Polyclonal Antibody Glycosylation Analysis Service
The glycosylation process functions as a crucial post-translational modification which determines the functionality of polyclonal antibodies by altering their binding affinity and effector functions as well as their behavior within living organisms. The structural diversity of polyclonal antibodies results from multiple B cell clones producing them and leads to complex glycosylation patterns throughout both Fc and Fab regions unlike monoclonal antibodies. The variations that occur across polyclonal antibodies affect essential properties including how the immune system recognizes them, their duration in serum, and their effectiveness as therapeutic agents. Through our glycosylation analysis services of antibodies at Creative Biolabs, we provide solutions that decipher complex glycosylation patterns to reveal essential pAb functions for research applications.
Introduction
The production of polyclonal antibodies results from diverse B cell clones reacting to one antigen which leads to pAbs having broad specificity that enables them to identify multiple epitopes and makes them essential in such applications. Yet, this strength comes with a challenge: The natural diversity in glycosylation serves as a structural modification of antibodies that determines their functional characteristics. A typical IgG polyclonal antibody shares the iconic Y-shaped structure: The structure of a typical IgG polyclonal antibody consists of two heavy chains and two light chains which create Fab arms that bind antigens and an Fc domain for effector functions. pAbs represent combinations of different IgG subclasses such as IgG1 and IgG2), each with subtle structural differences. Glycosylation in pAbs is a key player. Immune cell interactions change due to glycan structure variations in the Fc region while changes in glycosylation patterns in Fab regions affect antigen-binding affinity. Optimizing pAb performance requires an essential understanding of their functional nuances. That's where we step in. Creative Biolabs provides glycosylation analysis services that decode intricate patterns with advanced techniques to advance your research and development efforts. Our team provides fast clarity when you need to troubleshoot a problematic batch or characterize a new pAb.
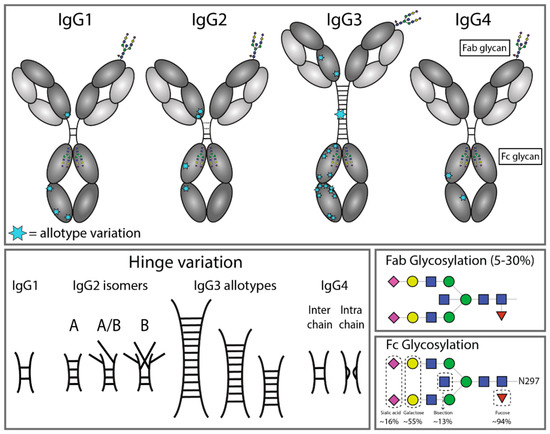 Fig.1 Structural variation of immunoglobulin G subclasses.1
Fig.1 Structural variation of immunoglobulin G subclasses.1
Key Glycosylation Hotspots
- Fc Region (Asn297): This conserved N-glycosylation site in the CH2 domain is a critical hub. The glycan here isn't just a passenger; it's a driver of Fc receptor binding, shaping processes like antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement activation. A missing fucose or extra sialic acid here can drastically alter immune responses.
- Fab Region: About 30% of pAbs carry glycosylation in Fab domains, often near the antigen-binding site. These glycans can fine-tune specificity, either enhancing or dampening how tightly an antibody clings to its target.
Sources of Glycosylation Heterogeneity
pAbs have many diverse glycan profiles for their mix-and-match nature of their production:
- Subclass Variability: Each IgG subclass has unique glycosylation "preferences," leading to differences in core structures or terminal sugars.
- B Cell Diversity: Every B cell clone adds its own "glyco-signature," resulting in a mosaic of glycan types within a single pAb preparation.
- Host Influence: The organism producing the antibody—whether rabbit, mouse, or human—imposes its own glycosylation machinery, leaving species-specific marks on the glycans.
mAbs vs. pAbs: Glycosylation Patterns and Functional Implications
| Feature | mAbs Glycosylation | pAbs Glycosylation |
|---|---|---|
| Glycosylation Sites | Predominantly at the Fc region, specifically at Asn297. Rare glycosylation at Fab regions. | Glycosylation observed at both Fc (Asn297) and Fab regions. Approximately 20–30% of IgG molecules exhibit Fab glycosylation. |
| IgG Subclass Variations | IgG1 is the predominant subclass; limited subclass diversity. | Presence of all four IgG subclasses (IgG1–IgG4); each subclass exhibits distinct glycosylation patterns and effector functions. |
| Glycan Heterogeneity | Low heterogeneity; primarily influenced by host cell expression systems. | High heterogeneity due to diversity in B cell clones, IgG subclasses, and environmental factors. |
| Core Fucose (Fuc) | Presence of core fucose can reduce FcγRIIIa binding, thereby modulating antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). | Fucosylation levels vary among different IgG subclasses (e.g., IgG1 vs. IgG2), influencing ADCC efficacy. |
| Sialic Acid (Sia) | Sialylation at the Fc region can prolong serum half-life and modulate immune responses. | Sialylation patterns exhibit high variability; associated with inflammatory regulation and immune modulation. |
| High-Mannose Glycans | Typically present in low levels (<5%); higher proportions may accelerate clearance. | Potentially higher levels; associated with immune activation and recognition by lectin receptors. |
Our Analytical Techniques for Glycosylation Profiling
Bottom-Up, Middle-Up, and Native Mass Spectrometry (MS)
We dissect glycans at multiple levels:
- Bottom-Up: Enzymatic digestion (e.g., trypsin) breaks antibodies into peptides, allowing isolation of glycopeptides for detailed MS analysis. This reveals which sites are glycosylated and with which glycan structures.
- Middle-Up: Partial digestion generates Fc and Fab fragments, simplifying analysis of subclass-specific glycosylation without the complexity of the full antibody.
- Native MS: Analyze intact antibody glycoforms directly, preserving their native state to capture heterogeneity in real time. No denaturation, no bias—just pure, unfiltered data.
Glycopeptide Enrichment & Labeling
Glycopeptides are tricky to isolate due to their low abundance and hydrophilic nature. Our workflow uses high-specificity lectin affinity chromatography or HILIC (hydrophilic interaction chromatography) to pull them out of the mix, followed by labeling (e.g., stable isotopes) for precise quantification. This ensures even rare glycoforms don't slip through the cracks.
Lectin Microarrays for High-Throughput Screening
Need a quick snapshot of glycan types? Lectin microarrays are your answer. These arrays use carbohydrate-binding proteins (lectins) to spot specific glycan motifs, letting us map patterns like sialylation, fucosylation, or mannose content in a flash. Perfect for comparing batches or screening for subtle changes.
Comprehensive pAbs Glycosylation Characterization Services
Glycan Composition Analysis
Using techniques like enzymatic release followed by HPAEC-PAD or MS, we identify and quantify monosaccharides (mannose, galactose, fucose, sialic acid). This forms the foundation for understanding antibody function, stability, and immune interactions.
Glycoform Heterogeneity Assessment
HILIC chromatography coupled with fluorescence detection or MS evaluates glycoform distribution (e.g., G0F, G1F, high-mannose). This assessment is critical for linking glycosylation variability to functional outcomes in pAbs.
Glycosylation Site Mapping
LC-MS/MS analysis pinpoints glycosylation sites, such as Asn297 in Fc and Fab regions. This mapping uncovers how glycan modifications influence antibody structure, binding affinity, and effector functions.
Applications in Research & Development
Vaccine Development
When assessing vaccine-induced pAbs, glycan patterns tell a story. High sialylation might indicate long-lived antibodies, while fucose depletion could signal potent effector functions. Our analyses help you correlate glycosylation with vaccine efficacy, ensuring your candidates deliver on both breadth and durability.
Therapeutic pAb Engineering
Designing pAbs for therapy? We'll help you characterize baseline glycosylation, then work with you to tweak it—via cell culture optimization or glycoengineering—to boost desired traits, like reduced immunogenicity or enhanced ADCC. No more trial-and-error; just data-driven refinement.
Diagnostic Assays
Batch-to-batch variability in pAbs can wreck diagnostic reliability. Our services monitor glycosylation consistency, flagging deviations in critical glycan markers to keep your assays accurate and reproducible.
Why Choose Us?
Mastery of Heterogeneity
The sheer diversity of pAbs makes analysis daunting. But our multi-technique approach—combining MS, lectin arrays, and bioinformatics—ensures comprehensive coverage, even for the messiest samples. We don't just report data; we interpret it, highlighting key glycoforms that matter for your goals.
Scaling for Speed & Sensitivity
Traditional methods are slow and insensitive to low-abundance glycans. Our advanced MS platforms and optimized workflows cut turnaround time without sacrificing detail. Even tiny samples get the royal treatment.
Customization for Your Needs
No two projects are alike. Whether you need a basic glycosylation profile or a deep dive into structure-function relationships, we tailor our services to your questions. Got a unique sample type? Unusual downstream application? Just ask—our team thrives on solving tricky challenges.
At Creative Biolabs, our Glycosylation Analysis Services of Polyclonal Antibodies are designed to make this process straightforward, insightful, and collaborative. From characterizing complex glyco-profiles to guiding engineering strategies, we're here to support your journey—whether you're in early-stage research, preclinical development, or quality control. Don't let glycosylation heterogeneity hold you back. Your pAbs deserve to be understood, optimized, and celebrated for the powerful tools they are—and we're here to make that happen. Ready to explore how glycosylation analysis can elevate your polyclonal antibody project? Contact us now to discuss a customized solution that fits your needs.
References:
- de Taeye, Steven W., Theo Rispens, and Gestur Vidarsson. "The ligands for human IgG and their effector functions." Antibodies 8.2 (2019): 30. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib8020030
- Sénard, Thomas, et al. "MS-based allotype-specific analysis of polyclonal IgG-Fc N-glycosylation." Frontiers in Immunology 11 (2020): 2049. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.02049
- de Haan, Noortje, et al. "The N-glycosylation of mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG)-fragment crystallizable differs between IgG subclasses and strains." Frontiers in immunology 8 (2017): 608. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00608
- Boune, Souad, et al. "Principles of N-linked glycosylation variations of IgG-based therapeutics: pharmacokinetic and functional considerations." Antibodies 9.2 (2020): 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9020022