Atherosclerosis stands at the center of most cardiovascular disease manifestations that continue to be the top mortality cause globally. Traditional cardiovascular risk factors like lipid metabolism and hypertension have received extensive research attention but carbohydrate chains are becoming recognized as vital yet insufficiently studied elements in heart disease pathology. The process of glycosylation within cardiovascular conditions influences protein stability and immune system function while maintaining vascular integrity thus representing a vital component in disease progression and treatment efforts.
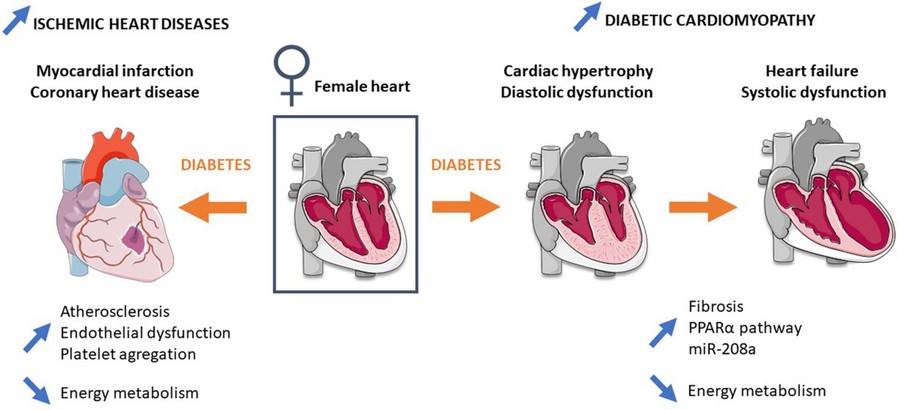 Fig.1 Ischemic heart disease and diabetic cardiomyopathy.1
Fig.1 Ischemic heart disease and diabetic cardiomyopathy.1
Carbohydrate Chains in Cardiovascular Health
Glycosylation, the enzymatic attachment of glycans to proteins and lipids, plays a pivotal role in cardiac homeostasis. These modifications regulate endothelial cell adhesion, platelet aggregation, and immune cell infiltration, all of which are integral to cardiac tissue homeostasis, influencing structural stability, cellular communication, and stress response mechanisms within the heart. The heart's dynamic environment, characterized by constant mechanical stress, high metabolic activity, and precise signaling networks, depends on properly glycosylated proteins and lipids to maintain function. Dysregulated glycosylation patterns in cardiovascular diseases contribute to endothelial dysfunction, cardiac fibrosis, and impaired contractility, ultimately predisposing individuals to heart failure and atherosclerosis. Creative Biolabs provides advanced glycan analysis technologies to analyze carbohydrate structures, aiding researchers in understanding the molecular basis of glycosylation and its impact on cardiovascular health.
|
Glycosylation Type
|
Major Targets in Cardiac Tissue
|
Physiological Function
|
Impact of Dysregulation
|
|
N-linked glycosylation
|
Ion channels (e.g., Nav1.5, Kv channels), Integrins
|
Regulates cardiac excitability, electrical conduction, and cell adhesion.
|
Arrhythmias, conduction defects, impaired cardiac repair.
|
|
O-linked glycosylation
|
Mucin-like proteins, Sarcolemmal glycoproteins
|
Maintains endothelial glycocalyx integrity, modulates protein-protein interactions.
|
Endothelial dysfunction, increased vascular permeability, thrombosis.
|
|
O-GlcNAcylation
|
Transcription factors (e.g., NFAT, MEF2), Mitochondrial proteins
|
Regulates cardiomyocyte metabolism, hypertrophic response, and stress adaptation.
|
Cardiomyopathy, oxidative stress, metabolic dysregulation.
|
|
Sialylation
|
LDL receptors, ECM glycoproteins (e.g., laminin)
|
Prevents inflammation and fibrosis, maintains lipoprotein clearance.
|
Atherosclerosis, cardiac fibrosis, defective lipid metabolism.
|
|
Core fucosylation
|
TGF-β receptors, Adhesion molecules
|
Modulates cardiac fibroblast activation, fibrosis development.
|
Increased myocardial stiffness, cardiac remodeling, heart failure.
|
Glycans as Modulators of Lipoprotein Metabolism
Glycans play a critical role in lipoprotein metabolism, influencing the structure, function, and clearance of lipoproteins such as Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL), High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL), Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL). (Know more about carbohydrate chains in lipid metabolism) The role of carbohydrate chains in atherosclerotic plaque formation is particularly evident in their impact on lipid transport:
-
LDL glycosylation affects receptor binding and clearance rates, influencing lipid accumulation in arterial walls.
-
O-glycan modifications on apolipoproteins regulate HDL function and cholesterol efflux capacity.
-
Glycan alterations in lipoprotein metabolism are linked to increased susceptibility to oxidation, a key event in glycans in atherosclerosis progression.
Aberrant glycosylation of lipoproteins promotes their retention in the vascular wall, enhancing foam cell formation and plaque growth. Creative Biolabs offers high-throughput glycan screening service, enabling researchers to conduct large-scale glycan analysis to identify key glycan modifications related to lipoprotein metabolism and cardiovascular diseases.
Carbohydrate Chains as Biomarkers for Heart Disease
Given their crucial role in cardiovascular health, carbohydrate chains as biomarkers for heart disease provide a promising avenue for early detection and risk assessment. Specific glycosylation changes have been associated with disease progression, inflammation, and plaque instability.
Serum Glycomics for Early Atherosclerosis Detection
Glycomic profiling has revealed that aberrant IgG glycosylation patterns, such as galactose-deficient IgG, correlate with vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis progression. Mass spectrometry-based approaches allow for high-throughput screening of these glycoforms, making them viable biomarkers for early cardiovascular risk assessment. To support early-stage diagnostics, Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive glycan profiling services to detect key biomarkers such as these, allowing for precise cardiovascular risk stratification. We also offer other types of glycoprofiling services, including antibody glycoprofiling service, serum glycoprofiling service, plasma glycoprofiling service, urine glycoprofiling service and cancer related services like tumor tissue glycoprofiling service and tumor cell line glycoprofiling service. Notable findings include:
-
Decreased sialylation of IgG correlates with increased systemic inflammation.
-
Elevated fucosylation has been linked to pro-thrombotic states.
-
Galactose-deficient IgA1 has been implicated in endothelial dysfunction and arterial stiffness.
Glycosylation Signatures in Lipoprotein Subclasses
The impact of glycosylation on lipoprotein subclasses extends beyond metabolism to their function in cardiovascular pathology. For instance:
-
Truncated O-glycans on apoB-100 enhance LDL oxidation and retention in arterial walls.
-
Defective glycosylation on HDL reduces its anti-inflammatory and cholesterol efflux capacities.
-
Glycosylation defects in VLDL have been associated with increased postprandial triglyceride levels, a marker of atherogenic dyslipidemia.
These findings support the use of glycosylation patterns in cardiovascular diseases as diagnostic and prognostic tools. Creative Biolabs also specializes in glycosylation site mapping, which can pinpoint exact glycosylation modifications in lipoproteins, improving the accuracy of diagnostic markers for heart disease.
Targeting Glycosylation Pathways in Cardiovascular Therapy
With increasing evidence implicating glycans in cardiovascular pathology, therapeutic strategies that target glycan-based cardiovascular therapies are being explored. By modulating glycan synthesis or blocking pathogenic glycan interactions, novel interventions for heart disease treatment and prevention are emerging.
Inhibiting Pathogenic Glycan-Protein Interactions
Pathogenic glycan-protein interactions facilitate immune cell infiltration and vascular inflammation. A notable example is galectin-3, a glycan-binding protein that enhances macrophage recruitment and promotes plaque destabilization. Creative Biolabs offers therapeutic glycoprotein development services to aid in the development of glycoprotein-based therapeutics targeting these pathways for cardiovascular diseases. Therapeutic approaches include:
-
Galectin-3 inhibitors, which prevent pro-inflammatory signaling and reduce fibrosis.
-
Blocking glycan-β1 integrin interactions, thereby reducing endothelial permeability and immune cell adhesion.
Enzymatic Remodeling of Atherogenic Glycans
Enzyme-based approaches to targeting glycosylation pathways in cardiovascular therapy focus on modifying pathogenic glycan structures:
-
Sialidase inhibitors prevent the desialylation of vascular endothelial cells, preserving glycocalyx integrity.
-
Recombinant sialyltransferases restore sialylation on lipoproteins, reducing their atherogenic potential.
-
Glycosyltransferase modulators are being explored to correct defective glycosylation patterns linked to CVD.
At Creative Biolabs, we also specialize in glycan remodeling services, a cutting-edge solution to modify glycans on proteins and lipids to improve cardiovascular outcomes.
Future Directions in Glycan-Centric Cardiovascular Research
As the field of glycomics advances, new technologies and interdisciplinary approaches are shaping the future of glycan-based strategies for heart disease prevention and treatment.
Glycoengineering for Precision Medicine
Gene-editing based glycoengineering represents a groundbreaking advancement in the field of glycan-based cardiovascular therapies, allowing precise modulation of glycosylation pathways at the genetic level. By selectively targeting glycosyltransferase and glycosidase genes, gene-editing technology enables the customization of glycan structures, which could significantly impact cardiovascular treatment and prevention strategies. Recent research highlights the potential to correct aberrant glycosylation patterns in cardiovascular diseases. The applications range from reducing atherogenic lipoprotein glycoforms to enhancing protective glycan modifications on endothelial and immune cells. Creative Biolabs offers multiple strategies of genetic glycoengineering, allowing for precise genetic modifications to control glycosylation processes, improving cardiovascular disease treatment and prevention.
|
Gene Target
|
Glycosylation Pathway Affected
|
Mechanism of Action
|
Therapeutic Potential in Cardiovascular Diseases
|
|
FUT8 (Fucosyltransferase 8)
|
Core fucosylation
|
Knockout reduces core-fucosylation of integrins and coagulation factors.
|
Reduced platelet aggregation, decreased thrombosis risk, protection against heart attacks and stroke.
|
|
MGAT1 (N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I)
|
N-linked glycosylation
|
Knockout inhibits complex N-glycan synthesis, affecting receptor signaling.
|
Prevents endothelial dysfunction and vascular inflammation, reduces plaque formation.
|
|
ST6GAL1 (Beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 1)
|
Sialylation
|
Overexpression enhances α2,6-sialylation, increasing anti-inflammatory glycan profiles.
|
Enhances endothelial glycocalyx integrity, reduces leukocyte adhesion and vascular inflammation.
|
|
GALNT2 (Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2)
|
O-linked glycosylation
|
Knockout modifies apolipoprotein O-glycans, altering LDL/HDL metabolism.
|
Improved lipid clearance, reduced oxidized LDL retention, lowered risk of atherosclerosis.
|
|
NEU1 (Neuraminidase 1)
|
Sialic acid cleavage
|
Knockdown preserves sialylation by reducing sialic acid cleavage.
|
Improved lipoprotein stability, reduced endothelial permeability and inflammation.
|
Integrative Glycomics and Multi-Omics Platforms
Advancements in multi-omics approaches, combining glycomics, proteomics, and lipidomics, offer comprehensive insights into glycosylation in cardiovascular diseases. Collaborative efforts in this space focus on:
-
Mapping tissue-specific glycomes to identify novel therapeutic targets.
-
Developing glycan-targeted biologics, such as anti-sialic acid antibodies, to modulate immune responses, which can be further explored with our sialic acid microarray.
-
Applying AI-driven glycoinformatics to predict cardiovascular risk based on glycan signatures, supported by our high-throughput glycan screening platform.
The role of carbohydrate chains in heart disease is increasingly recognized as a fundamental aspect of cardiovascular pathology. From their involvement in endothelial function and lipoprotein metabolism to their potential as biomarkers for heart disease, glycans provide valuable insights into disease mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Glycan-based cardiovascular therapies hold promise for precision medicine approaches, leveraging advances in glycomics and gene-editing technologies. Whether you're using glycprofiling for research, development, or quality control, we are committed to delivering high-quality, customized solutions that meet your unique requirements. Don't hesitate to reach out to us if you're interested in exploring our glycan profiling services to facilitate your heart disease-related research.
Reference
-
Fourny, Natacha, et al. "Sex differences of the diabetic heart." Frontiers in physiology 12 (2021): 661297. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.661297
Related Services
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Ischemic heart disease and diabetic cardiomyopathy.1
Fig.1 Ischemic heart disease and diabetic cardiomyopathy.1

