Bacterial Polysaccharide Introduction
Accelerate Your Glycan-Based Discoveries!
Creative Biolabs' Bacterial Polysaccharide Services provide tailored solutions for the intricate challenges associated with bacterial glycans, crucial components in pathogen biology and host immunity. We deliver precise characterization, high-quality antigen preparation, and robust antibody development, enabling advancements in vaccine design, diagnostic tool development, and antimicrobial strategies. Our deliverables empower your project with a deep understanding of these complex biomolecules and their applications.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Bacterial Polysaccharide
Bacterial polysaccharides function as key virulence determinants in many clinically isolated pathogens.
Structure of Bacterial Polysaccharide
Numerous bacterial species feature polysaccharide-coated surfaces. These exist as capsules, glycoproteins, or glycolipids. Carbohydrates—notably capsular polysaccharides (CPS) or lipopolysaccharides (LPS)—act as fundamental surface elements of bacteria. Common bacterial polysaccharide architectures appear in Fig.1. Capsules comprise homopolymeric and heteropolymeric carbohydrate chains anchored in membranes, while LPS contains three elements: lipid A, core-oligosaccharide, and O-polysaccharide (O-antigen). Teichoic acids are categorized as wall teichoic acids (WTA) and lipoteichoic acids (LTA).
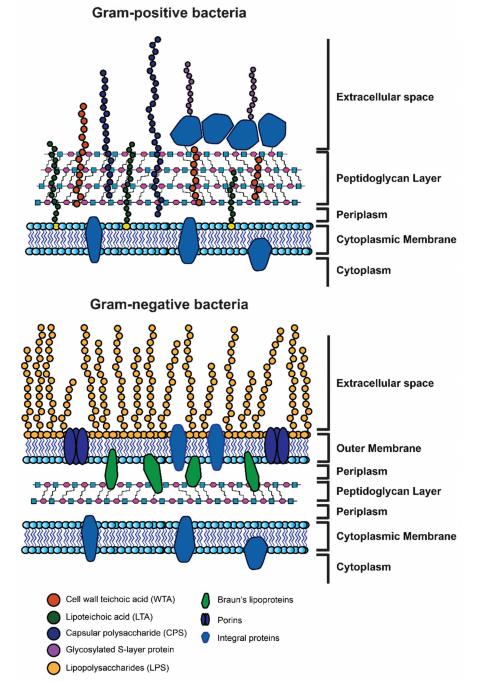 Fig.1 Structural illustration showing gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial cell walls.1,3
Fig.1 Structural illustration showing gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial cell walls.1,3
Function of Bacterial Polysaccharide
Microbes employ carbohydrate polymers for other unique roles; gram-negative species feature glycolipids forming the outer membrane's external layer, whereas diverse pathogens (gram-positive/negative) use sugar polymers to build capsules or external secretions. CPS serves to protect bacteria from phagocytosis, a component of the host's innate immunity. It inhibits phagocytic activation by reducing opsonin binding and obscuring ligands for phagocyte attachment. Fig.2 depicts multiple functions, including providing a physical antibiotic barrier and preventing antibody opsonization.
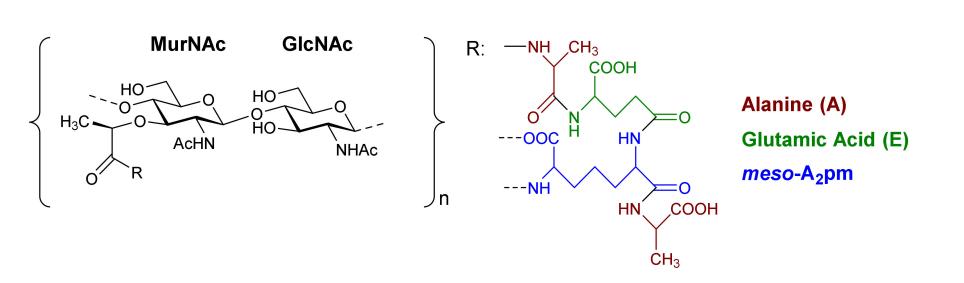 Fig.2 Core components illustrating peptidoglycan layer characteristics.1,3
Fig.2 Core components illustrating peptidoglycan layer characteristics.1,3
LPS represents the dominant outer membrane constituent vital for innate immune host-pathogen interplay. LPS modifications during chronic infection are believed to promote adhesion, host colonization, immune evasion, and niche adaptation. Immunity targeting bacterial polysaccharides provides disease protection. Most bacterial polysaccharides are T-cell independent antigens. Anti-polysaccharide immunity features absent T-cell memory, isotype restriction, and delayed ontogeny.
Published Data
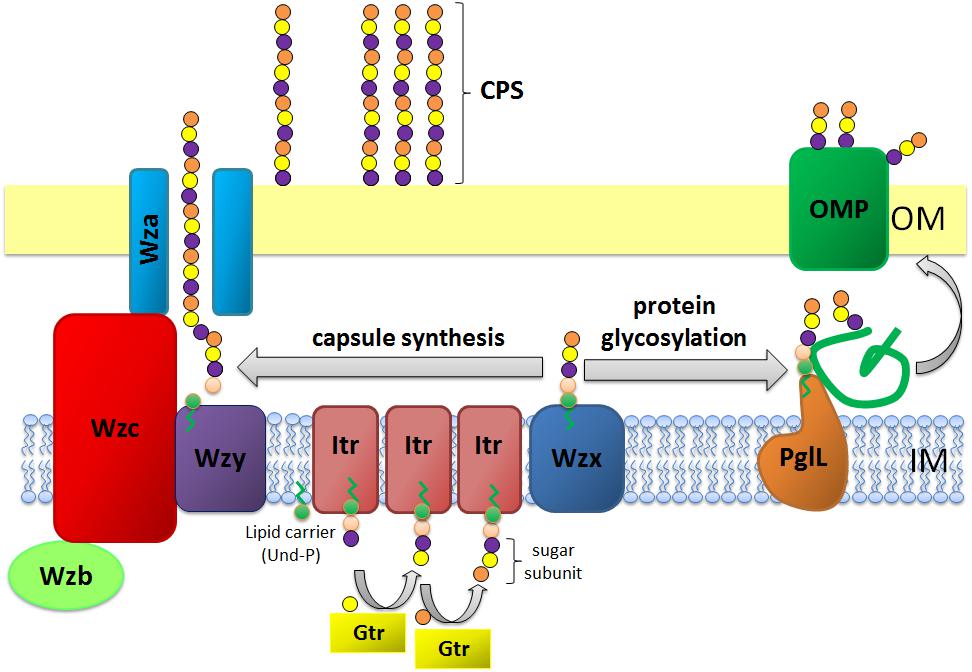 Fig.3 Assembly process diagram depicting capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis and transport mechanisms in A. baumannii.2,3
Fig.3 Assembly process diagram depicting capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis and transport mechanisms in A. baumannii.2,3
A recent study explored the diversity and function of capsular polysaccharide (CPS) in Acinetobacter baumannii, a significant causative agent of hospital-acquired infections. The research highlighted CPS as a major virulence determinant, providing crucial protection against environmental stressors and host immune responses. Experiments have revealed that A. baumannii exhibits over 100 distinct capsule types, incorporating a vast array of unique sugar compositions. The study investigated the genetic organization of K loci, the gene clusters responsible for CPS synthesis, and elucidated the critical role of CPS in bacterial virulence, conferring antimicrobial resistance, and enabling persistent colonization. These findings underscore the potential of A. baumannii CPS as a promising target for developing new therapeutic strategies, including antibody-based interventions and phage therapy, to combat this challenging pathogen.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive service array customized to address varied challenges in bacterial polysaccharide R&D. Leveraging extensive experience in antibody research and cutting-edge technology, we are proud to provide our clients with high-quality, cost-effective solutions.
- Bacterial Polysaccharide Isolation & Purification
- Anti-Carbohydrate Antibody Development (Monoclonal & Polyclonal)
- Immunological Characterization
- Analytical Method Development
Experience the Advantage – Obtain Pricing Now
Why Choose Us?
Selecting Creative Biolabs means partnering with glycobiology pioneers, recognized for technical precision, cutting-edge methods, and dedicated client focus.
- Deep Scientific Acumen
- State-of-the-Art Technology
- Customized Solutions
- Quality and Reliability
- Accelerated Research
FAQs
Here are some common scientific questions that arise in the context of bacterial polysaccharide research and development, providing insights into various aspects of glycan analysis and application.
Q: How do variations in polysaccharide structure impact their immunogenic properties and potential as vaccine targets?
A: Variations in bacterial polysaccharide structure profoundly influence their immunogenic properties. The specific monosaccharide composition, linkage types, and arrangement of repeating units define unique epitopes that are recognized by the host immune system. Differences in chain length, branching, and the presence of non-carbohydrate modifications can alter the polysaccharide's conformation and accessibility, thereby affecting its ability to elicit protective antibody responses. Understanding these structural-immunogenic relationships is critical for rational vaccine design, as highly conserved and immunodominant epitopes are preferred targets for broad-spectrum vaccines.
Q: What are the current challenges in isolating and purifying bacterial polysaccharides from diverse bacterial species?
A: Isolating and purifying bacterial polysaccharides present several challenges, largely due to their diverse chemical structures and association with other cellular components. Common challenges include the presence of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) contamination in capsular polysaccharide (CPS) preparations from Gram-negative bacteria, the variability in extraction efficiency across different bacterial strains, and the potential for degradation during purification. Additionally, highly viscous exopolysaccharides (EPS) can complicate filtration and chromatographic steps. Overcoming these challenges requires optimized extraction protocols, selective enzymatic treatments, and advanced chromatographic techniques to achieve high purity and yield.
Q: How can glycoanalytical insights contribute to the development of novel diagnostic tools for bacterial infections?
A: Glycoanalytical insights are fundamental to developing novel diagnostic tools for bacterial infections. Precise structural characterization of bacterial polysaccharides enables the identification of unique, species-specific, or serotype-specific glycan epitopes. These epitopes can then serve as highly selective targets for developing antibody-based diagnostic assays or carbohydrate-binding protein (lectin) arrays. Understanding the structural features that distinguish pathogenic from commensal bacteria also aids in designing more accurate and rapid diagnostic platforms, facilitating early and specific detection of infections.
Related Products and Services
To further advance your glycobiology R&D, we provide a portfolio of solutions:
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Polyclonal Antibodies
- Secondary & Tag Antibodies
- Isotype & Loading Control Antibodies
- Carbohydrate Antigens
Creative Biolabs also provides related services, click the buttons to find more details.
Creative Biolabs offers a series of anti-glycan antibody-related services for worldwide customers. To explore these capabilities, please contact us for more information.
References:
- Riu, Federico et al. "Antibiotics and Carbohydrate-Containing Drugs Targeting Bacterial Cell Envelopes: An Overview." Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 15,8 942. 29 Jul. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080942
- Singh, Jennifer K et al. "Diversity and Function of Capsular Polysaccharide in Acinetobacter baumannii." Frontiers in microbiology vol. 9 3301. 9 Jan. 2019, https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.03301
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
