking via stargazin O-GlcNAcylation.
-
Presynaptic vesicle cycling through complex N-glycans on SV2.
-
Post-synaptic density organization via heparan sulfate proteoglycans.
Creative Biolabs offers Glycoprotein Analysis Services and Glycan Profiling Service to facilitate your research in identifying:
-
Sialylated gangliosides (GM1, GD1a) in lipid raft signaling platforms.
-
Keratan sulfate-dependent LAR-RPTP clustering at synaptic clefts.
-
Galectin-3-mediated crosslinking of N-cadherin during LTP.
Role in Synapse Formation and Function
Synapse formation relies on the precise regulation of carbohydrate chains in synaptic function. During synaptogenesis, the interactions between glycoproteins and glycosylated molecules in the extracellular matrix (ECM) guide the growth cones of axons and dendrites towards their synaptic targets. The glycosylation of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) on the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes is crucial for synaptic recognition and the formation of stable synaptic connections. Moreover, carbohydrates in cell membrane proteins facilitate the insertion of receptors into the synaptic membrane, which is essential for synaptic efficacy. The carbohydrate chains in neurotransmitter release machinery involve:
-
Sialylated complex N-glycans on synaptotagmin-1 regulating Ca²⁺ sensitivity.
-
O-mannosyl glycans on α-dystroglycan maintaining neuromuscular junctions.
-
HS proteoglycan-dependent clustering of neuroligin-neurexin complexes.
Glycoproteins and Neuronal Health
Types and Functions of Neuronal Glycoproteins
The types and functions of neuronal glycoproteins are highly diverse. For instance, NCAM is involved in regulating neuronal adhesion and migration during development, while L1 is critical for axon guidance and synaptic plasticity. Neuroligins and neurexins, on the other hand, regulate synapse formation and function by interacting with neurotransmitter receptors and signaling pathways. Critical glycoproteins in neurons include:
|
Glycoprotein
|
Glycan Type
|
Function
|
|
L1CAM
|
HNK-1
|
Axonal guidance
|
|
Reelin
|
O-GalNAc
|
Cortical layering
|
|
NCAM
|
PSA
|
Synaptic plasticity
|
|
Contactin
|
N-glycan
|
Node of Ranvier formation
|
At Creative Biolabs, our custom glycan synthesis services deliver precision-crafted glycans, tailored to accelerate your glycoscience research and meet your unique needs. Our neuronal glycoprotein characterization service analyzes:
Glycoproteins in Cellular Signaling
Glycosylation in brain cells modulates signaling through:
-
Tandem Ig-FnIII domains with conserved N-glycosylation sites.
-
Galectin-1 crosslinking of GM1 ganglioside in growth cone collapse.
-
Sialic acid-dependent Siglec interactions in microglial surveillance.
Carbohydrates in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Carbohydrate chains in neurodegenerative diseases are central to the progression of various neurological disorders. In particular, the glycosylation of proteins and lipids in the brain undergoes significant alterations in diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's. These modifications can disrupt protein function, lead to the accumulation of misfolded proteins, and cause neuroinflammation, all of which contribute to disease onset and progression. At Creative Biolabs, we provide advanced solutions for identifying glycoprotein biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases, helping accelerate your research in precision medicine and disease diagnostics.
Carbohydrate chains in neurodegenerative diseases exhibit:
-
Reduced α2,6-sialylation in AD cerebrospinal fluid.
-
Increased bisecting GlcNAc in Parkinson's disease-associated α-synuclein.
-
Aberrant O-GlcNAcylation of tau in neurofibrillary tangles.
Pathological consequences include:
-
Impaired carbohydrate chains in neural regeneration due to CSPG upregulation.
-
Carbohydrate chains in neuroinflammation via microglial Trem2 glycosylation.
-
Disrupted carbohydrate chains in brain signaling through Aβ-glycan interactions.
Role in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's
|
Alzheimer's Disease
|
-
BACE1 cleavage preference for bisected N-glycans on APP.
-
Galectin-3 aggregation of Aβ42 through LacNAc recognition.
-
Loss of hippocampal HS sulfation patterns.
|
|
Parkinson's Disease
|
-
Galactosylation ratio changes in CSF α-synuclein.
-
LRRK2-mediated phosphorylation of Rab GTPase glycoproteins.
-
Glucocerebrosidase glycoform-specific activity loss.
|
The intricate landscape of carbohydrate chains in the brain presents both challenges and therapeutic opportunities. Creative Biolabs continues to pioneer glyco-neuroscience research through advanced platforms for analyzing glycosylation in neurons and developing glycan-targeted interventions.
References
-
Wu, Hsueh-Fu, et al. "O-GlcNAcylation is crucial for sympathetic neuron development, maintenance, functionality and contributes to peripheral neuropathy." Frontiers in Neuroscience 17 (2023): 1137847. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2023.1137847
-
He, Mengyuan, Xiangxiang Zhou, and Xin Wang. "Glycosylation: mechanisms, biological functions and clinical implications." Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 9.1 (2024): 194. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01886-1
-
Image retrieved from Figure 3 "Glycosylation: mechanisms, biological functions and clinical implications". He, Mengyuan et al., 2024, used under CC BY 4.0. The original image was modified by extracting and using only part "Signaling transduction" and the title was changed to "Glycosylation involved in cell signaling processes".
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 O-GlcNAcylation in sympathetic neurons.1
Fig.1 O-GlcNAcylation in sympathetic neurons.1
 Fig.2 Glycosylation involved in cell signaling processes.2,3
Fig.2 Glycosylation involved in cell signaling processes.2,3

