Bone marrow is the principal site where blood cells are generated, and it is heavily regulated by a variety of molecular interactions that determine the fate of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Among these critical interactions, carbohydrate chains play an indispensable role in facilitating the process of hematopoiesis. Creative Biolabs provides advanced Technologies for Glycoprotein Analysis to better understand how these carbohydrate chains function in hematopoiesis.
Why Do Carbohydrate Chains Matter in Bone Marrow?
Bone marrow carbohydrate chains are a group of biomolecules that possess specific structures and functions. These structures and functions are associated with the homing and implantation of hematopoietic stem cells. Research has demonstrated that galactosyl carbohydrate residues on hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) are imperative for homing and implantation into the bone marrow. Transplanted bone marrow cells lacking β-1,4-galactosyltransferase-1 (β4GalT-1) do not support the survival of mice exposed to lethal doses of radiation. Furthermore, bone marrow cells obtained from mice lacking β4GalT-1 exhibited normal colony-forming activity and hematopoietic stem cell counts. However, colony-forming cells were found to be scarce in the bone marrow of recipient mice 24 hours after the transplantation of β4GalT-1-deficient bone marrow. Marrow cells, suggesting that β4GalT-1 deficiency severely impairs homing. These results imply that galactosyl groups in the glycoproteins are essential for the transfer of HSPC homing and engraftment into the bone marrow is critical.
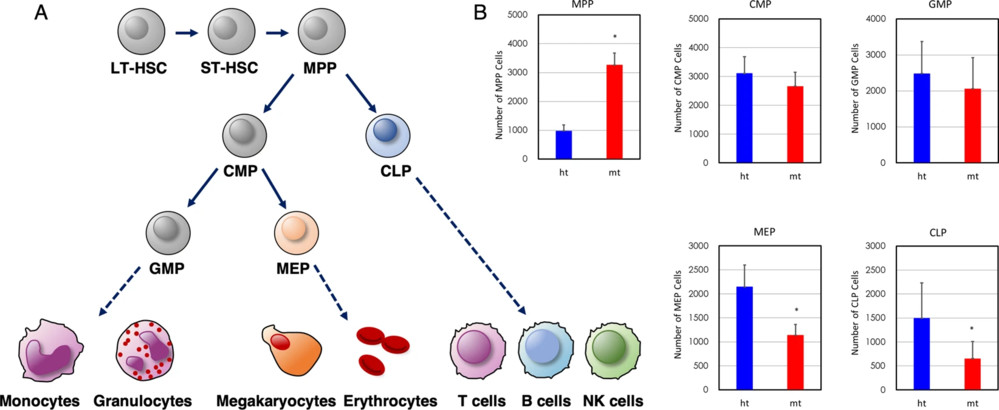 Fig.1 Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell (HSPC) development and differentiation.1,3
Fig.1 Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell (HSPC) development and differentiation.1,3
Moreover, the bone marrow extracellular matrix (ECM), which provides structural support to stem cells, heavily relies on glycosylated components. These glycosylated ECM molecules create a scaffold for HSCs, promoting cell adhesion, survival, and differentiation. For instance, heparan sulfate, a glycosaminoglycan, binds to growth factors and cytokines, facilitating their controlled release in response to physiological demands. Our Carbohydrate Analysis Services can help further investigate how these carbohydrate structures influence bone marrow functions.
Glycosylation Patterns in Hematopoietic Stem Cells
How to Spot Glycosylation Patterns in Stem Cells?
To understand the significance of glycosylation patterns in hematopoietic stem cells, researchers use several sophisticated techniques:
|
Technique
|
|
|
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
|
Mass spectrometry is used to ionize glycoproteins or glycolipids from hematopoietic stem cells, separating ions based on mass-to-charge ratio. It provides detailed insights into glycan types and arrangements.
|
|
Lectin Microarray
|
Lectins bind specifically to certain sugar residues, and when conjugated with fluorescent tags, they allow visualization of glycosylation patterns on the cell surface.
|
|
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
|
NMR spectroscopy determines the fine structure and linkage of sugar residues, helping to analyze the detailed architecture of glycosylation in stem cells.
|
|
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
|
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) can be used to analyze these glycosylation patterns in detail, aiding the study of erythropoiesis and other blood cell differentiation processes.
|
What Do These Patterns Mean for Stem Cells?
The glycosylation patterns found in hematopoietic stem cells are dynamic and change in response to cellular signals. High levels of mannose glycosylation, for instance, are typically associated with HSCs in a quiescent or dormant state. This pattern of glycosylation allows HSCs to interact with the bone marrow niche, maintaining their self-renewal capacity and preventing premature differentiation. Disruption of this glycosylation pattern can lead to excessive proliferation of HSCs and deplete the stem cell pool.
How Glycosylation Affects Stem Cell Function
Signaling pathways that depend on glycosylation control stem cell self-renewal which is vital for sustaining stem cell identity. The Wnt signaling pathway plays a vital role in stem cell regulation because it controls stem cell population maintenance. The glycosylation process increases the attachment between Wnt ligands and stem cell receptors which activates signaling pathways that maintain self-renewal while blocking differentiation. Glycosylation functions in both self-renewal maintenance and stem cell differentiation regulation. During hematopoietic stem cell differentiation into specialized cells specific glycosylation patterns regulate transcription factor activities. The function of transcription factors includes the regulation of gene expression, which guides cells toward their specific lineage commitments. Glycosylation during megakaryocyte differentiation affects transcription factor-DNA binding which in turn impacts the expression of essential genes required for this differentiation process.
Carbohydrate Chains' Double Roles in Hematopoiesis
Carbohydrate chains play an essential role in regulating the differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells into various blood cell types. They influence how these cells interact with cytokines and growth factors. For example, erythropoietin (EPO), a key regulator of red blood cell production, requires proper glycosylation for efficient binding to its receptor on HSCs. This interaction is essential for promoting the differentiation of stem cells into erythrocytes.
In addition to direct glycosylation events, carbohydrate chains in bone marrow also influence hematopoiesis by affecting the bone marrow's extracellular matrix. The ECM is made up of glycosylated molecules such as heparan sulfate, which binds to growth factors and cytokines, creating a molecular reservoir for their controlled release. This dynamic system supports the differentiation and function of blood cells by providing a stable and responsive environment. For further exploration of glycosylation's role in the bone marrow niche, check out our Glycan Profiling Service.
Glycosylation's Influence on Blood Cell Differentiation
The Changing Glycosylation during Differentiation
As HSCs differentiate into specific blood cell types, their glycosylation patterns undergo significant changes. For example, when HSCs differentiate into B lymphocytes, certain glycosyltransferases are upregulated, leading to the addition of sialic acid residues to cell surface glycoproteins. This change is essential for the B cell's ability to produce antibodies. Similarly, the differentiation of monocytes into macrophages is influenced by changes in the fucosylation pattern on the cell surface, which is associated with the acquisition of phagocytic ability. Our Glycosylation Site Mapping Service can help analyze the shifts in glycosylation during these processes, offering crucial insights into differentiation pathways.
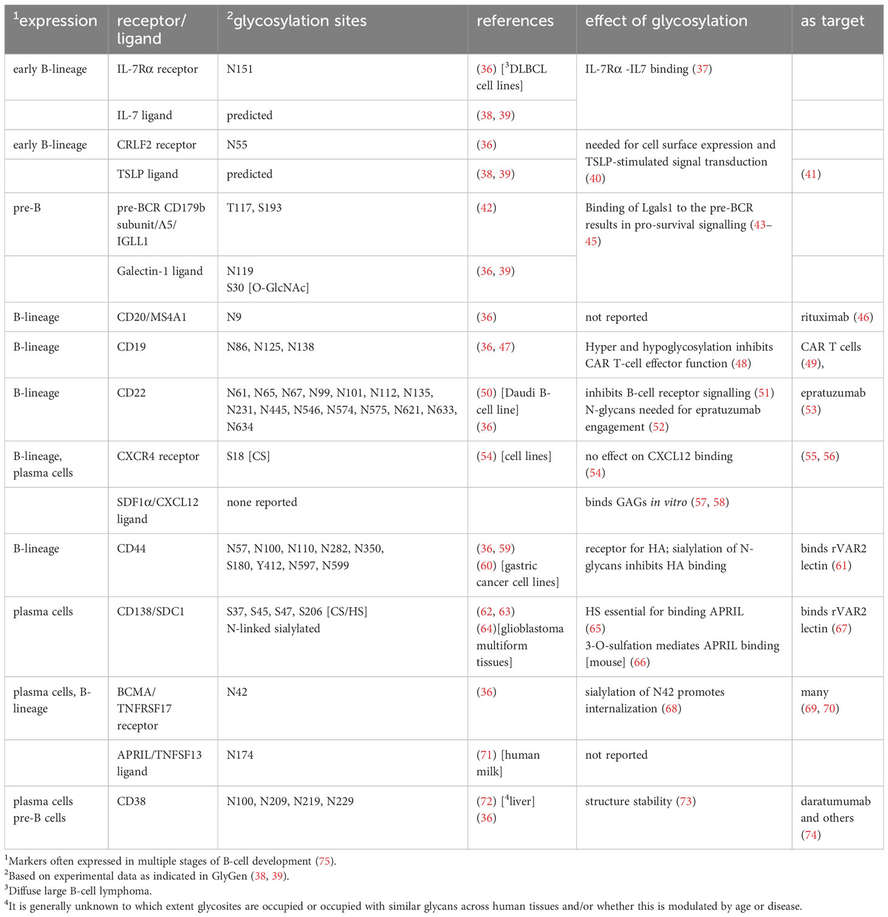 Fig.2 Key glycoproteins in human BM B-cell homeostasis and development.2,3
Fig.2 Key glycoproteins in human BM B-cell homeostasis and development.2,3
Glycosylation as a Decision-Maker in Differentiation
Glycosylation plays a pivotal role in the decision-making process during differentiation. In the Notch signaling pathway, glycosylation regulates the interaction between the Notch receptor and its ligand on thymic epithelial cells, guiding the differentiation of stem cells into T cells. Any disruption in the glycosylation of the Notch receptor can lead to defective differentiation or failure to differentiate altogether. Creative Biolabs offers Glycomic Profiling Services and Glycan Sequencing Services to analyze glycosylation-related changes in stem cell differentiation pathways.
How Our Services Support Your Bone Marrow Research
Research into the role of glycosylation in hematopoiesis is poised to revolutionize the treatment of hematological disorders. Therapies targeting specific glycosylation enzymes, such as those involved in blood cancer-related glycosylation anomalies, could help restore normal differentiation pathways and inhibit tumor cell growth. Additionally, CRISPR-based genetic glycoengineering could be used to modify glycosylation-related proteins in HSCs, providing novel treatment strategies for genetic diseases associated with abnormal glycosylation. At Creative Biolabs, we offer cutting-edge tools to aid researchers in understanding and manipulating glycosylation processes in hematopoiesis:
References
-
Heisterkamp, Nora. "Glycosylation as regulator of human B-cell leukaemias in bone marrow." Frontiers in Hematology 2 (2023): 1279863. https://doi.org/10.3389/frhem.2023.1279863
-
Takagaki, Soichiro, et al. "Galactosyl carbohydrate residues on hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells are essential for homing and engraftment to the bone marrow." Scientific reports 9.1 (2019): 7133. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43551-6
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell (HSPC) development and differentiation.1,3
Fig.1 Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell (HSPC) development and differentiation.1,3
 Fig.2 Key glycoproteins in human BM B-cell homeostasis and development.2,3
Fig.2 Key glycoproteins in human BM B-cell homeostasis and development.2,3

