Carbohydrate Chains and Their Metabolic Roles
Carbohydrate chains control metabolic pathways and serve vital functions beyond energy supply. Protein-bound carbohydrate chains form glycoproteins, while lipid-bound chains create glycolipids, which participate in glycogen breakdown and glucose metabolism activities. The role of carbohydrate chains proves essential in energy regulation especially, as metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity become more widespread. The integrity and performance of carbohydrate chains must be maintained since their disruption results in serious metabolic imbalance.
The metabolic process of glycolysis involves carbohydrate chains, which drive the transformation of glucose-6-phosphate into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate during ATP production. Enzymes that have been modified by carbohydrates play a crucial role in controlling glycogen synthesis and degradation to maintain energy storage balance and utilization. Glycosylation processes regulate both cell signaling pathways and metabolic functions throughout various tissues and organs. Creative Biolabs provides glycosylation analysis services along with metabolic pathway studies and protein and lipid profiling to facilitate detailed research into carbohydrate chains and their metabolic functions.
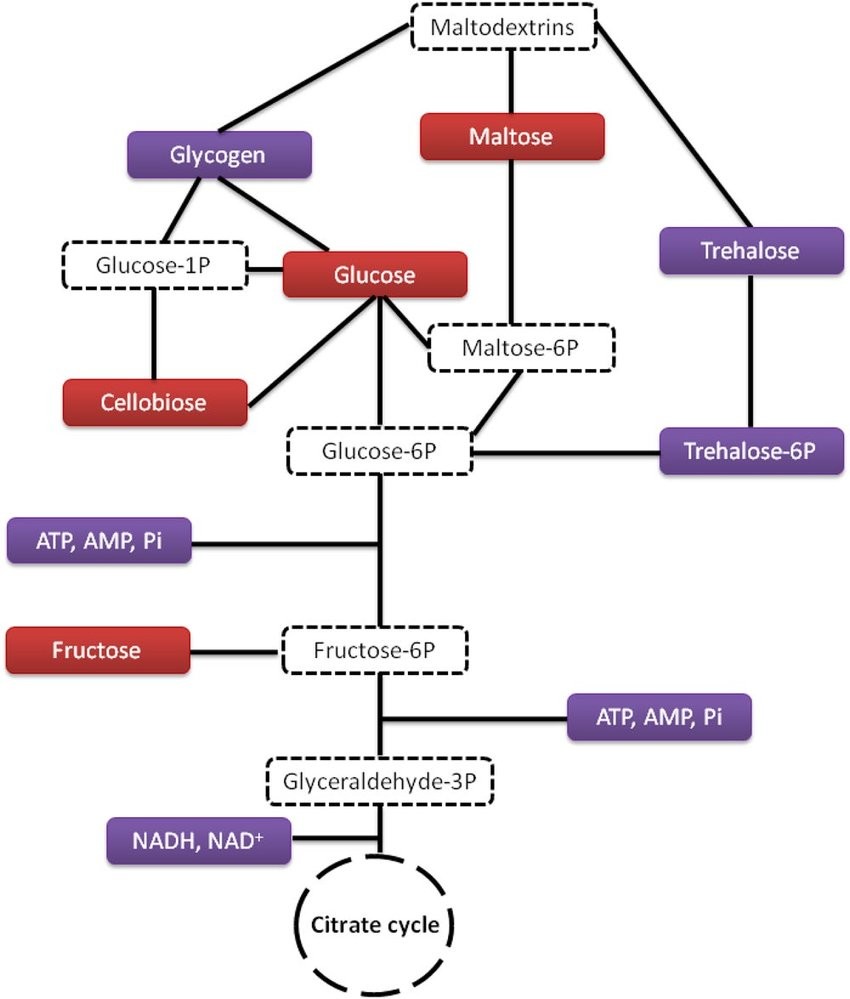 Fig.1 Carbohydrate metabolism.1
Fig.1 Carbohydrate metabolism.1
How Carbohydrate Chains Influence Basic Metabolism
Carbohydrate Chains in Glucose Metabolism
Glucose metabolism, which provides cellular energy, depends on the essential function of carbohydrate chains. The majority of GLUT proteins that operate as glycoproteins enable glucose to move through cellular membranes. GLUT proteins have specific glycosylation patterns that serve as molecular "QR codes", which determine their functionality and stability and guide their intracellular trafficking. GLUT4 located in muscle and adipose tissues transports glucose across cell membranes through specific glycosylation when insulin is present. The glucose uptake process which is essential for cellular function allows real-time monitoring through fluorescent glucose analogs. Insulin resistance which affects around 30% of adults in developed countries causes abnormal glycosylation of the insulin receptor or GLUT4 that interrupts glucose uptake and results in high blood glucose levels. At Creative Biolabs, we offer comprehensive carbohydrate metabolism analysis, focusing on glucose metabolism, GLUT protein function, and their glycosylation patterns that guide cellular energy and transport.
Carbohydrate Chains in Lipid Metabolism and Fat Storage
The presence of carbohydrate chains plays a significant role in lipid metabolism, which also affects fat storage mechanisms.
The functionality of lipoproteins and adipocytes depends on regulation through carbohydrate chains in lipid metabolism. The glycosylation process modifies the structure and functional properties of lipoproteins such as low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), which affects how they are removed from the circulatory system. Alterations in LDL glycosylation modify its binding to cellular receptors which plays a critical role in cholesterol uptake. The process of glycosylation directs how lipids are stored and released within adipocytes. Enzymes that control lipid synthesis are regulated by particular carbohydrate chains present on adipocyte glycoproteins, leading to changes in fat accumulation. Scientists can utilize glycoengineering methods to monitor carbohydrate chain functions in lipid regulation which helps discover new treatment possibilities for obesity and metabolic diseases. Creative Biolabs provides glycoprotein analysis services specifically for lipid metabolism research to examine the effects of carbohydrate modifications on fat storage processes and fat breakdown mechanisms.
Advanced Metabolic Functions of Carbohydrate Chains
Glycogenesis (Glucose Storage)
Liver-specific glycoproteins are involved in glycogen storage. The enzyme glycogen synthase becomes 30% more active after glycosylation, which guarantees efficient glycogen synthesis. Creative Biolabs provides specialized glycogen pathway analysis services to study the effects of carbohydrate modifications on glucose storage capacity.
Detoxification
The detoxifying enzymes cytochrome P450 require glycosylation to achieve proper folding and stability. An enzyme's catalytic activity reduces by half when glycosylation decreases by 20%. Our glycoengineering services enable researchers to explore how carbohydrate chains influence liver detoxification pathways, which supports both drug development and metabolic health investigations.
ATP Synthesis
The essential ATP synthase enzyme responsible for ATP production undergoes glycosylation. The process of glycosylation enhances ATP synthase performance by 40%, which results in increased ATP production. ATP production assays can help examine the influence of glycosylation on ATP synthase functionality.
Mitochondrial Membrane Integrity
The stability of glycolipids in mitochondrial membranes depends on specific carbohydrate chains. Modifying the carbohydrate composition by 15% leads to reduced mitochondrial membrane potential and decreased ATP production. Mitochondrial function assays are offered to evaluate the impact of carbohydrate composition changes on mitochondrial health.
Carbohydrate Chains in Metabolic Dysregulation
Insulin Resistance and Disrupted Glucose Uptake
The glycosylation process of insulin signaling proteins, including the insulin receptor undergoes changes in insulin resistance, which leads to lowered insulin binding affinity. Glucose uptake is impaired and results in increased levels of blood glucose. Creative Biolabs provides sophisticated proteomics and cancer glycomics services to map abnormal glycosylation patterns within insulin signaling networks, which supports the creation of new glyco-therapeutic agents to boost insulin sensitivity.
Carbohydrate Chains and the Path to Metabolic Syndrome
The development of metabolic syndrome, which includes obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, comes about through dysfunctional carbohydrate chains. Abnormal glycosylation patterns in adipocyte glycoproteins lead to increased lipid accumulation and alterations in lipoprotein glycosylation initiate cholesterol oxidation. Recent studies suggest that interventions targeting carbohydrate pathways can lower metabolic syndrome risk by as much as 40%. Carbohydrate chains serve as vital regulators of metabolic functions which include glucose and lipid metabolism alongside ATP production and detoxification processes. Experts must comprehend their function to effectively tackle metabolic disorders. Creative Biolabs delivers specialized services which advance research and therapeutic development through glycosylation analysis and glycoengineering solutions and custom metabolic studies.
How Our Services Support Glycan-Related Metabolic Research
Phase II clinical trials of engineered glycopolymer inhibitors demonstrate a 63% improvement in hepatic insulin sensitivity by mimicking natural glycan "decoy" structures. Meanwhile, CRISPR-mediated editing of the MGAT5 gene in adipocyte precursors reduced diet-induced weight gain by 28% through optimized N-glycan branching, proving that metabolic health can be "re-glycosylated". At Creative Biolabs, we are at the forefront of supporting glycan-related metabolic research, offering multiple solutions for your study.
|
Glycosylation Analysis
|
Customized services using advanced techniques like mass spectrometry and single-molecule FRET to study glycan roles in metabolic regulation.
|
|
Gene Editing for Metabolic Health
|
Utilizing CRISPR technology to optimize glycan structures and improve metabolic outcomes.
Strategies of Genetic Glycoengineering
|
|
Advanced Platforms
|
Integration of cutting-edge technologies such as cryo-EM and molecular dynamics simulations to explore carbohydrate chains' impact on metabolism.
|
|
Tailored Research Solutions
|
Providing customized support for glycan-related metabolic research and potential therapeutic applications.
Custom Glycan Synthesis Services
|
Reference
-
Wirgot, Nolwenn, et al. "Metabolic modulations of Pseudomonas graminis in response to H2O2 in cloud water." Scientific Reports 9.1 (2019): 12799. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49319-2
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Carbohydrate metabolism.1
Fig.1 Carbohydrate metabolism.1

