Carbohydrate Chains in Signal Transduction Mechanisms
Carbohydrate chains, including glycoproteins and glycolipids, play a crucial role in a wide range of biological processes (Carbohydrate Chains in Biological Processes), particularly in signal transduction mechanisms. Creative Biolabs, specializing in exploring and leveraging these carbohydrate-mediated interactions, provides Custom Glycan Synthesis Services, Carbohydrate Analysis Services and Glycan Profiling Service to develop innovative solutions tailored for your research.
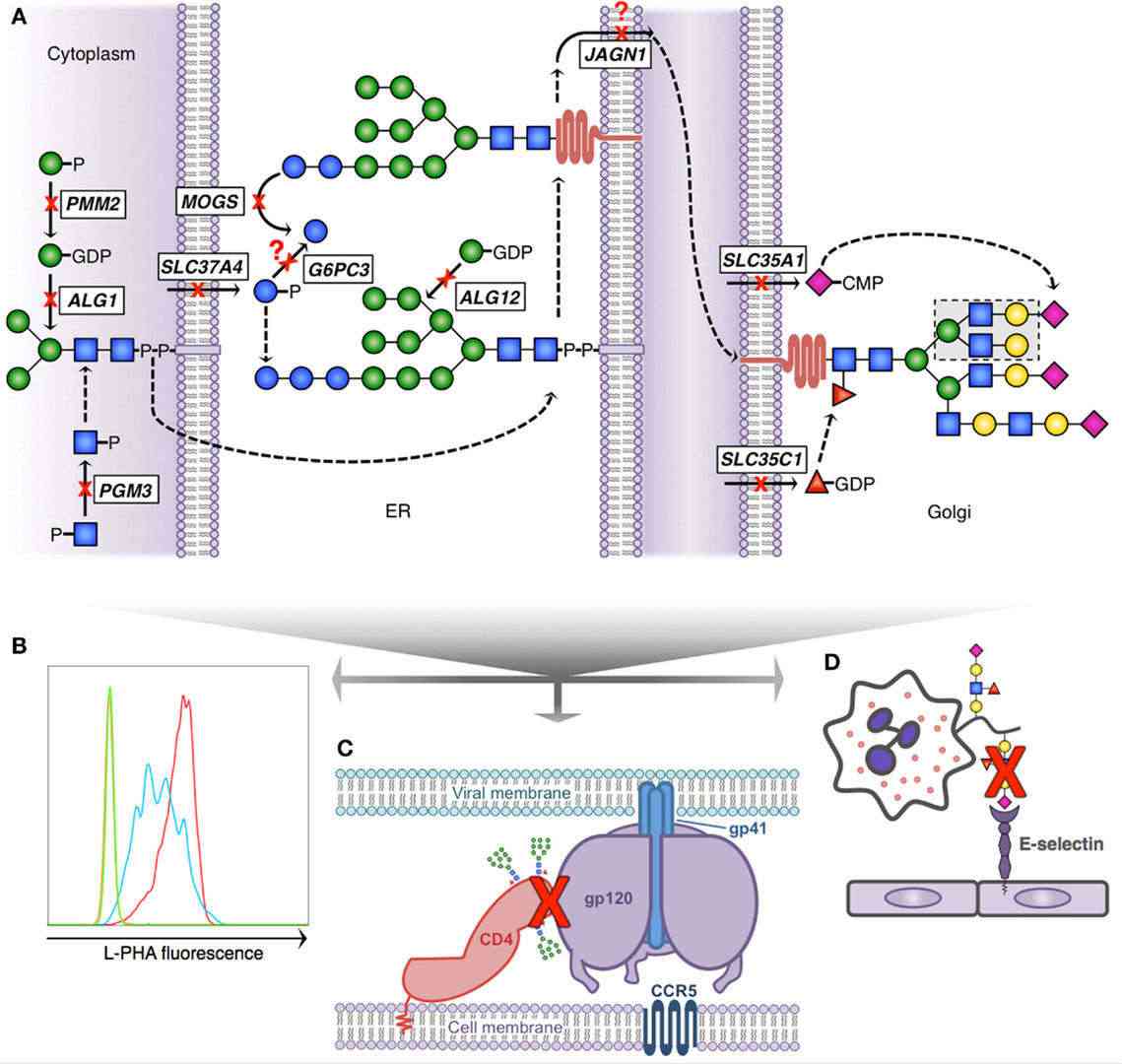 Fig.1 Defects in glycosylation pathways and their known impacts on immune function.1
Fig.1 Defects in glycosylation pathways and their known impacts on immune function.1
Glycosylation-Dependent Receptor Activation
Enter the complex world of proteins, where N-linked glycosylation is a vital "life-code" and a key post-translational modification. It affects cell surface receptors like EGFR and the insulin receptor, acting as a "blueprint" for their proper folding, stability, and smooth function. N-linked glycans, the "matchmakers", enable receptor dimerization, a crucial step for activation that triggers downstream signaling pathways regulating cell growth, differentiation, and survival. Adjusting glycosylation status gives researchers control over receptor activity and cellular responses.
O-GlcNAc modification, a small but powerful process inside the cell, attaches an O-GlcNAc moiety to proteins. This simple act impacts protein stability, location, and activity. In NF-κB signaling, it acts as a "dimmer switch" for gene expression, influencing immune-related genes. Targeting this modification could lead to treatments for inflammatory and immune-related diseases.
Carbohydrate-Mediated Protein Interaction Networks
Now, let's turn our attention to heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs). These little-known yet incredibly important substances are like the silent guardians within the extracellular matrix and on the cell surface. They play a critically essential role in mediating protein-protein interactions. Think of HSPGs as the most trustworthy partners for a variety of growth factors, for instance, fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) and vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs). When they bind to these growth factors, they are just like the super-efficient couriers, boosting the signaling efficiency and specificity to an astonishing extent. This function is as indispensable as the foundation to a towering building for angiogenesis, tissue repair, and embryonic development. These processes are the very cornerstones that underpin life's growth and development. Here at Creative Biolabs, armed with our profound expertise in HSPG interactions, we are like fearless adventurers sailing in the vast sea of science.
Galectin-3, an outstanding member of the galectin family, is like a watchful guard in the microscopic cell universe. It has an extraordinary ability to identify and attach to specific glycans. On the cell surface, it constructs lattice-like structures, which are similar to the exquisitely designed control systems that regulate the clustering of T cell receptors (TCRs). This clustering is like the key that starts a high-power engine, being of utmost importance for T cell activation and immune responses. By deftly influencing the formation and stability of these galectin-3 lattices, we are like the seasoned coaches of a top-notch sports team. We can manage T cell activity and come up with highly effective immune modulation strategies. Galectin-3 inhibitors and modulators are like the sharpest swords in the battle against autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
Glycans in Cell Surface Receptor Signaling and Immune Regulation
At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in advancing research and therapies across several key areas, including immune checkpoint modulation, antigen presentation, and tissue engineering. Our services focus on targeting Siglec-sialic acid interactions for cancer and autoimmune treatments, enhancing immune activation through DC-SIGN-pathogen recognition, and regulating integrin function via mucin O-glycans. We also provide expertise in ER quality control, using calnexin-mediated glycoprotein folding to address protein misfolding diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. By combining our scientific expertise with innovative technologies, we help researchers develop new strategies for treating a range of diseases.
|
Topic
|
Key Points
|
Applications & Services
|
|
Siglec-Sialic Acid Interactions
|
- Sialic acids on cell surfaces interact with Siglecs, such as CD22 on B cells.
- This interaction regulates B cell activation and tolerance.
|
- Modulate Siglec-sialic acid interactions for immunotherapy development.
- Quantitative Sialic Acid Analysis Service
- Sialic Acid Microarray
|
|
DC-SIGN & Pathogen Recognition
|
- DC-SIGN (DC-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non integrin,CD209) on dendritic cells binds mannose on pathogens, facilitating antigen presentation to T cells.
|
- Enhance antigen presentation and immune activation.
- Develop strategies for vaccine development and infectious disease treatments.
- Mucin Detection Service
|
|
Mucin O-Glycans & Integrin Regulation
|
- Mucin O-glycans protect integrin binding sites from premature activation, ensuring proper adhesion and signaling.
|
- Modulate cell adhesion and migration for tissue engineering and cancer metastasis management.
|
|
ER Quality Control via Calnexin
|
- Calnexin in the ER helps fold glycoproteins, ensuring protein homeostasis and preventing misfolding.
|
- Study ER quality control to develop therapies for protein misfolding diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
|
Therapeutic Targeting of Carbohydrate Signaling Hubs
Tn Antigen: The Oncogenic Culprit in Colorectal Cancer
Aberrant glycosylation is a common trait in many cancers, and colorectal cancer is no exception. The Tn antigen, a truncated form of O-linked glycans, acts like a malicious agent within the body. In colorectal cancer cells, it often overexpresses, as if plotting to disrupt the normal cellular balance. This overexpression then drives the oncogenic signaling pathways, similar to an out-of-control wildfire, causing chaos in the cellular environment. But we, as determined researchers, have a plan. By precisely targeting this Tn antigen, we can develop innovative cancer therapies. These therapies are designed to specifically inhibit the oncogenic signaling, offering a more effective way to fight colorectal cancer. This could be the hope that patients with this dreadful disease need, bringing a glimmer of light to their difficult situation.
Sialyl-Lewis X/Selectin Interactions: The Hidden Driver of Metastatic Inflammation
Sialyl-Lewis X (sLeX), a carbohydrate antigen, plays a crucial role in the complex process of cancer metastasis. It's key in the interaction between cancer cells and selectins, a family of adhesion molecules on endothelial cells. This interaction is like a hidden, dangerous path that cancer cells use to their advantage. It enables cancer cell adhesion and extravasation, allowing cancer cells to spread and form new "outposts" in the body, thus contributing to metastasis. However, we're not defenseless. By blocking these sLeX-selectin interactions, we can potentially stop this metastatic process and reduce inflammation. This offers new therapeutic strategies for both cancer treatment and inflammatory diseases, giving patients a better chance at a good outcome.
Glycoengineering is an innovative approach to modify antibody glycosylation for enhanced therapeutic effect. For example, afucosylated anti-PD-1 antibodies are developed to better engage immune cells and boost anti-tumor activity. At Creative Biolabs, we're proud of our expertise in glycoengineering. We offer customized glycoengineered antibodies, carefully crafted to meet specific therapeutic needs. These antibodies can provide improved efficacy and fewer side effects, making them a promising option in cancer immunotherapy. They're like a beacon of hope for patients fighting cancer, offering a potentially life-changing treatment.
Small-Molecule Inhibitors: Disrupting Galectin-3's Harmful Role
Small-molecule inhibitors targeting galectin-3-carbohydrate interactions show great promise in regulating immune responses and affecting cancer progression. By blocking these interactions, we can disrupt the formation of the galectin-3 lattice, which is like breaking a complex web that galectin-3 uses to manipulate the immune system. This disruption also impacts the downstream effects on T cell receptor clustering and immune modulation. At Creative Biolabs, we're actively involved in this research. We offer services for developing and optimizing small-molecule inhibitors.
Carbohydrate chains play a pivotal role in signal transduction mechanisms, influencing receptor activation, protein interactions, immune regulation, and disease progression. At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in carbohydrate-based solutions for drug development, offering glycoengineering services, carbohydrate analysis services, and antibody development. Our team of experts can help you explore the role of glycans in signal transduction and immune regulation, providing valuable insights and tools for your research and therapeutic development.
Reference
-
Lyons, Jonathan J., Joshua D. Milner, and Sergio D. Rosenzweig. "Glycans instructing immunity: the emerging role of altered glycosylation in clinical immunology." Frontiers in pediatrics 3 (2015): 54. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Defects in glycosylation pathways and their known impacts on immune function.1
Fig.1 Defects in glycosylation pathways and their known impacts on immune function.1

